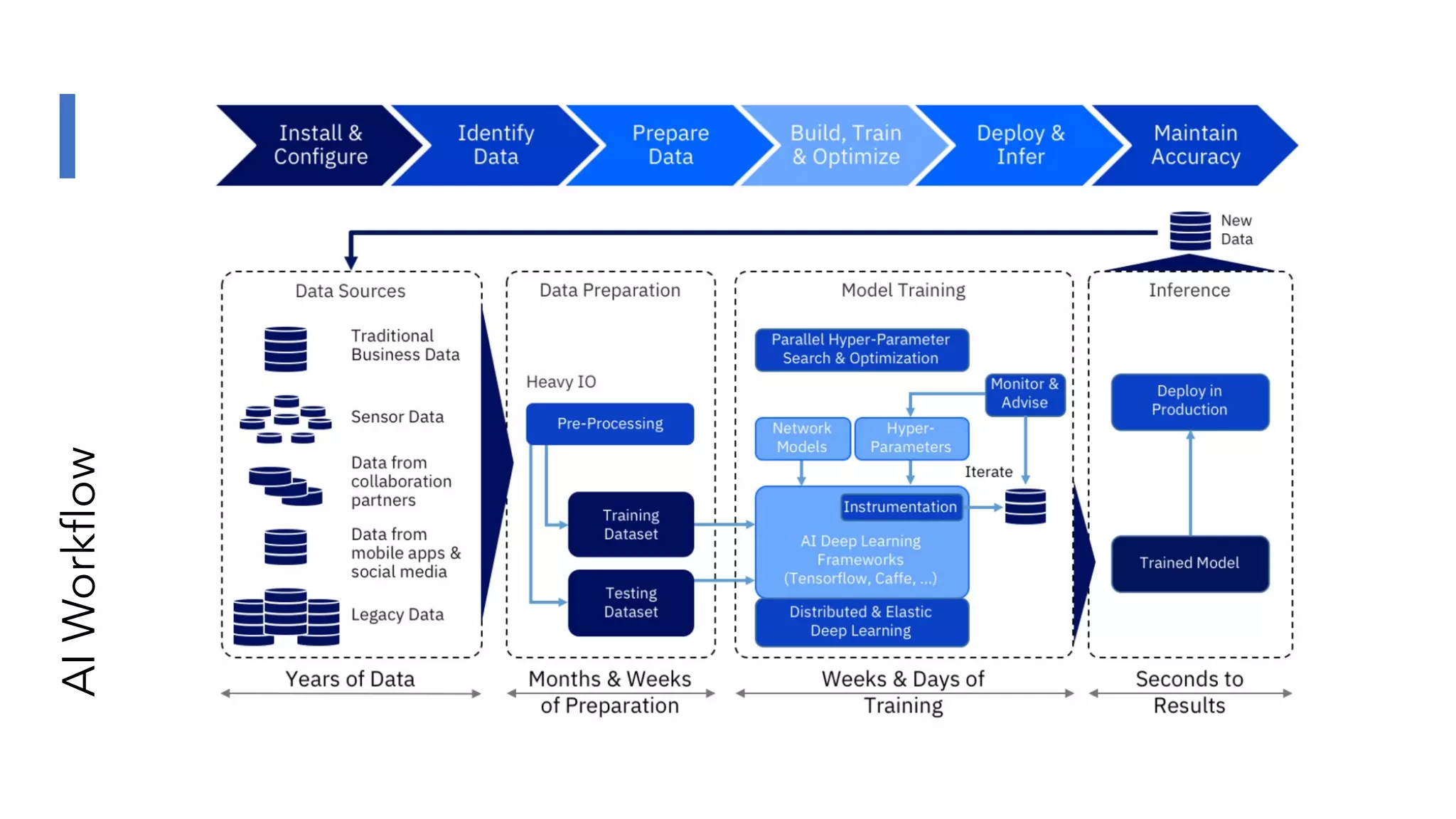
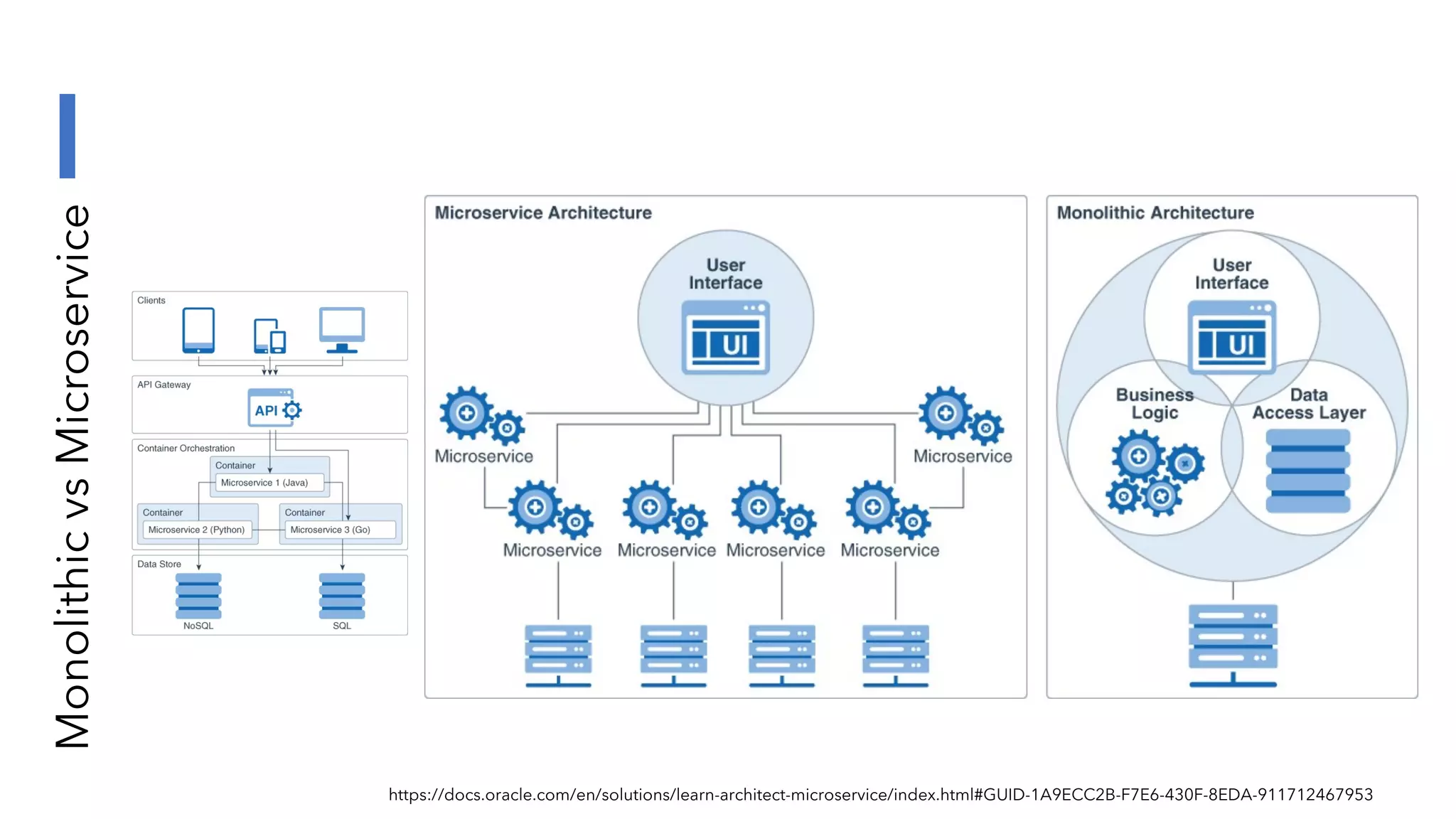
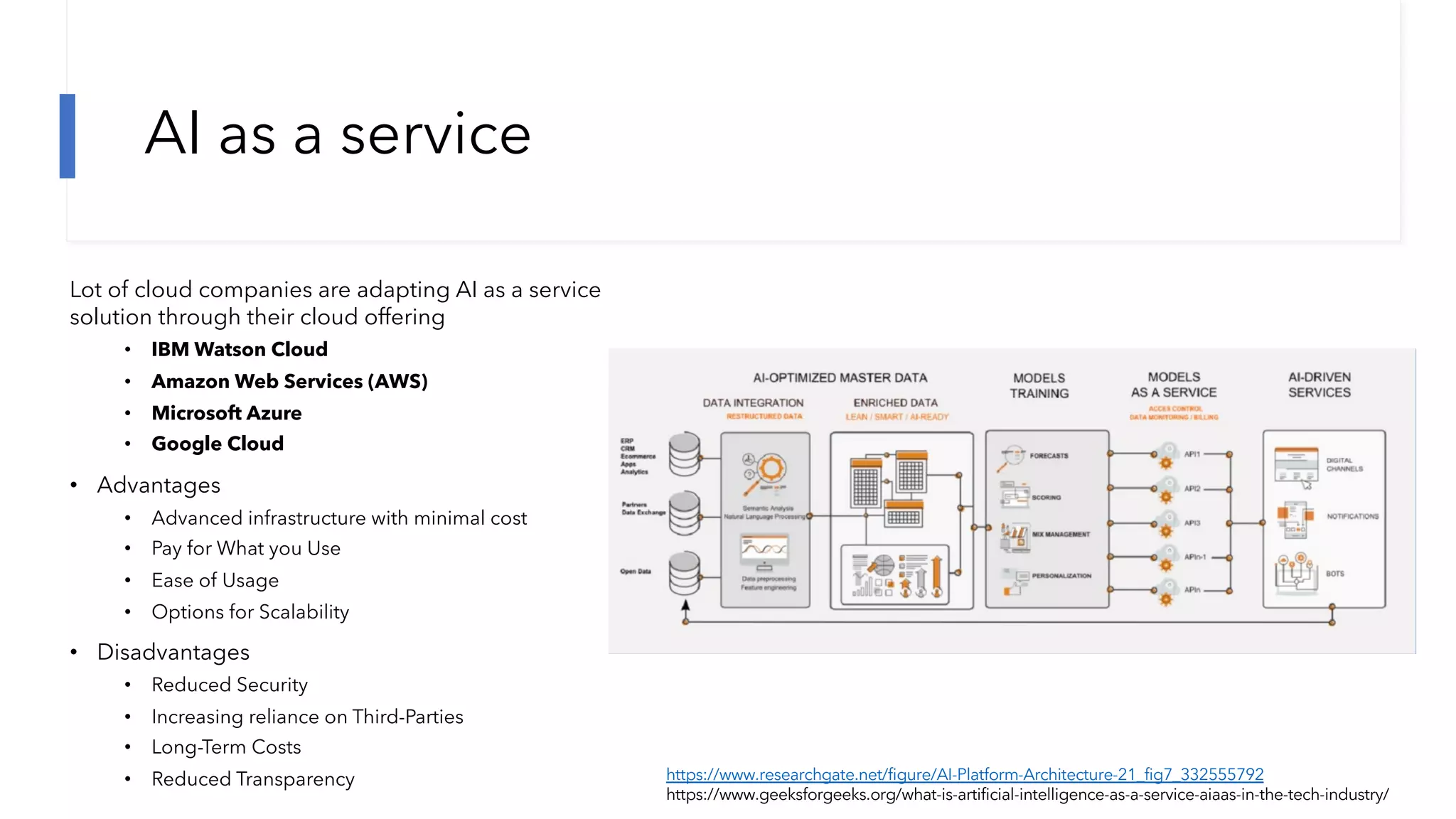
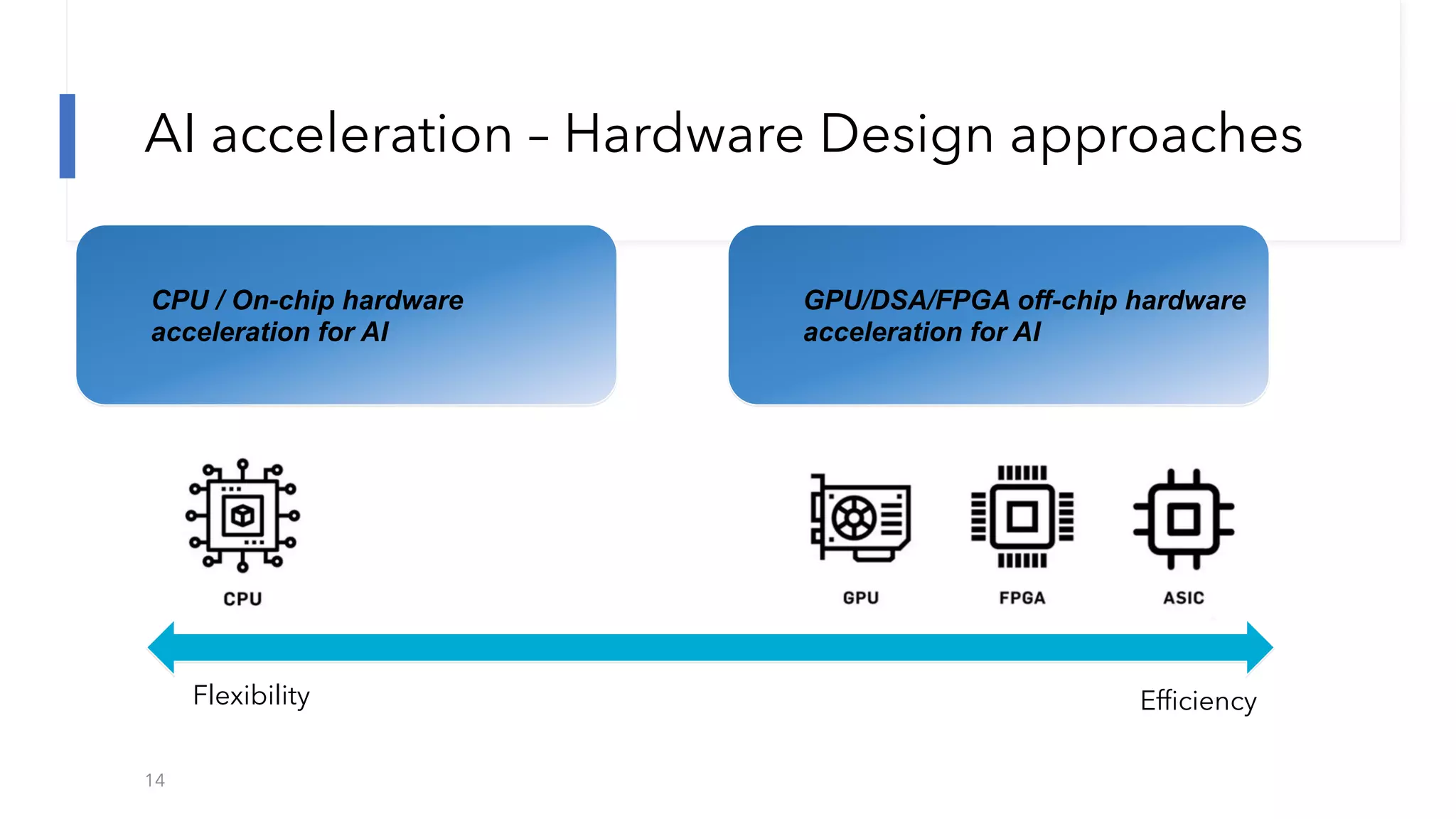
