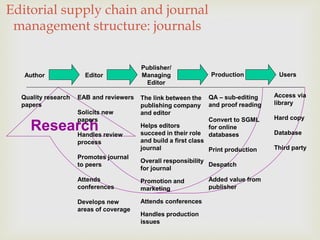
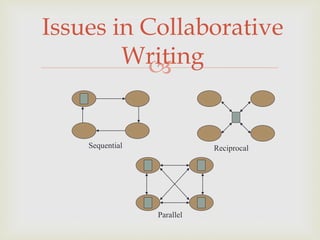
The document discusses the management and editorial processes of academic journals, emphasizing the roles of authors, editors, and reviewers in the publication and promotion of research papers. It also explores collaborative writing practices within higher education, addressing issues such as organization, communication, and conflict management. Additionally, it reviews the application of action research as a pivotal approach in improving academic teaching practices and student engagement.