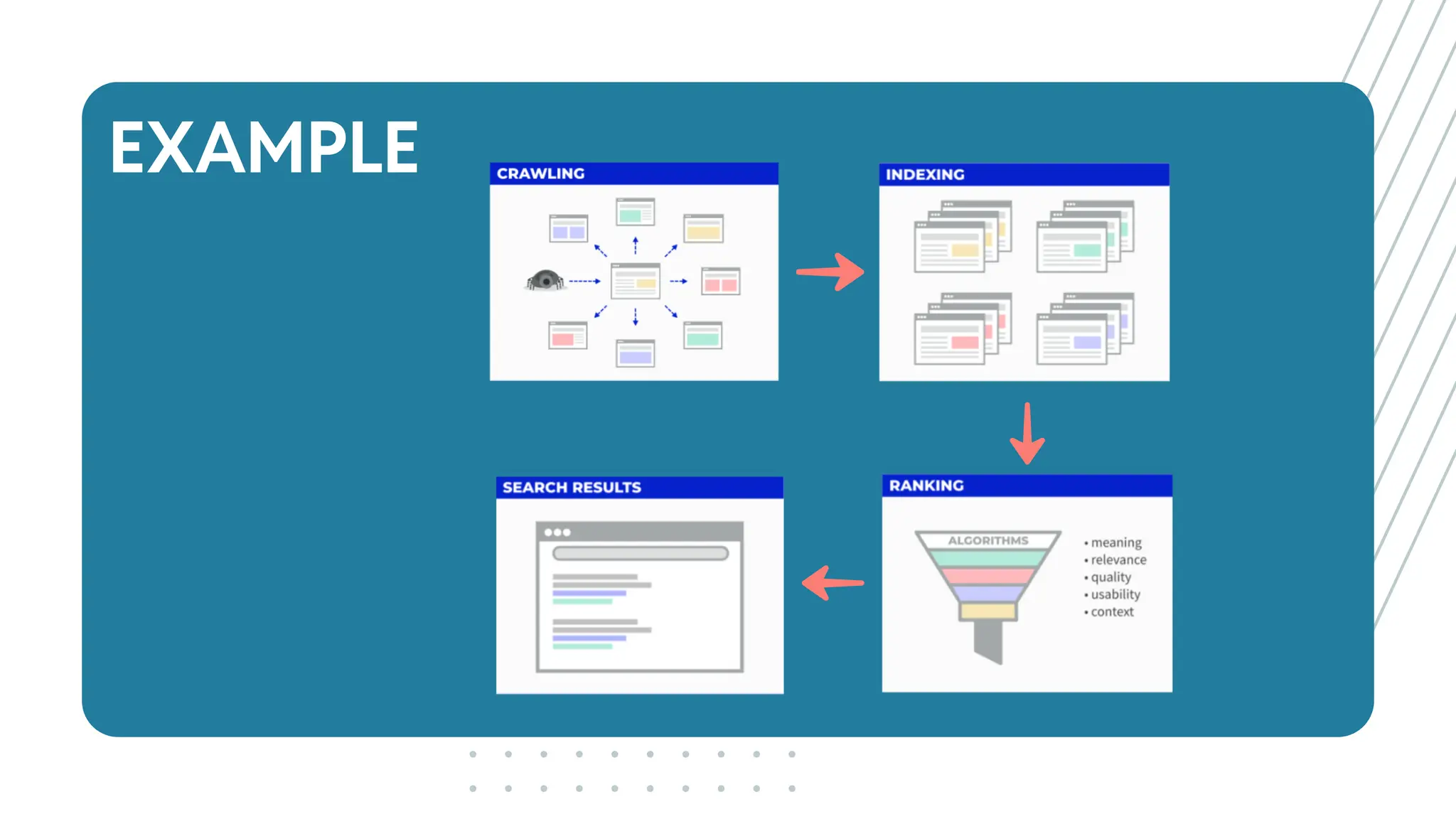
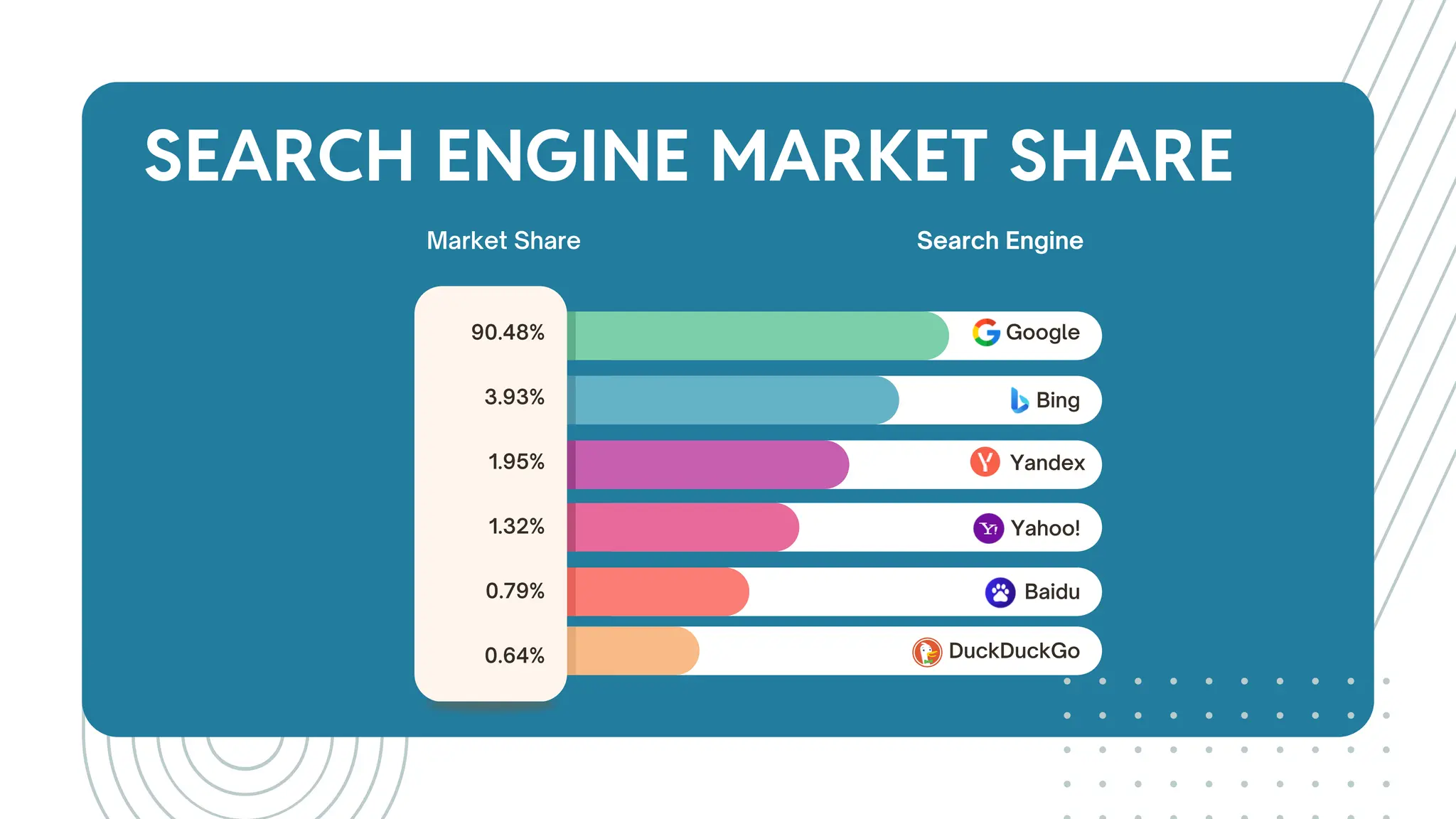
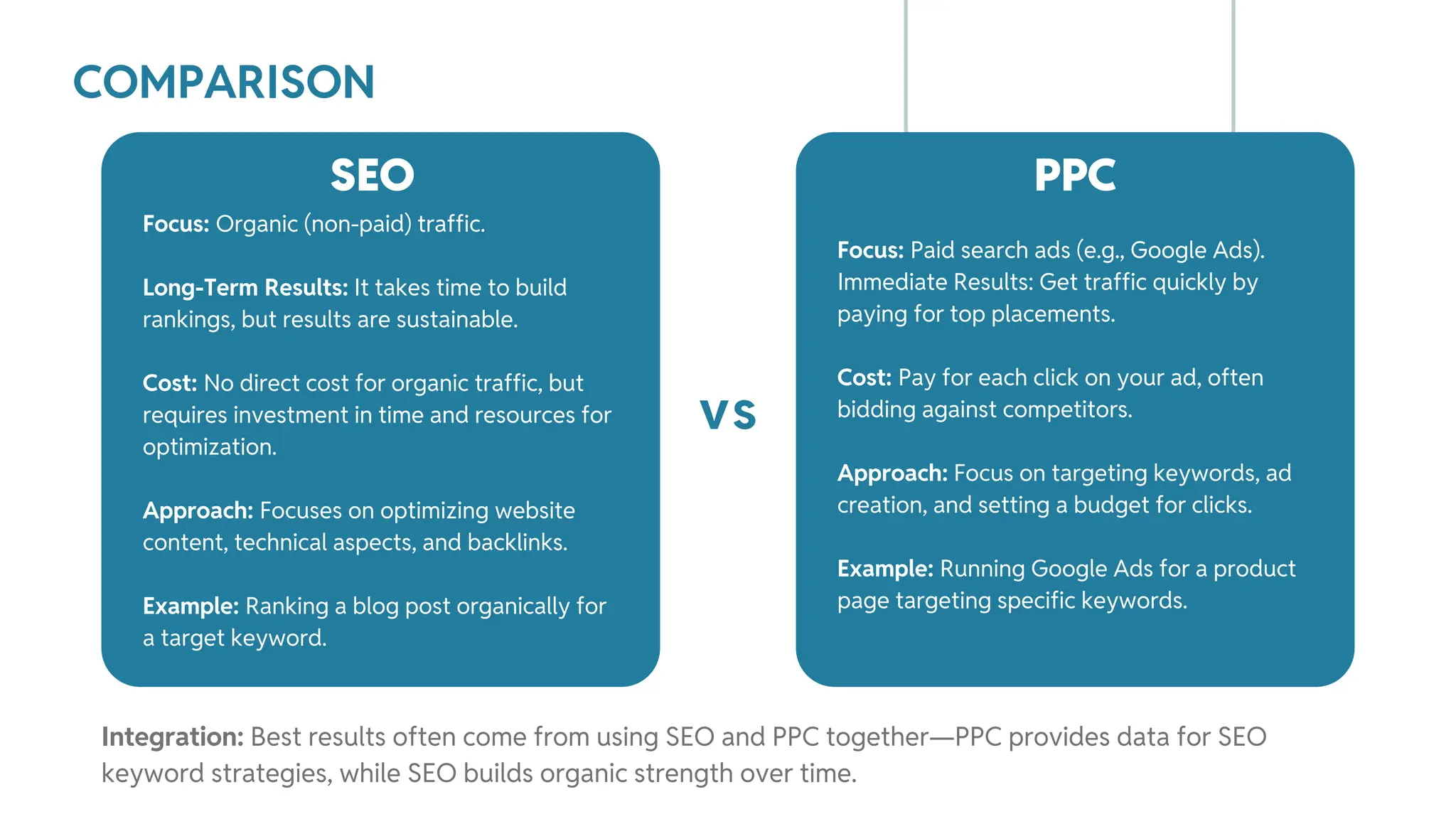
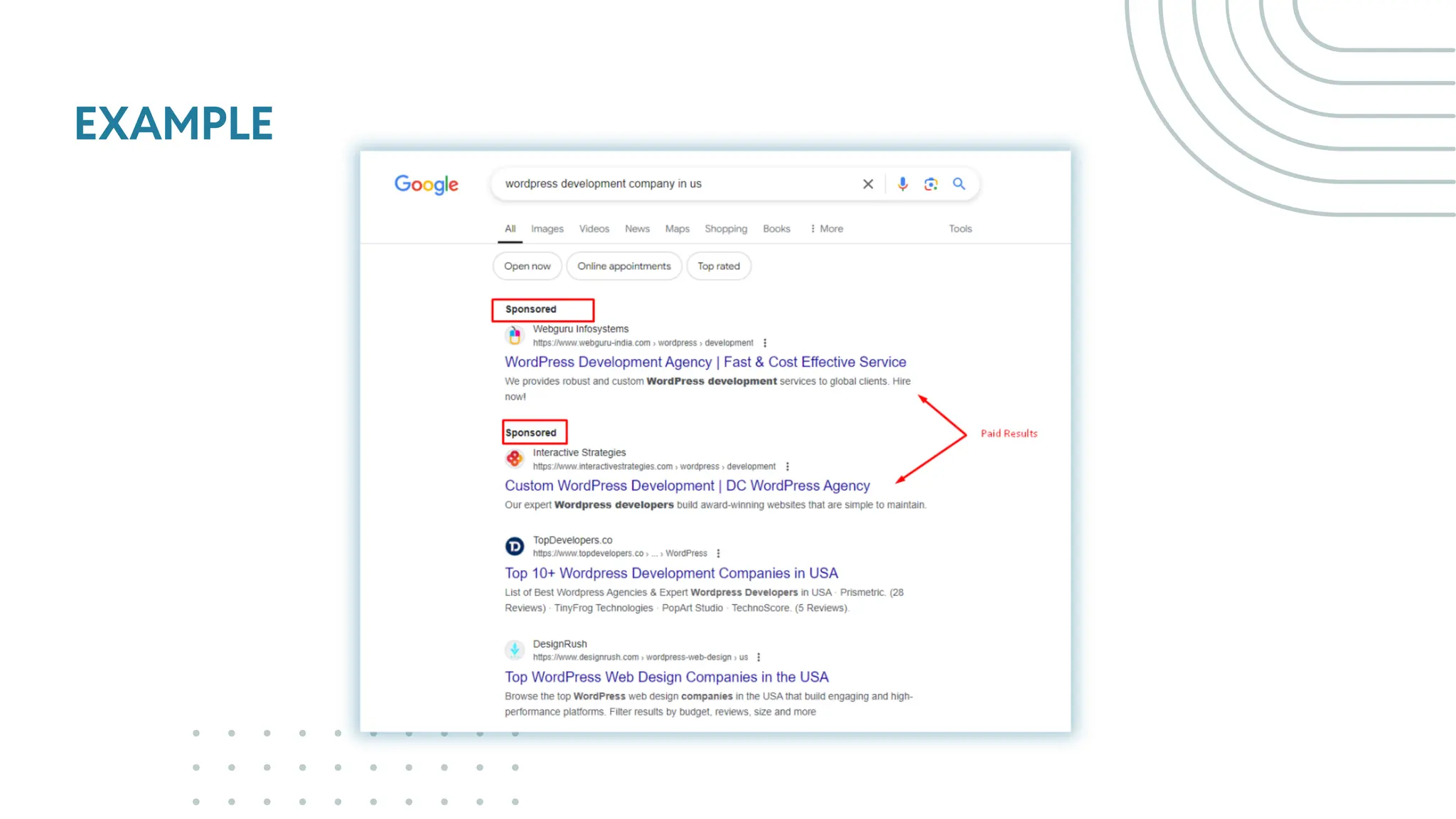