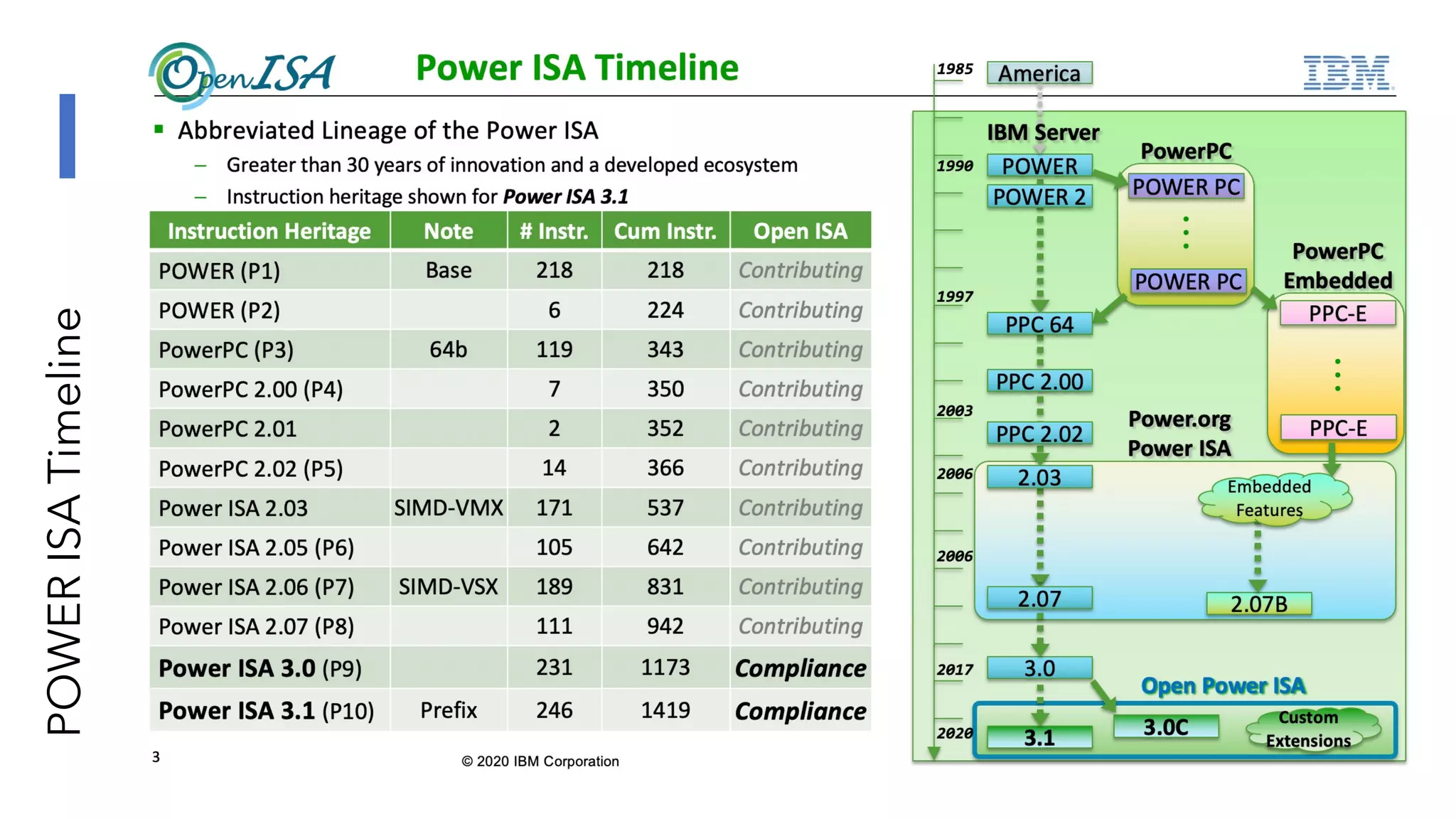
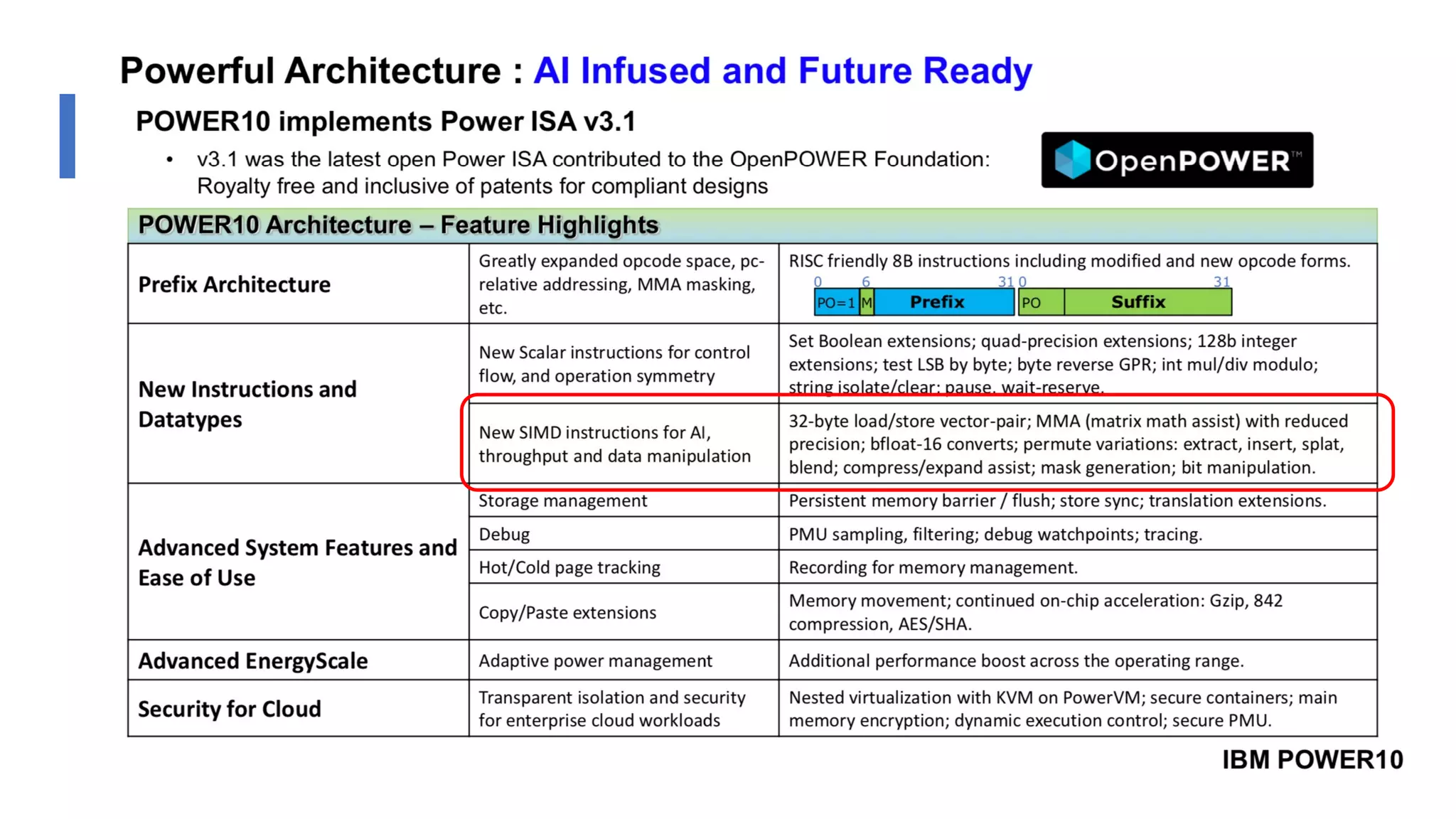
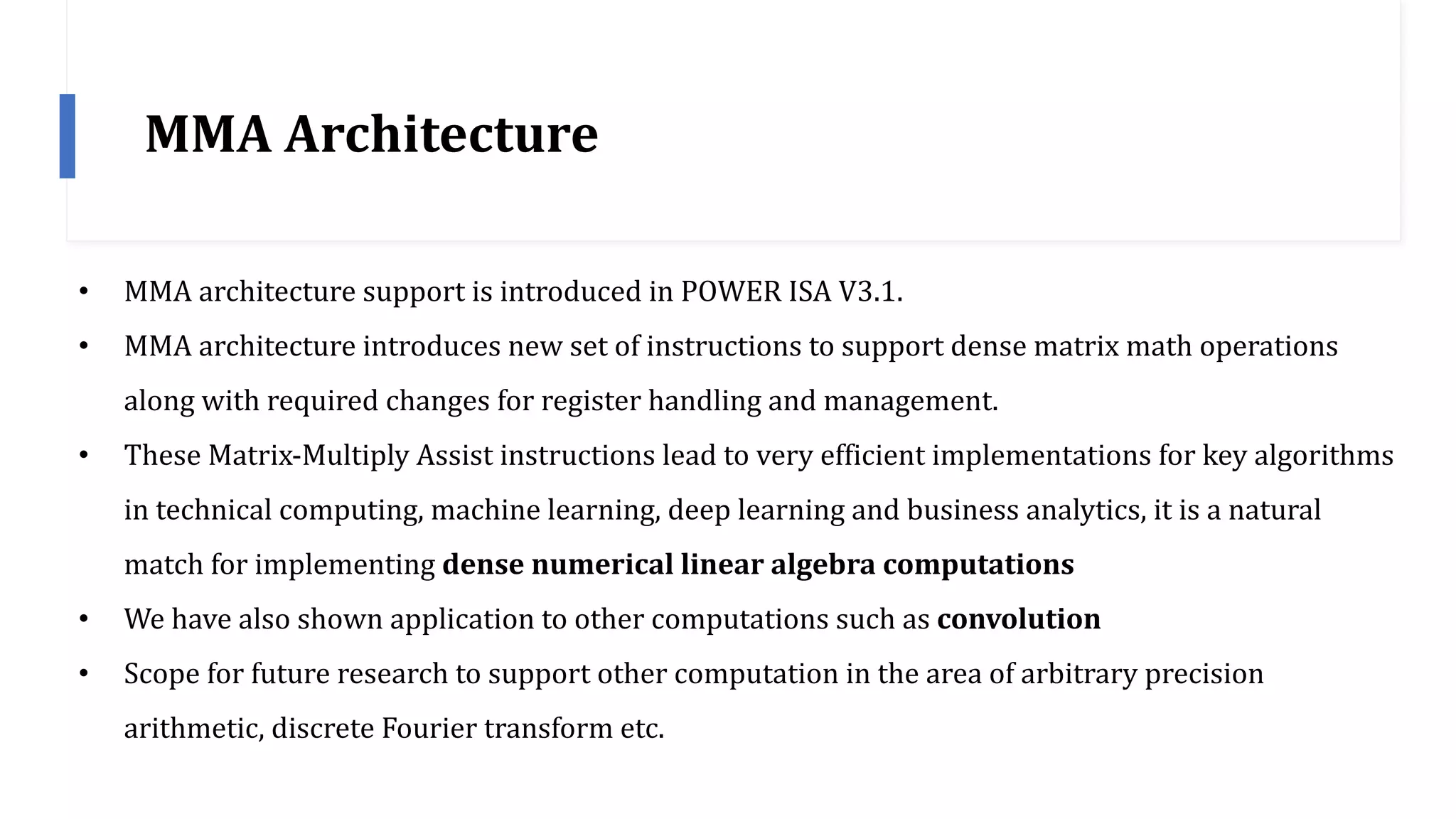
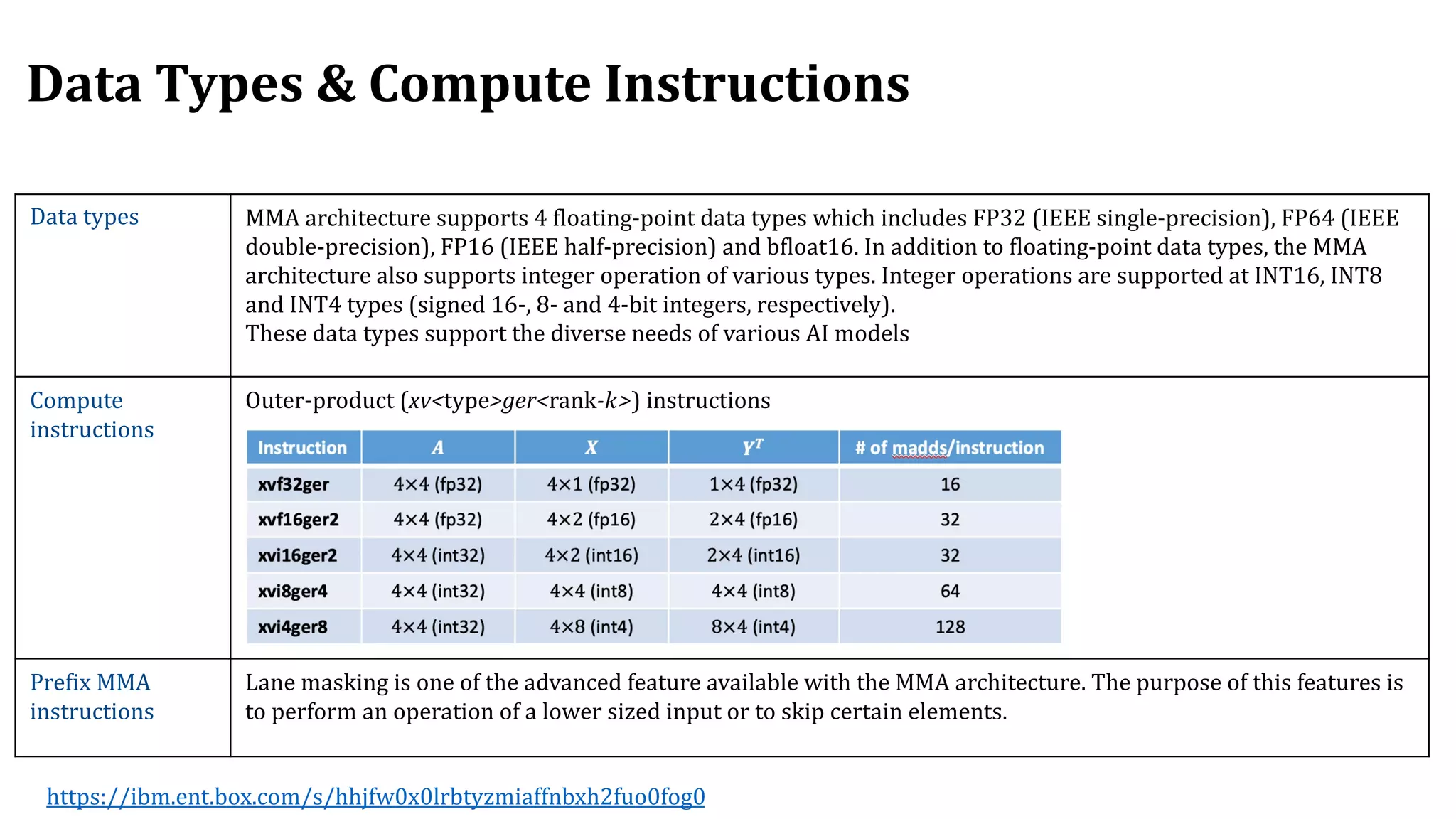
