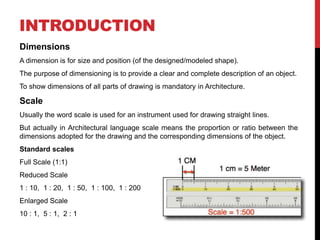
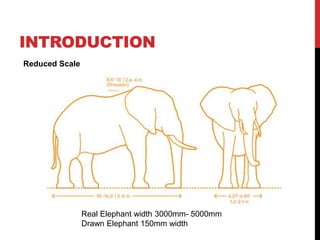
The document presents workshop basics on measurement drawing, emphasizing the importance of dimensions in architecture for object representation. It discusses scales, including full, reduced, and enlarged scales, with examples of converting dimensions. Additionally, it explains the concept of representative fraction (r.f.) and the use of plain scales for precise measurements.