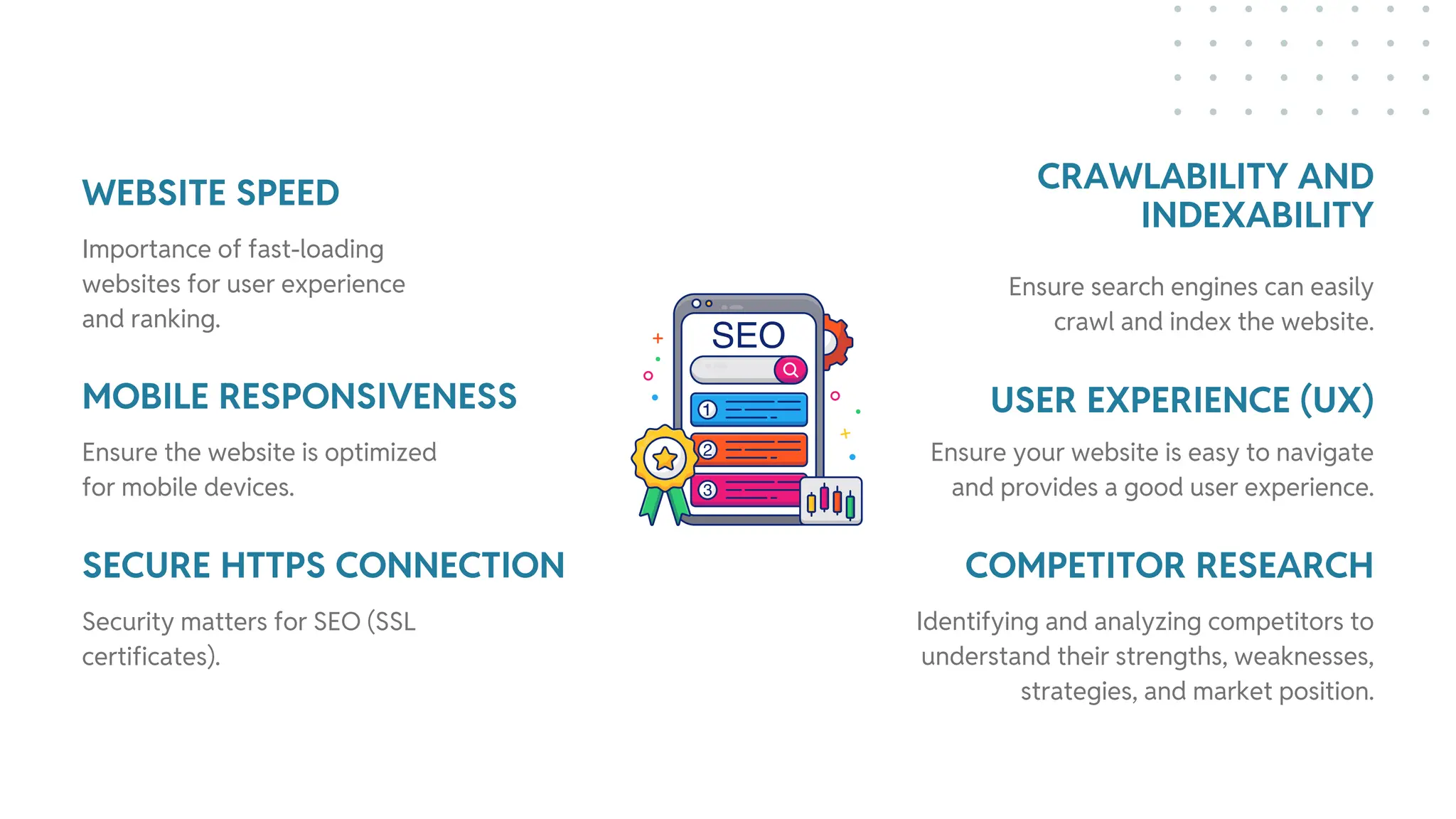
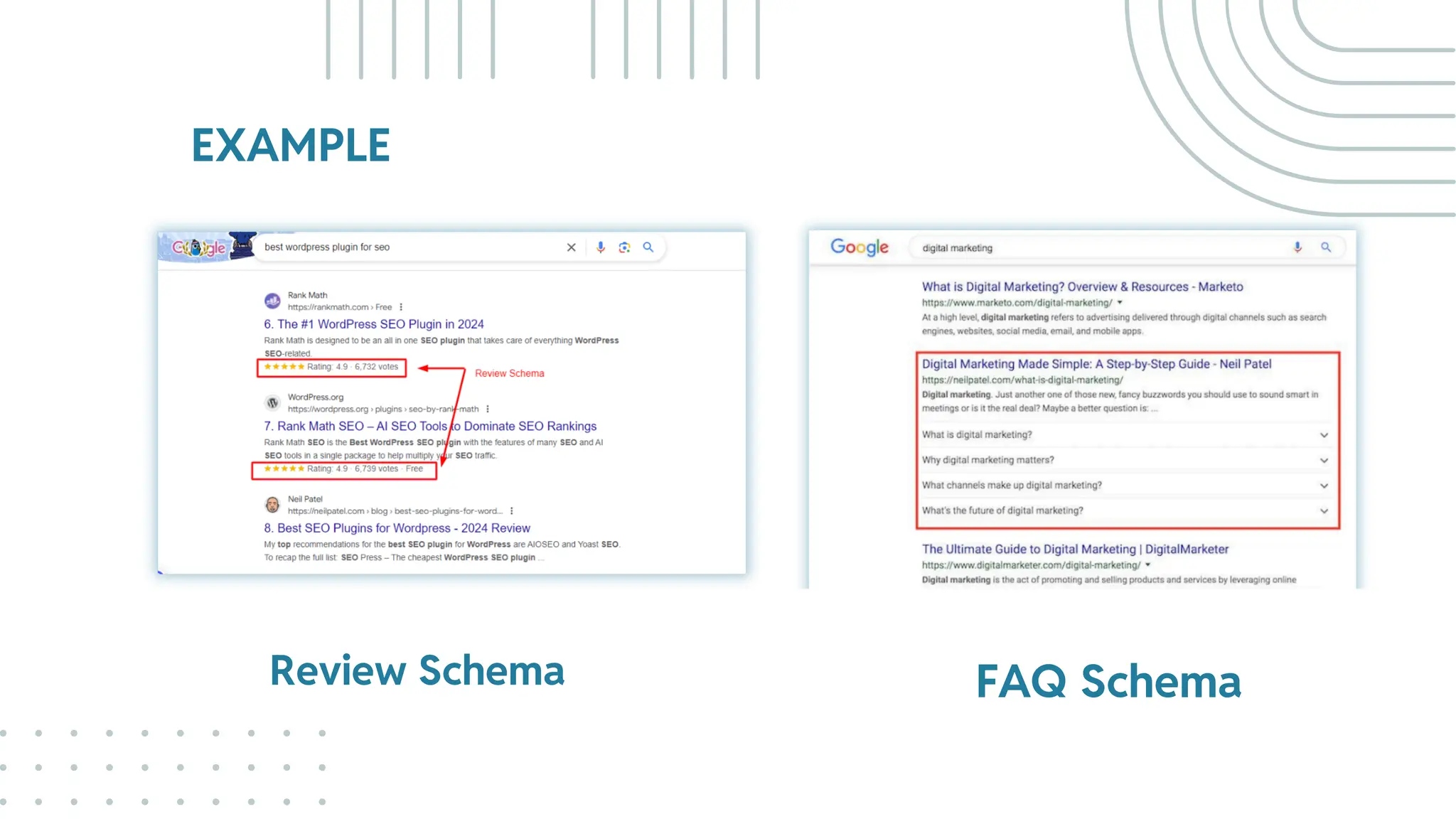
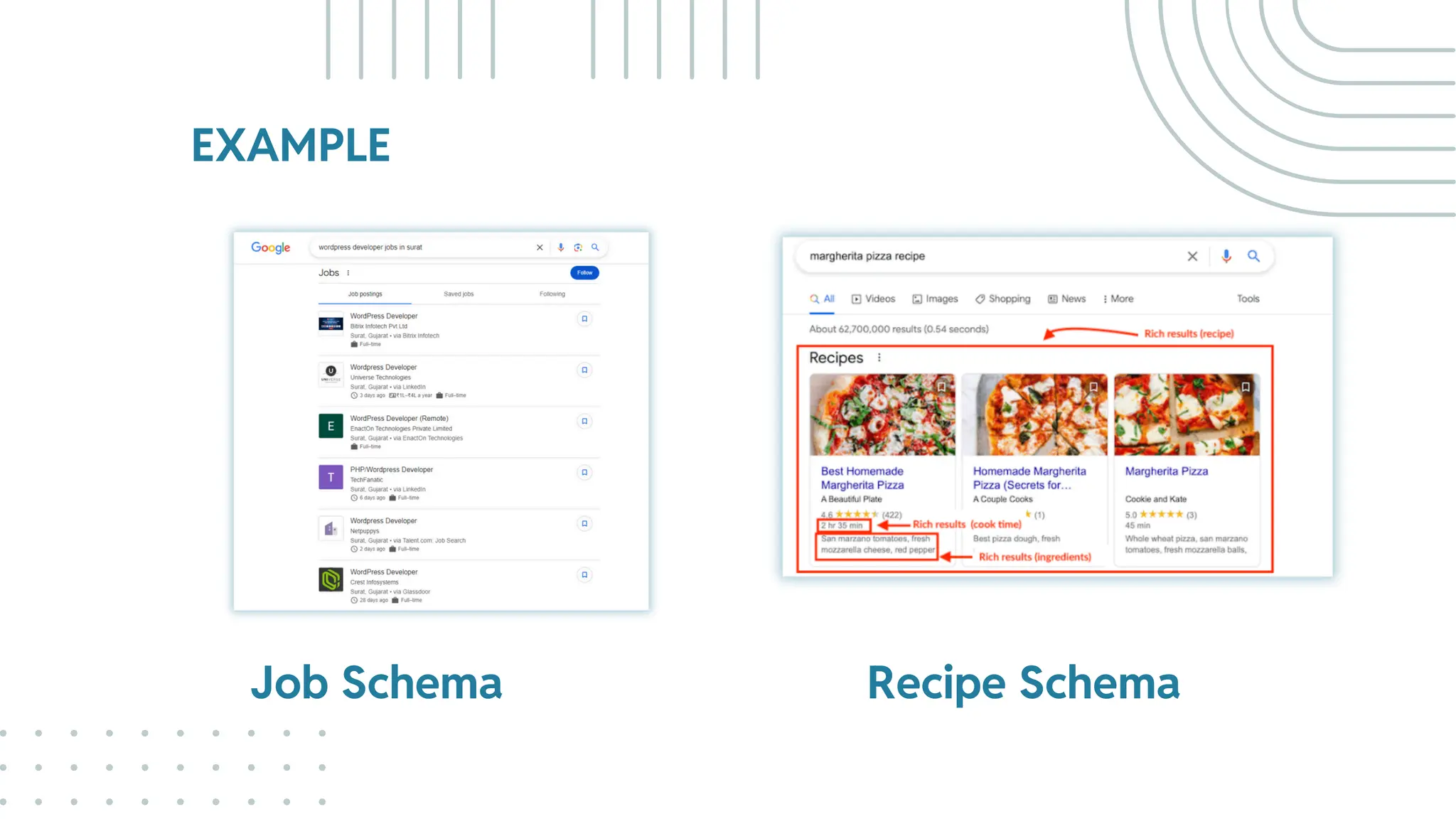
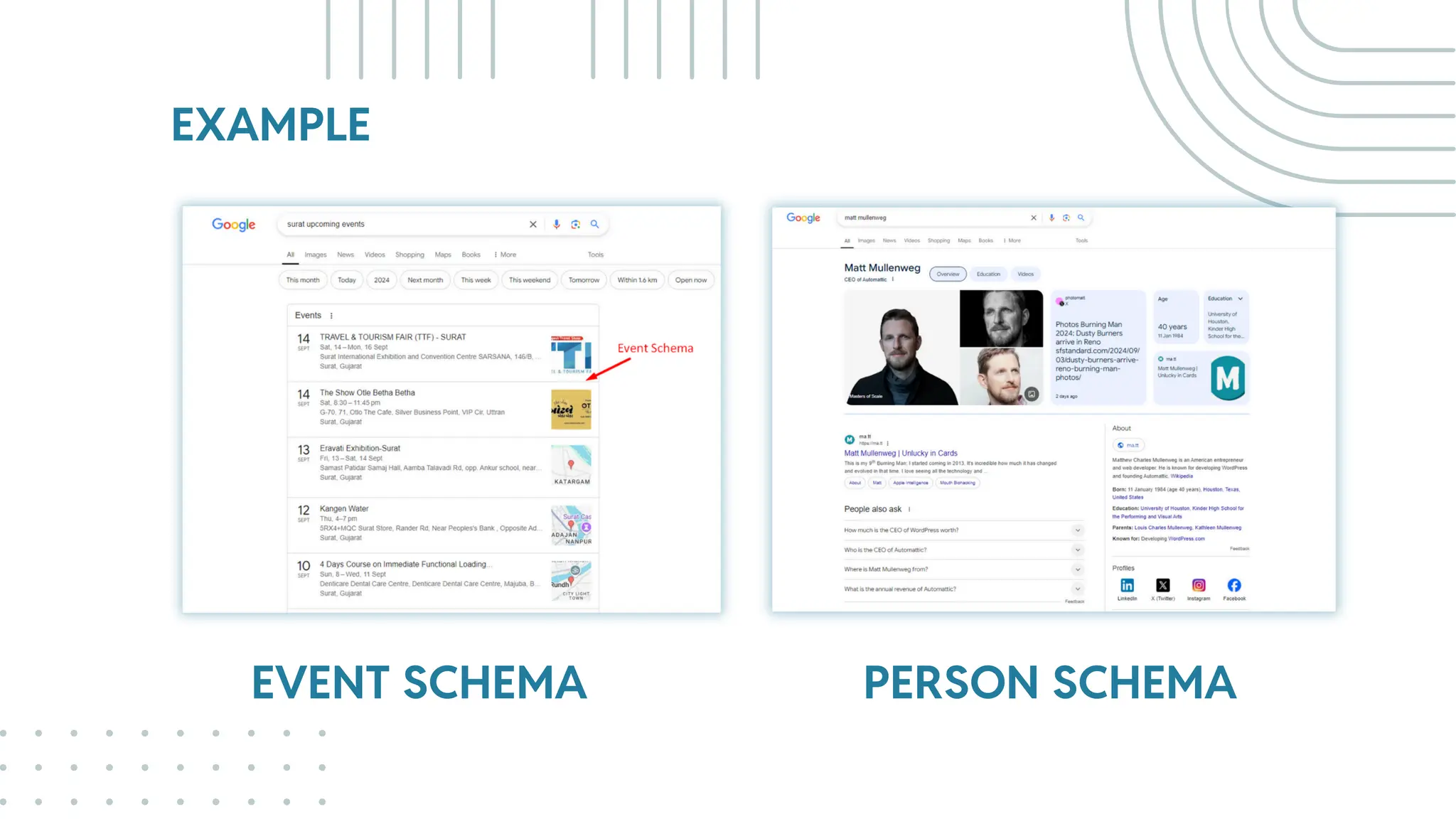