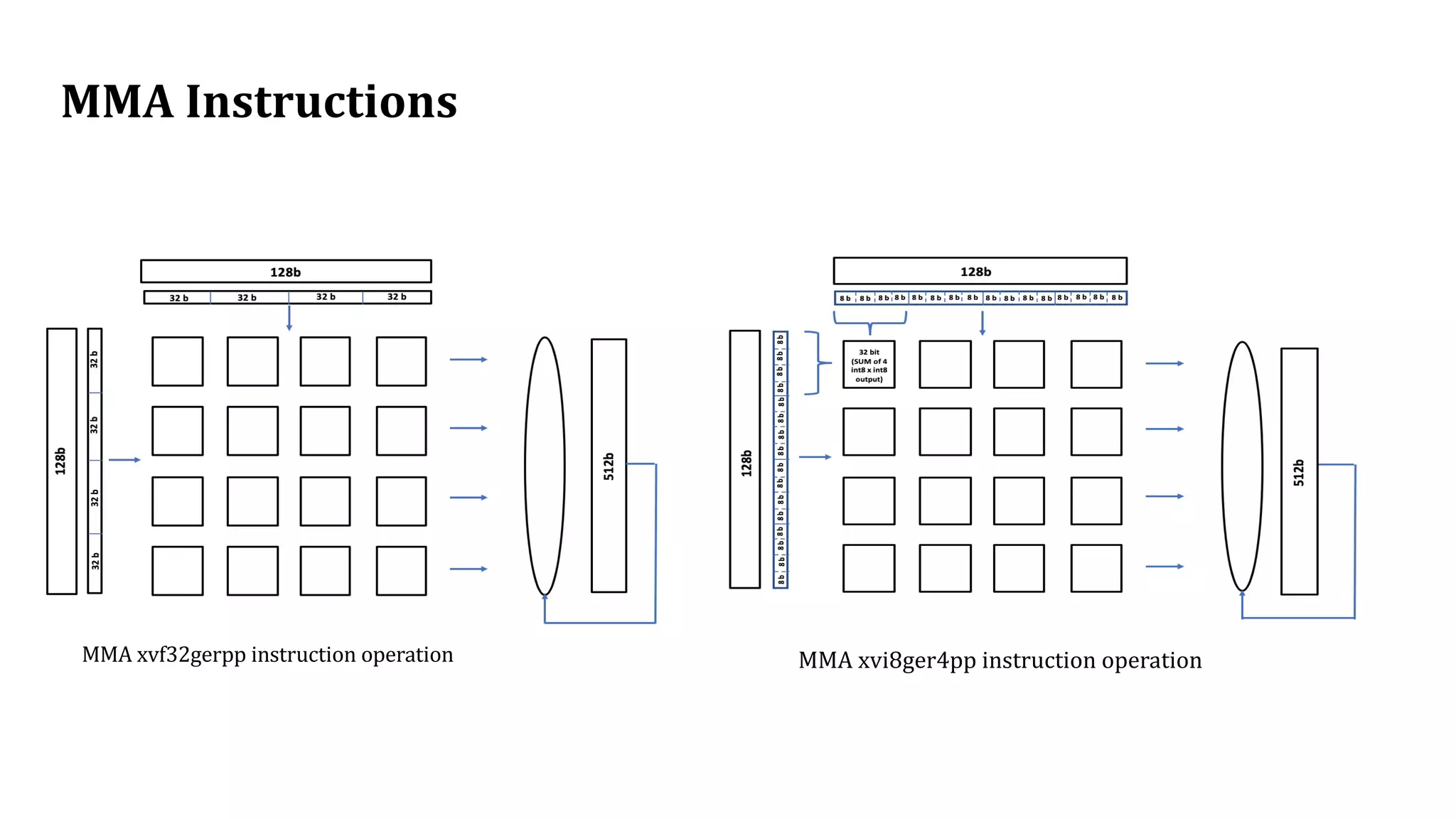
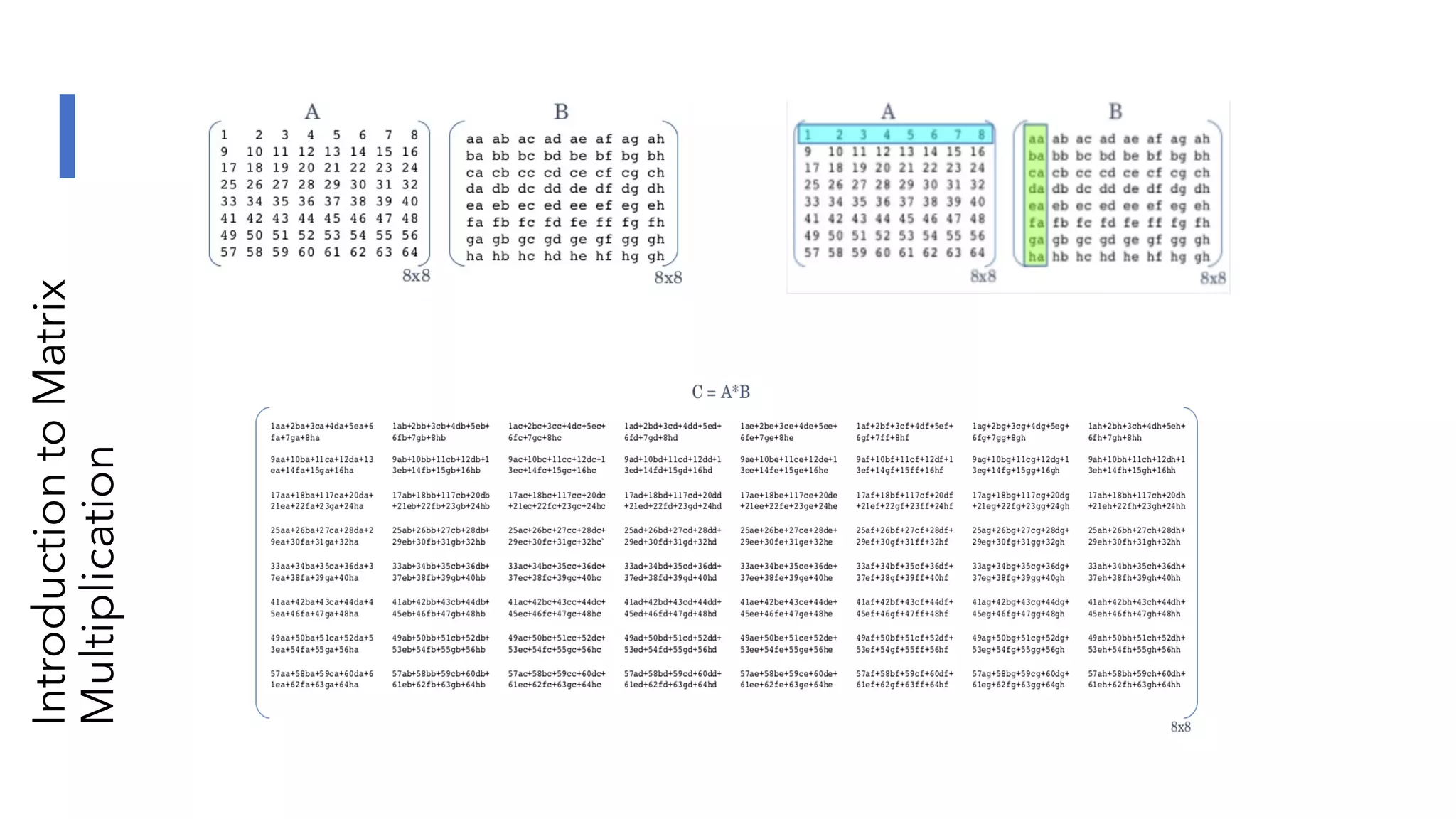
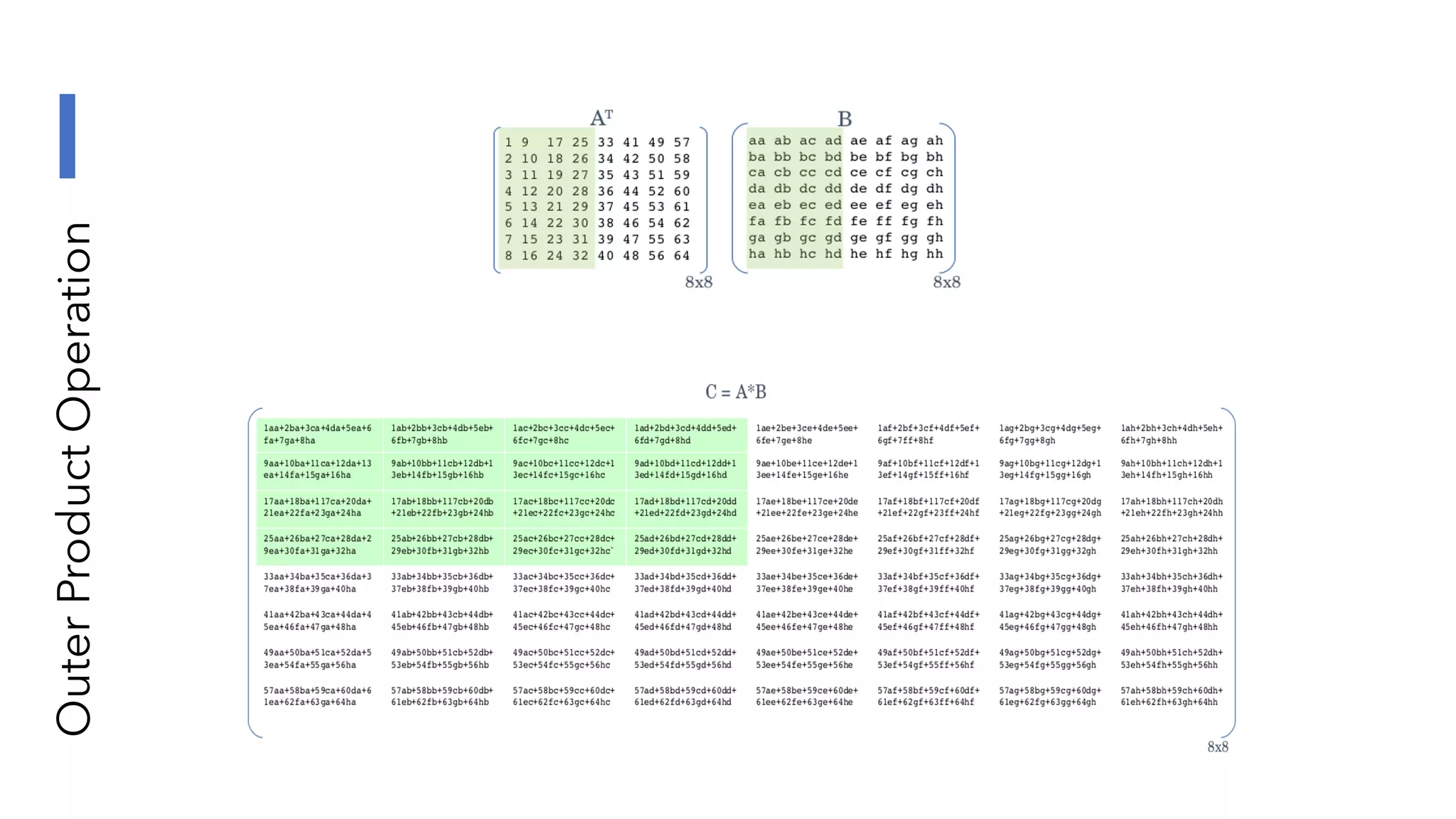
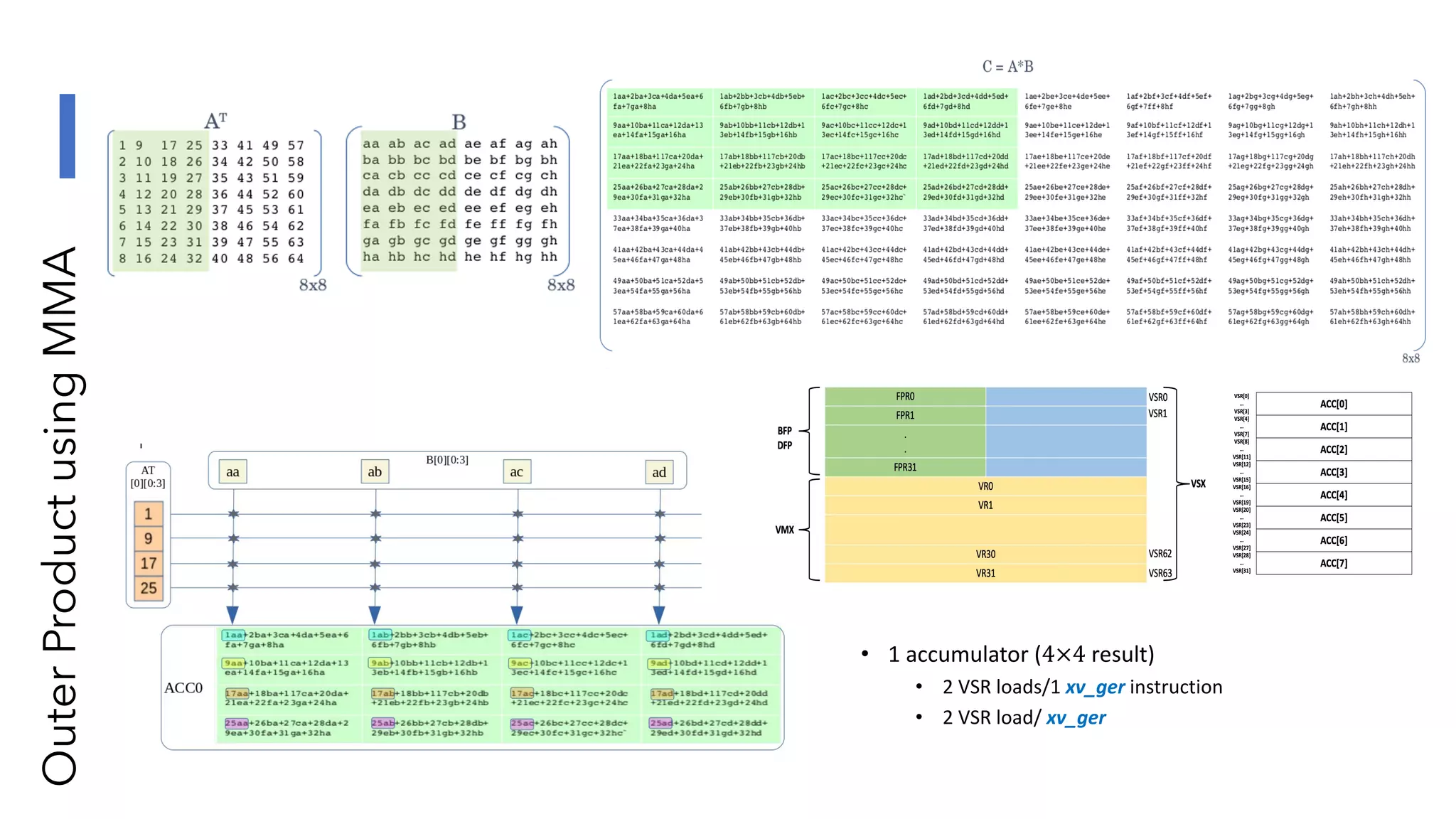
