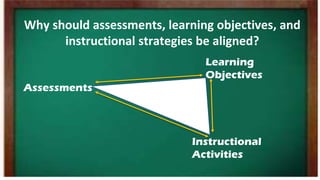
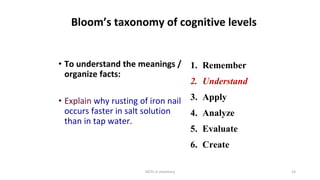
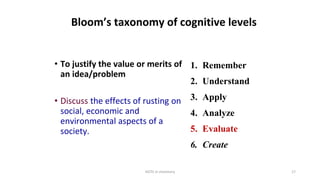
The workshop focused on aligning assessments, learning objectives, and instructional strategies to enhance student learning outcomes. It emphasized the importance of creating appropriate assessments for different cognitive levels defined by Bloom's Taxonomy, and provided examples of tasks to assess knowledge, application, analysis, and creation. Participants were instructed to define measurable objectives for each cognitive level to improve educational effectiveness.