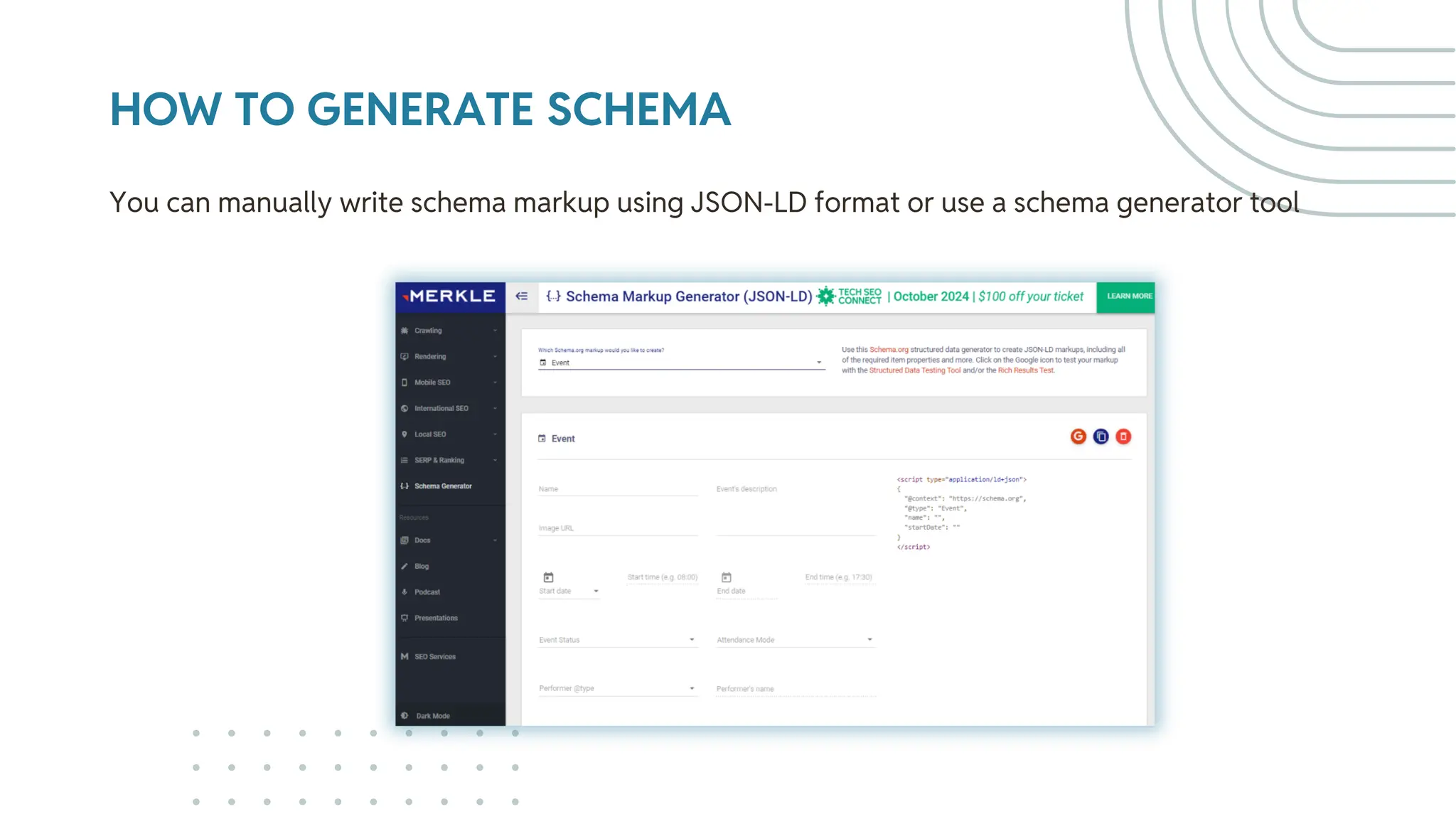
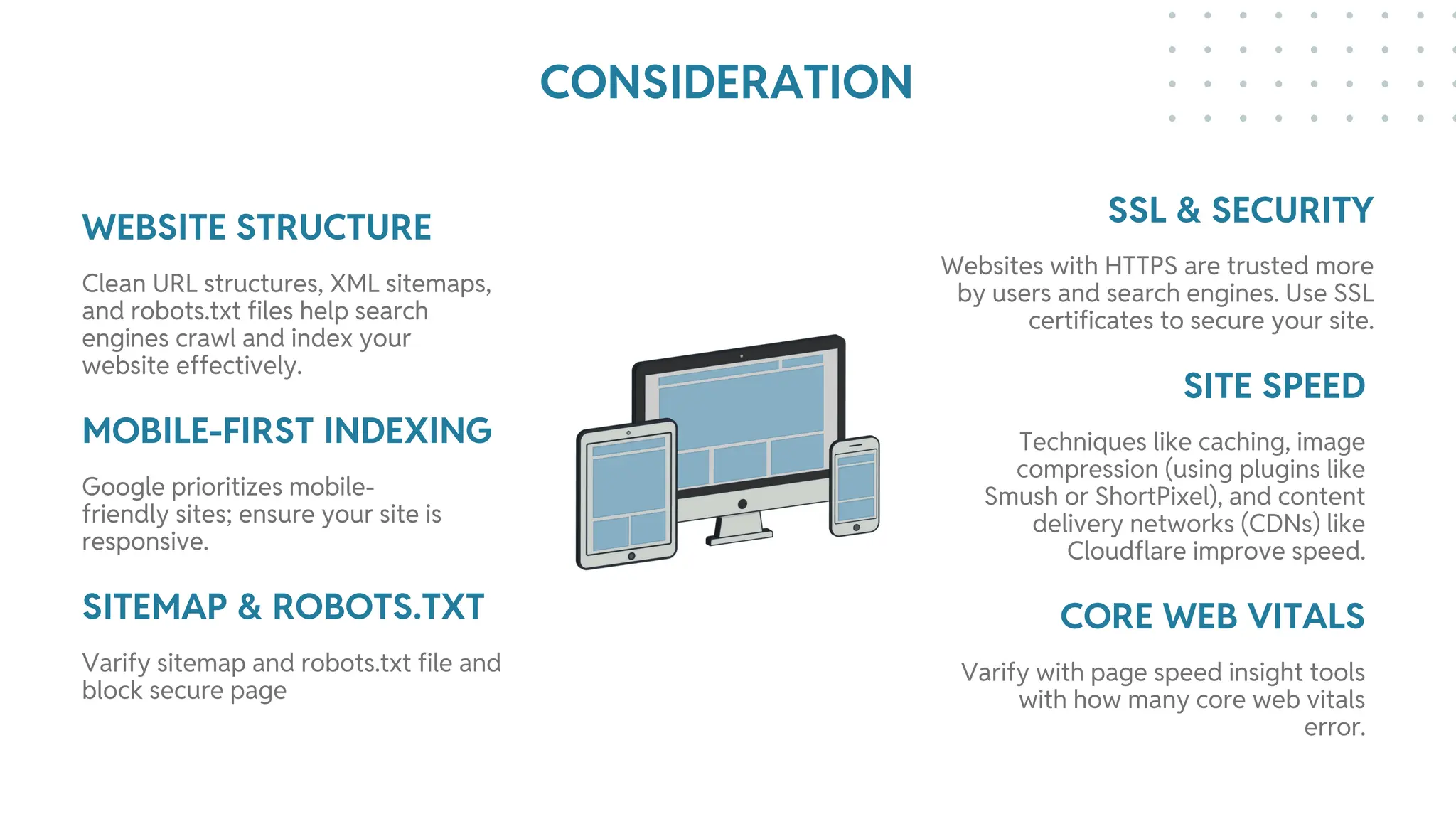
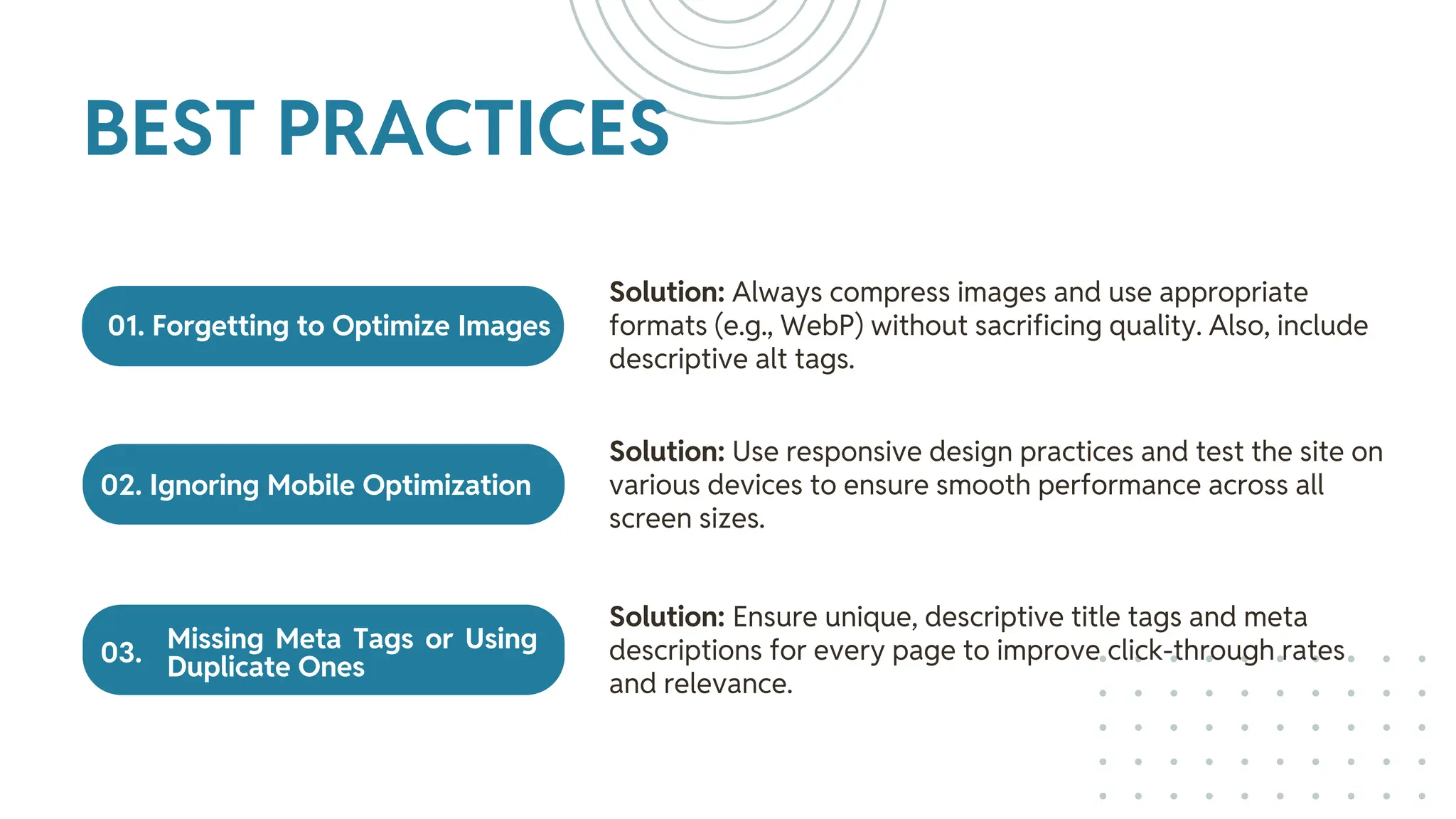