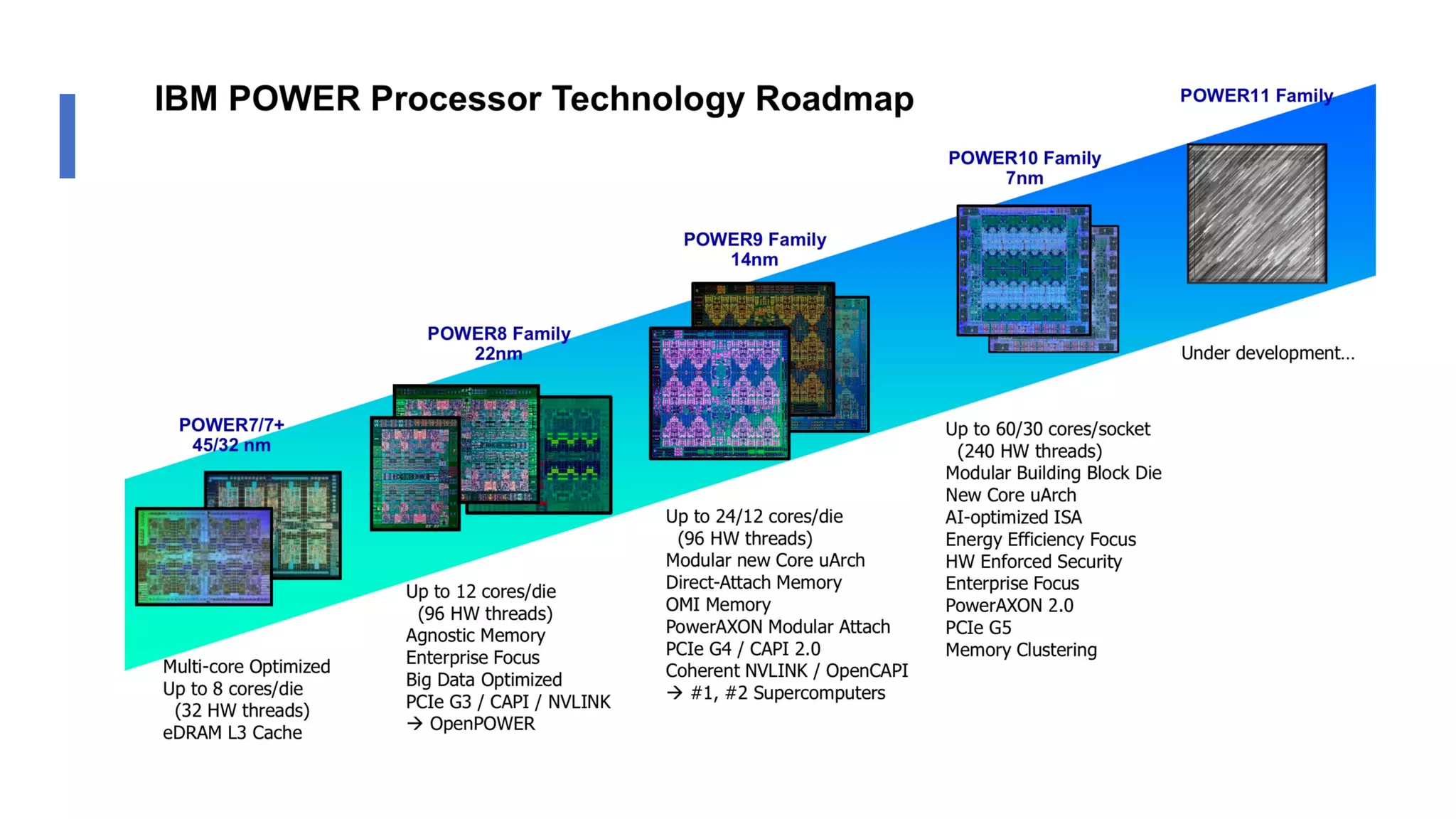
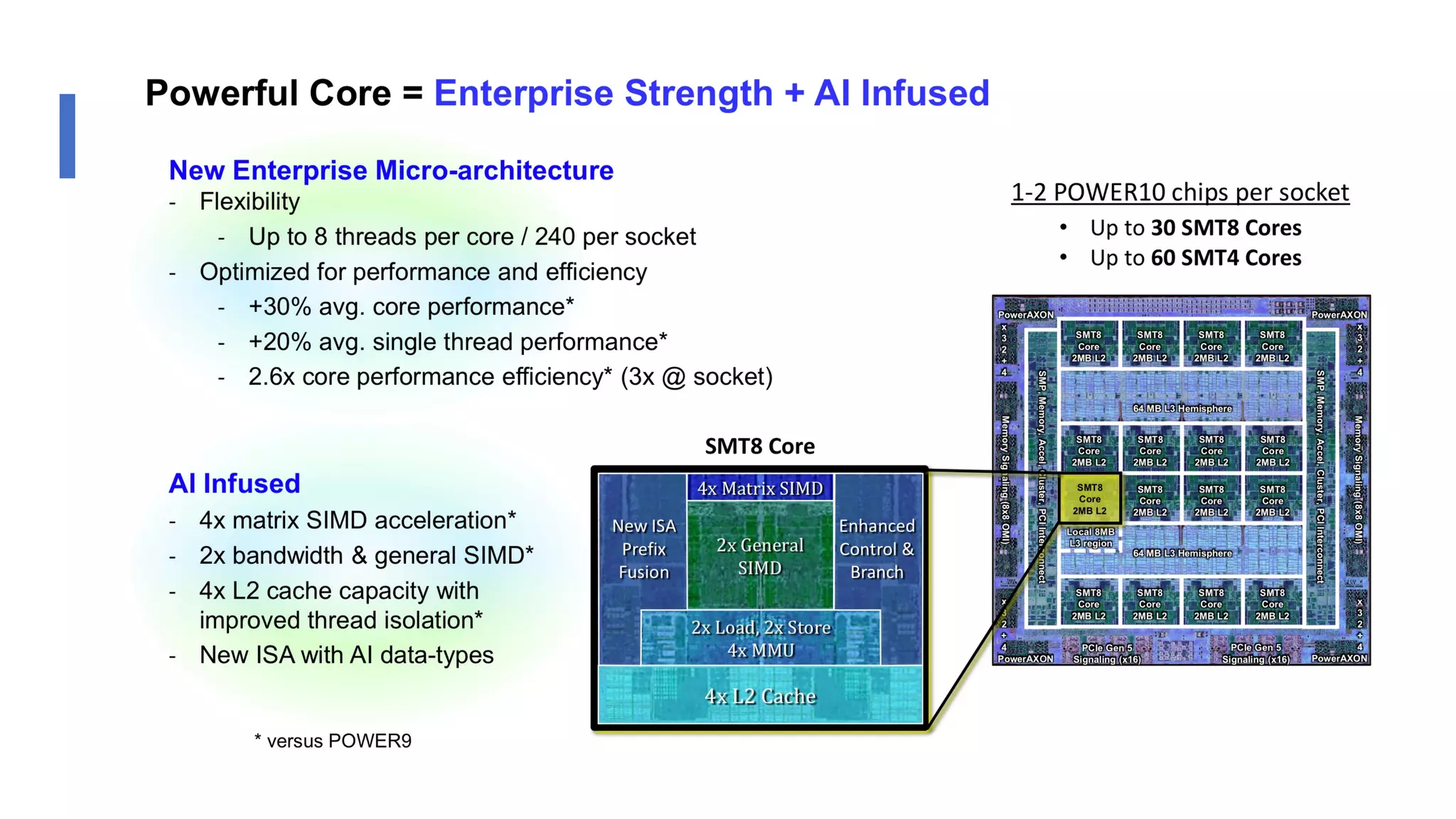
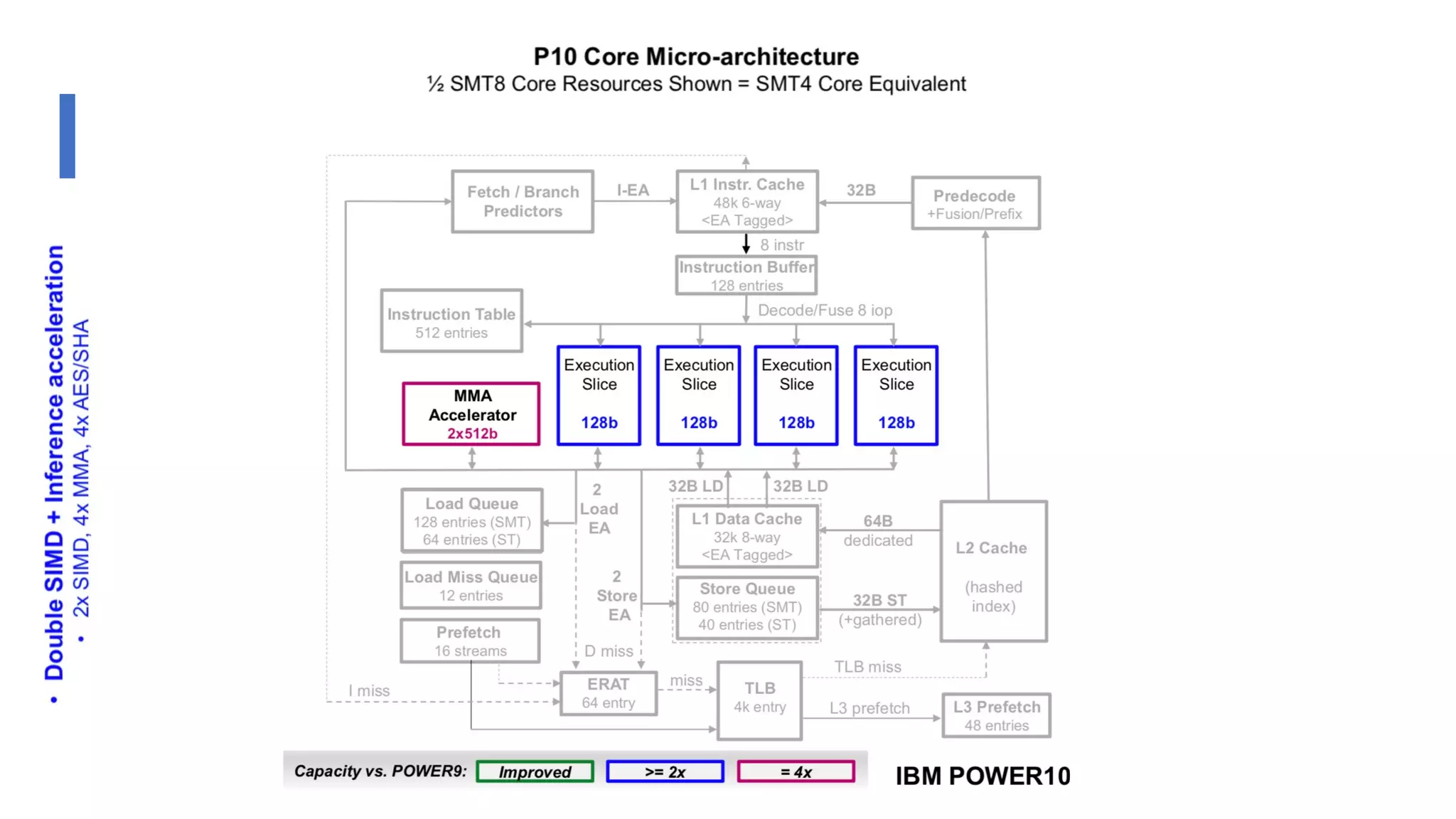
