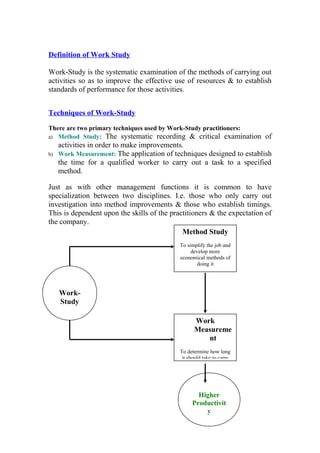
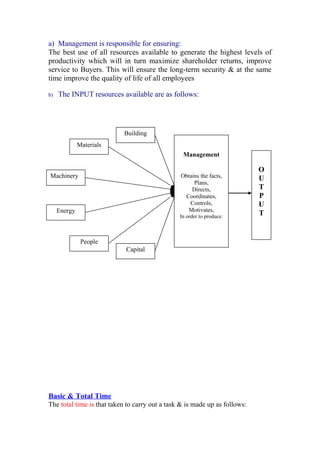
Work-study methods were developed during World War II to increase productivity and were later applied in industries around the world, including Bangladesh starting in 1991. Work-study techniques like method study and work measurement are used to examine current work methods, simplify or modify processes, reduce unnecessary work, and set time standards to improve productivity. Key aspects of work-study include breaking down jobs into individual tasks, creating work layouts to distribute tasks efficiently among workers, measuring cycle times to understand bottlenecks, and conducting regular studies to identify areas for further improvement. The overall goal is to systematically analyze work processes and set performance standards to increase productivity through more effective use of resources.