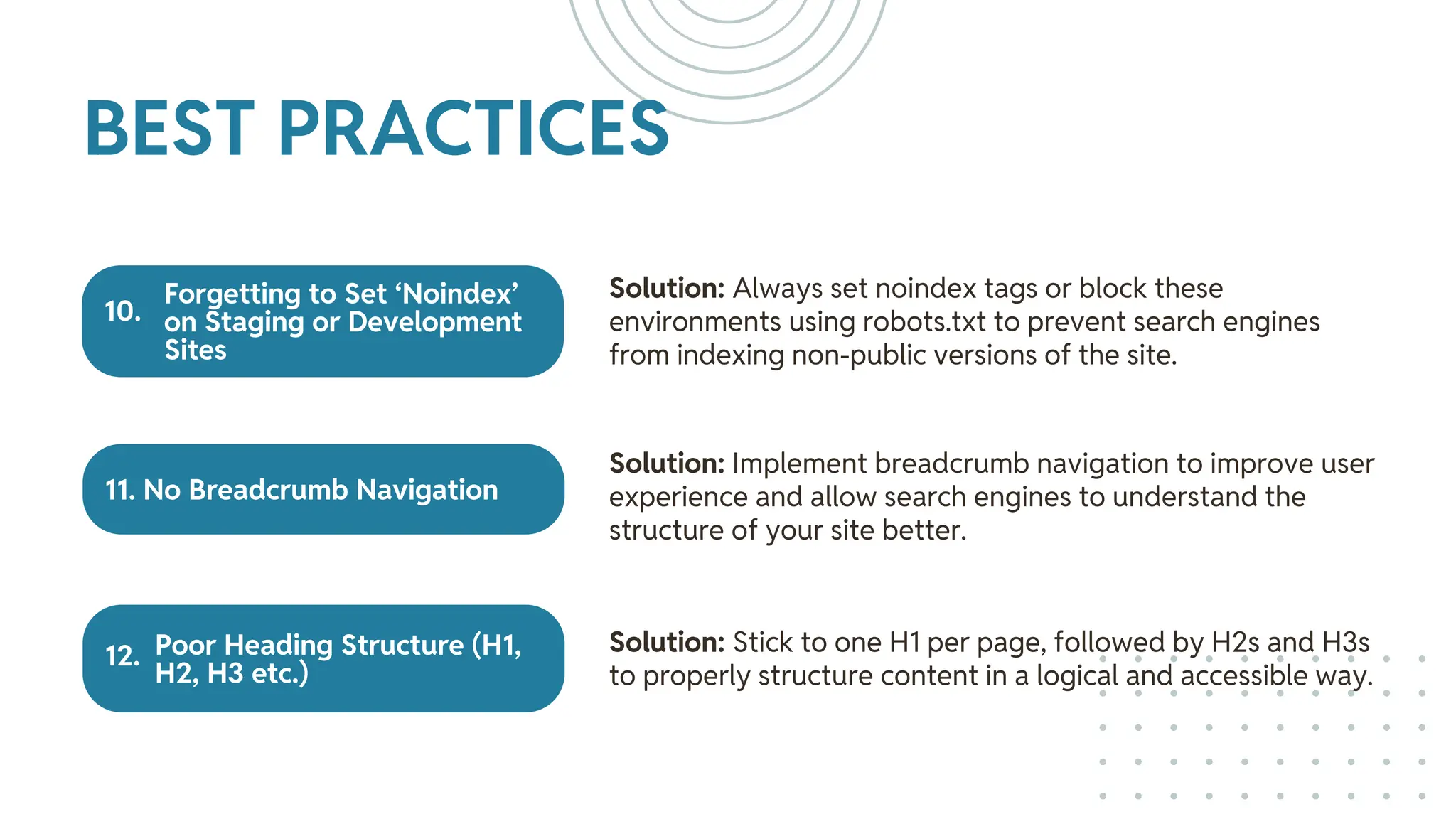
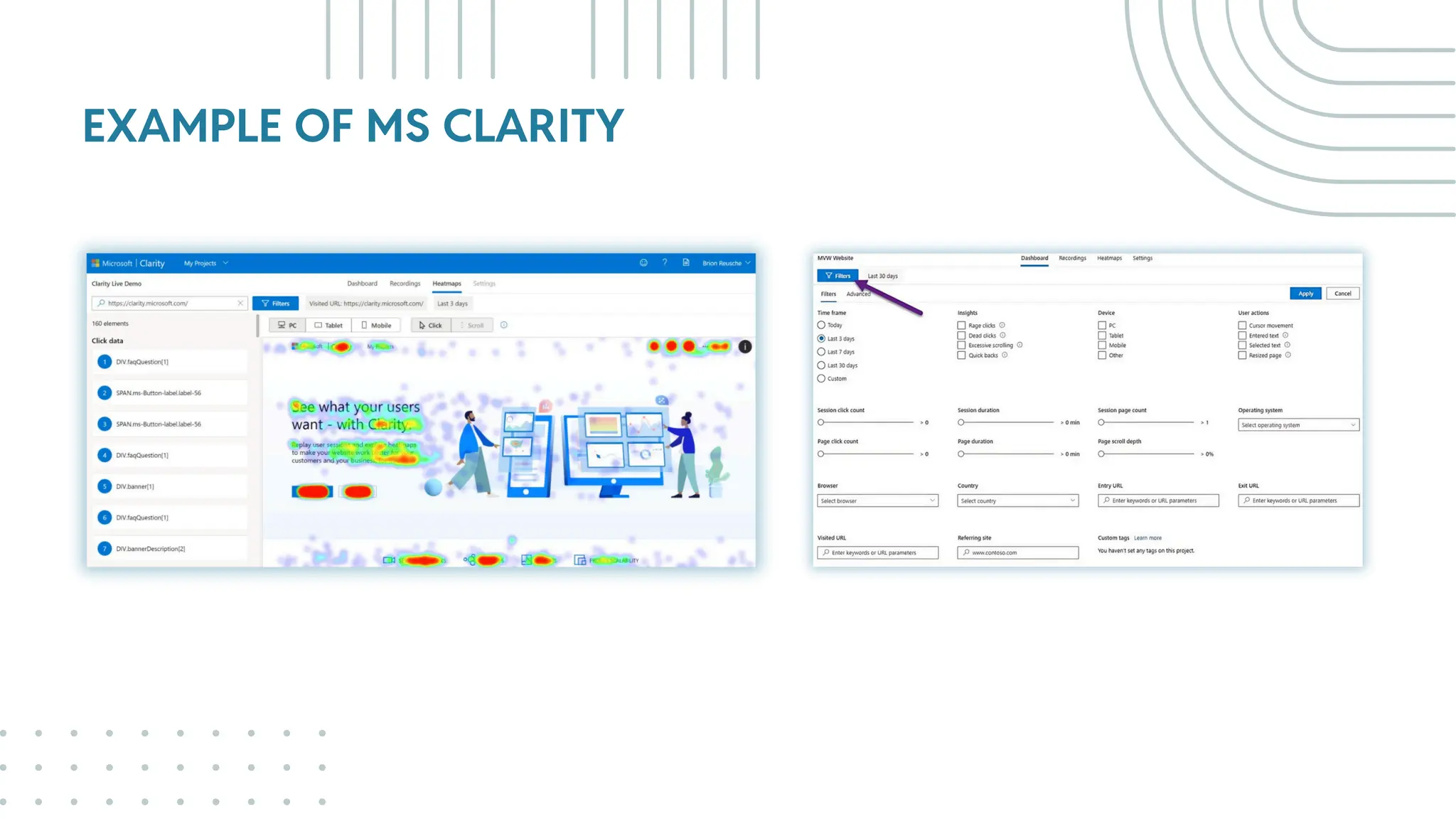
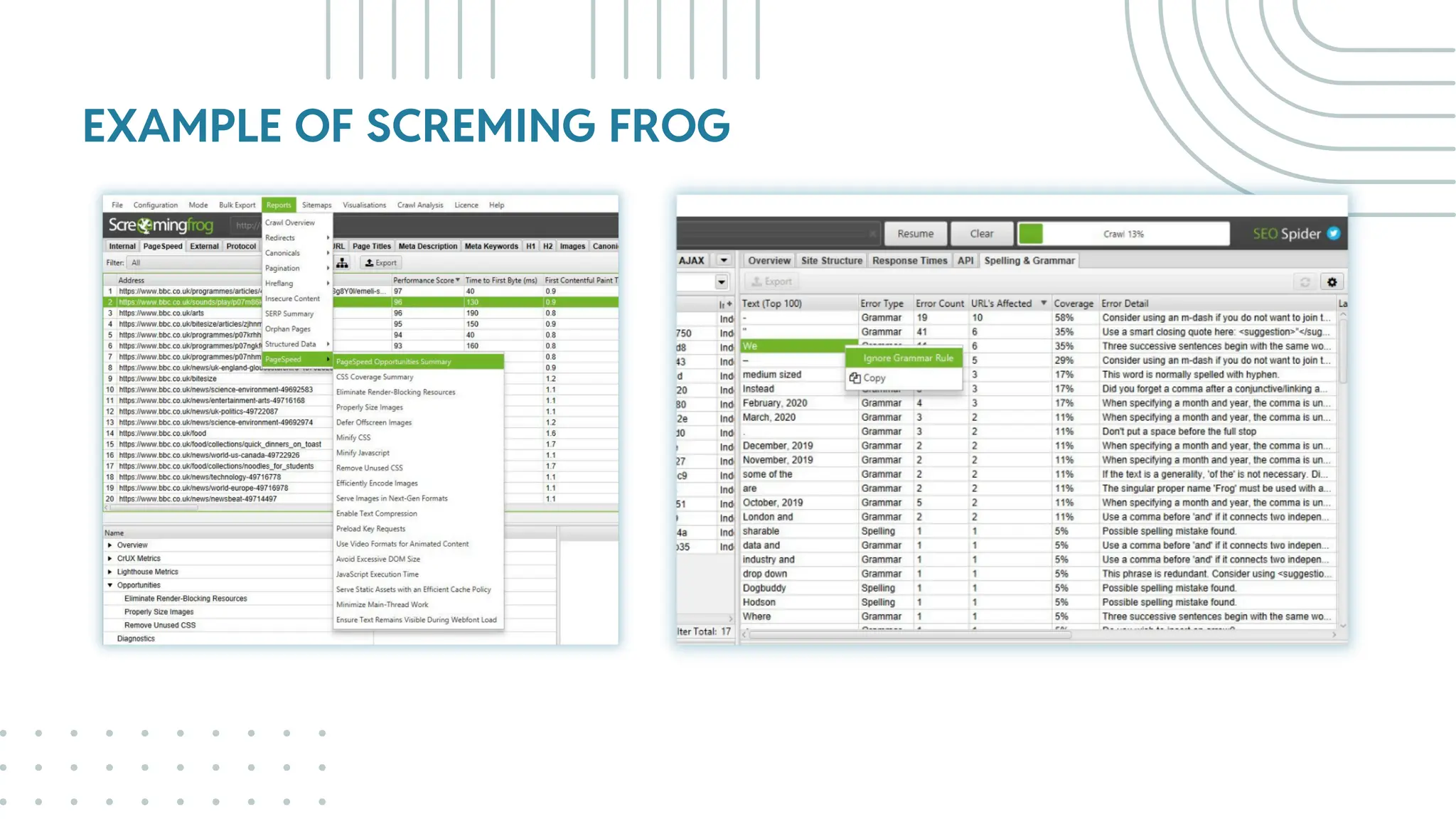
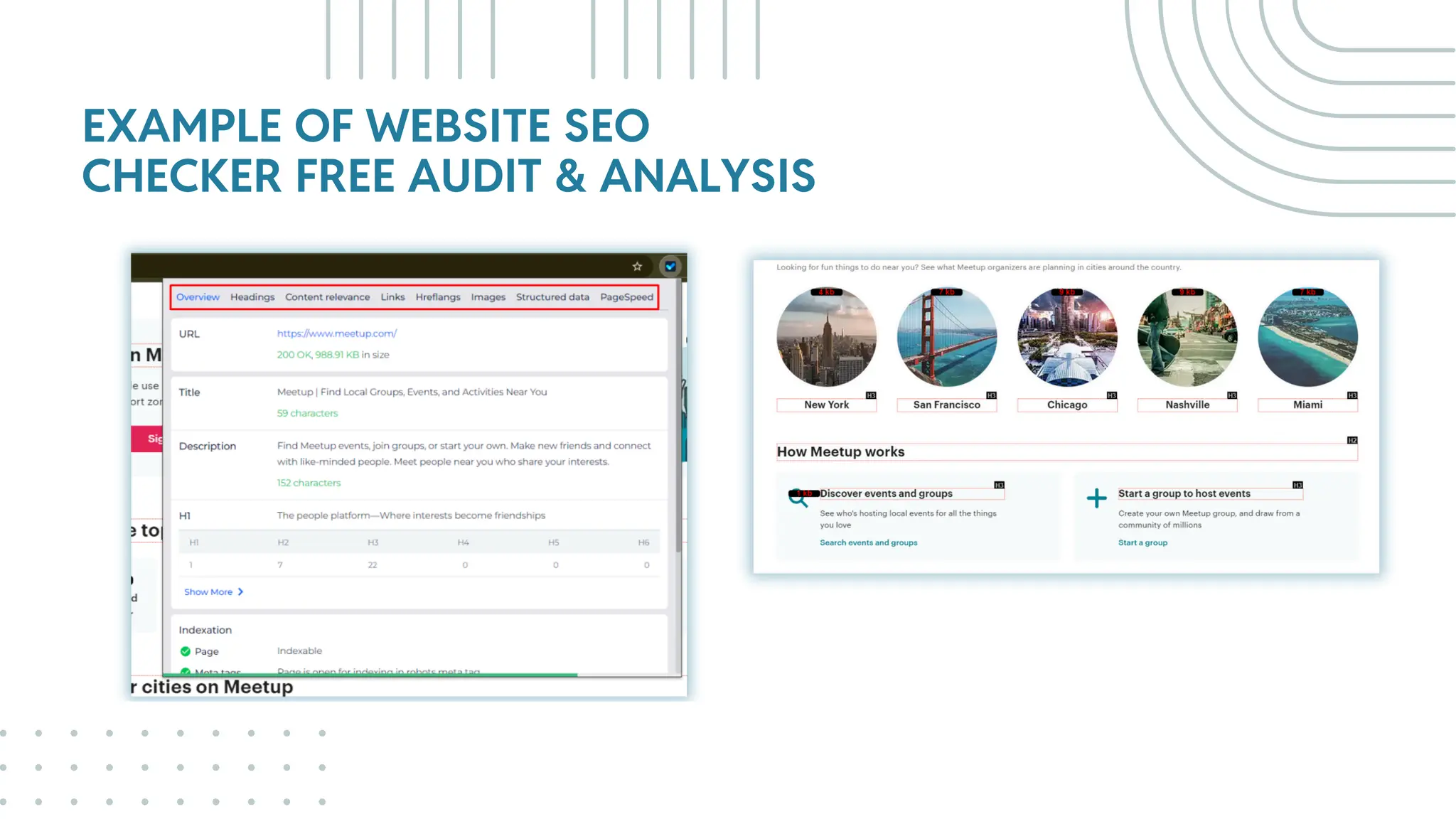