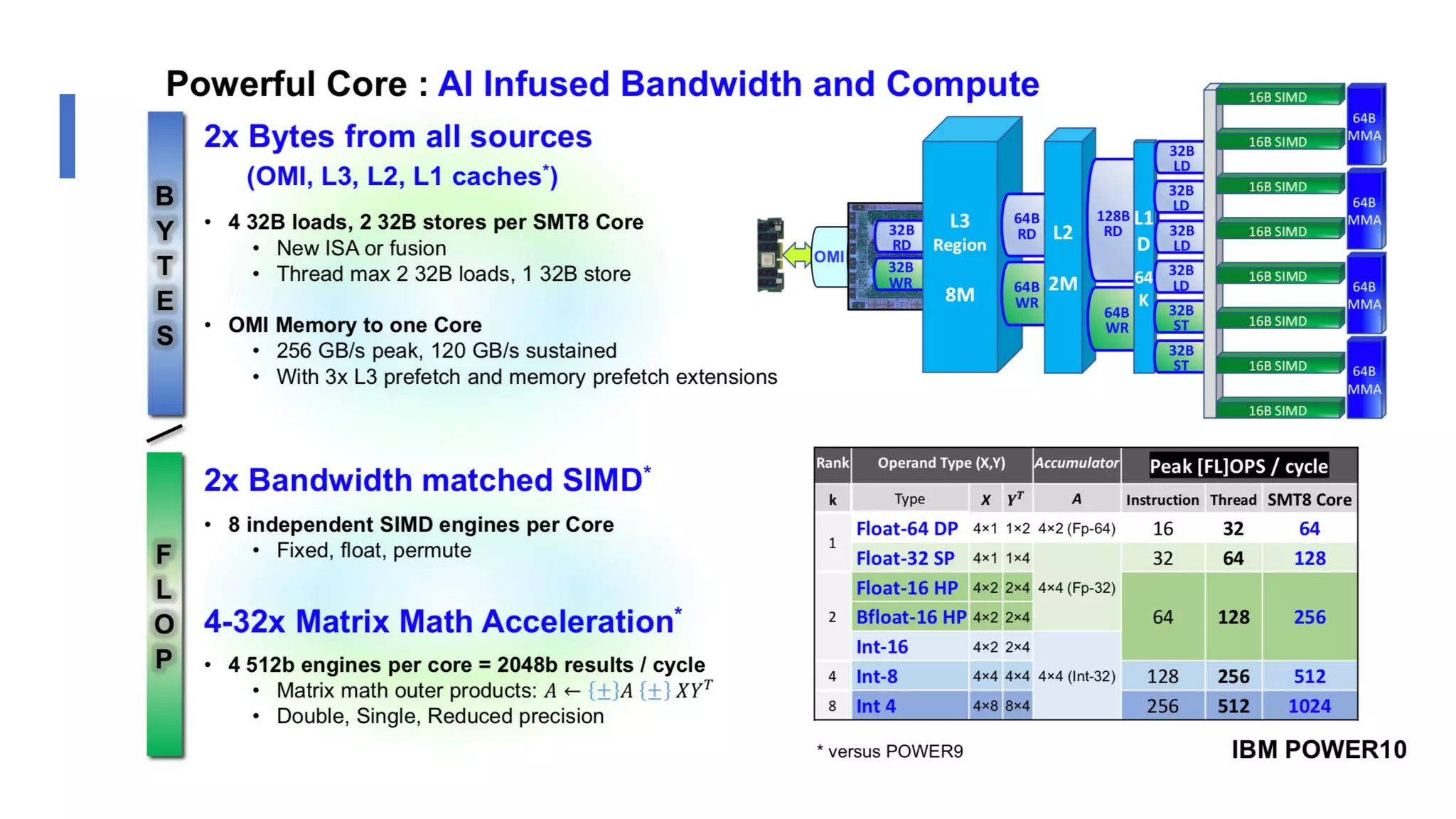
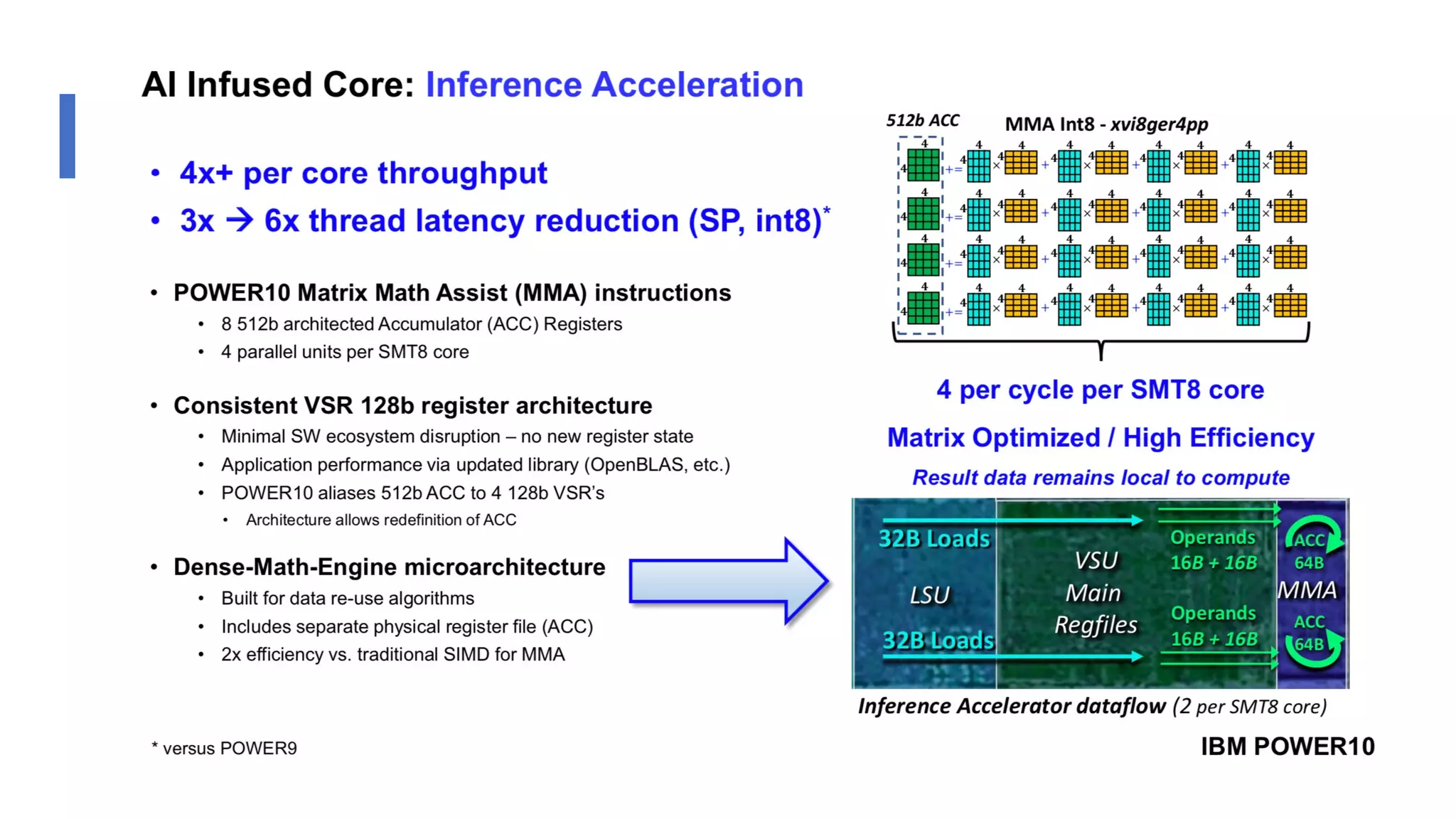
The document discusses the transformation and innovation in power architecture as presented by Satish Kumar Sadasivam during an invited talk at IIT Roorkee on July 16, 2021. It outlines the impact of AI and cloud computing on enterprise workloads, emphasizing the shift towards microservices, AI as a service, and the need for enhanced compute infrastructure. Key elements include the evolution of architectures, AI acceleration capabilities, and the introduction of the matrix multiplication assist architecture in power ISA to support advanced computational demands.