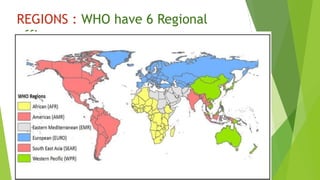
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. Formed in 1948 with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, WHO aims to coordinate international health work, provide health assistance to governments, and promote scientific collaboration. Governed by the World Health Assembly and Executive Board, WHO works through 6 regional offices to address priorities like disease prevention, health services development, and improving health technologies. WHO has contributed to global health initiatives including smallpox eradication and polio elimination efforts in India. Challenges include reliance on voluntary funding and addressing new global health threats.