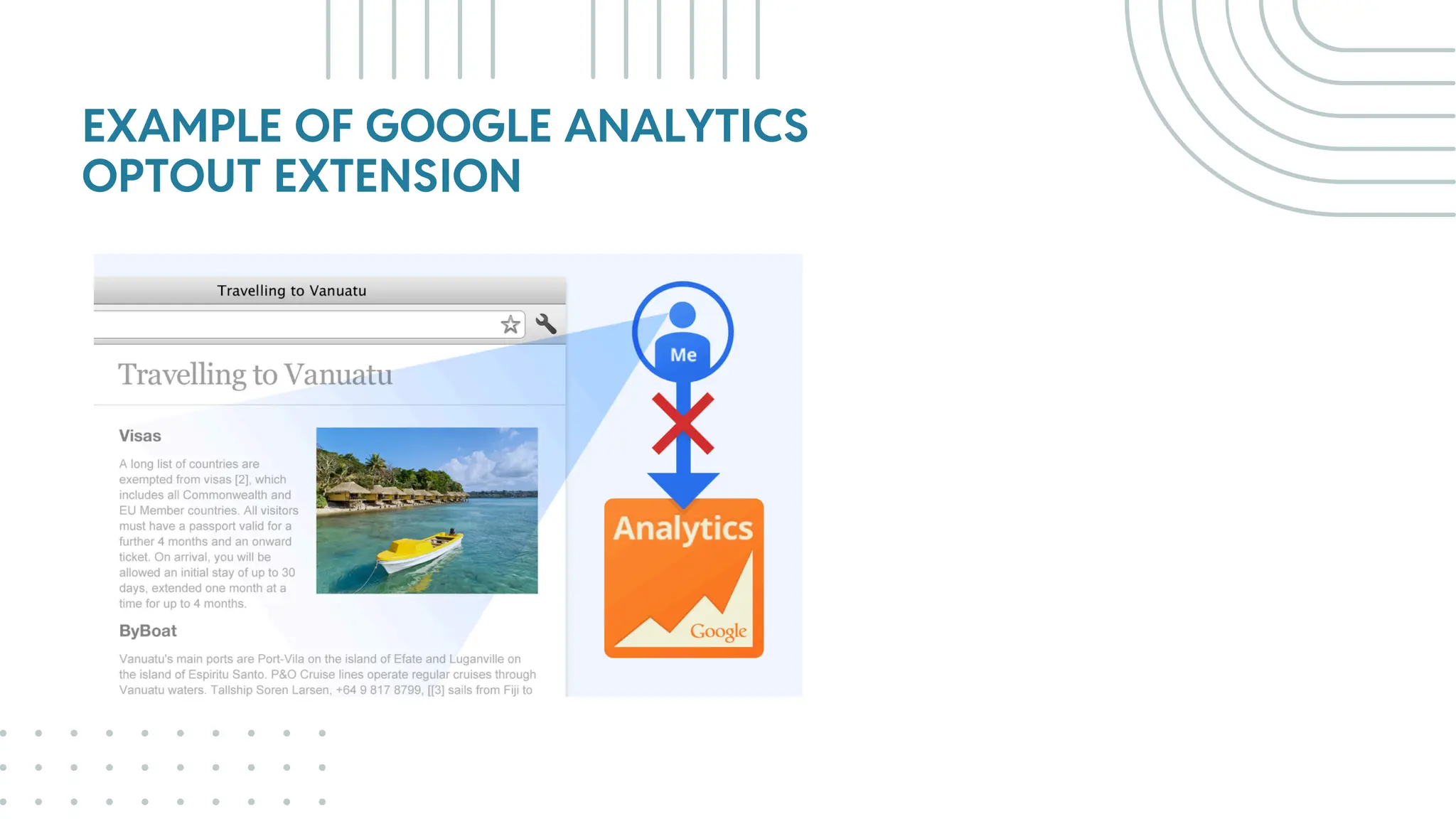
The document outlines best practices for WordPress SEO targeted at developers, covering essential topics such as how search engines operate, the importance of SEO, pre-SEO considerations, and various SEO strategies including on-page, off-page, and technical SEO. Key points emphasize the importance of website speed, mobile optimization, structured data (schema markup), and tools available for effective SEO management. The conclusion reinforces that developers play a crucial role in the SEO performance of websites by making informed decisions about site architecture and user experience.