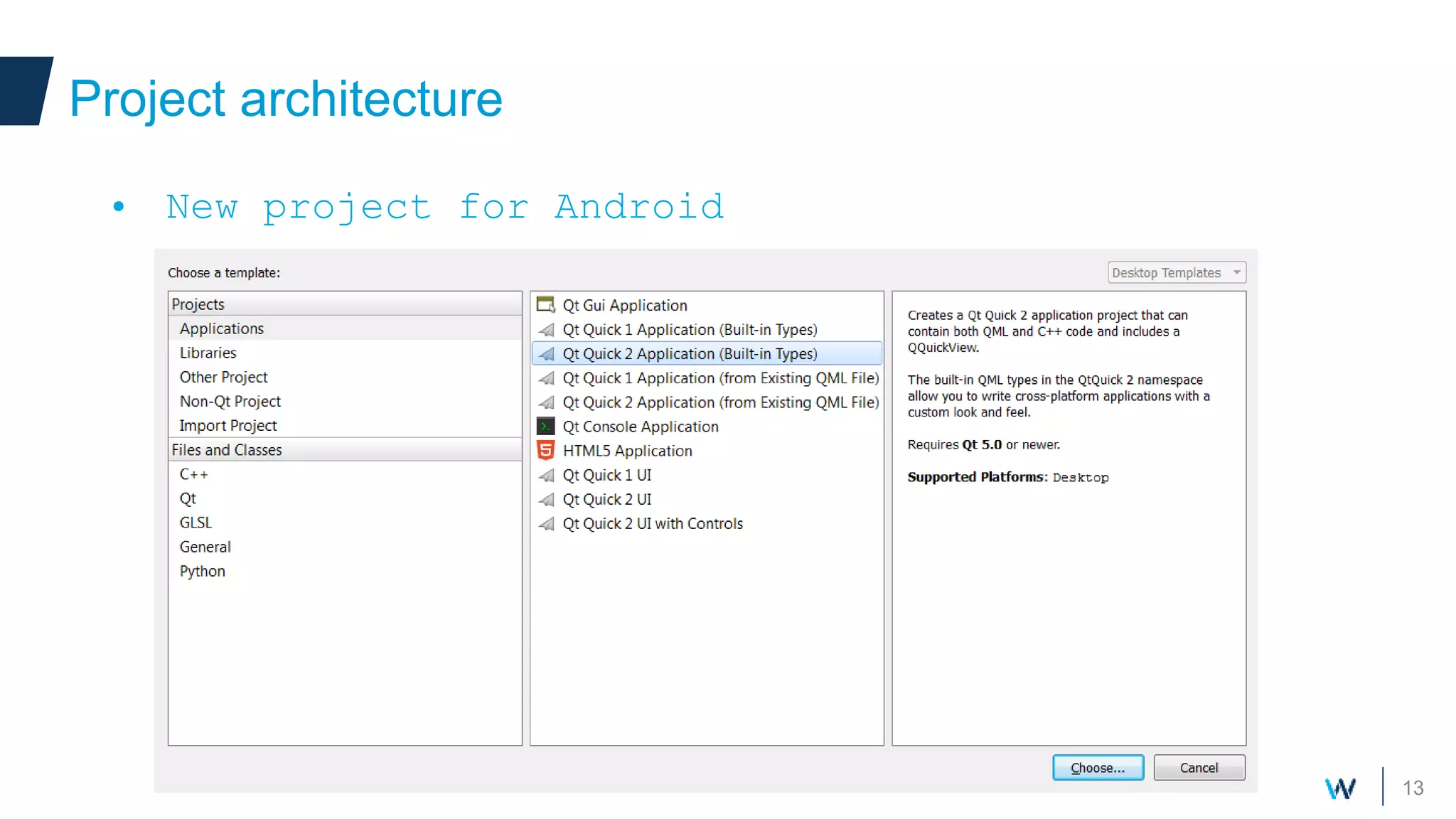
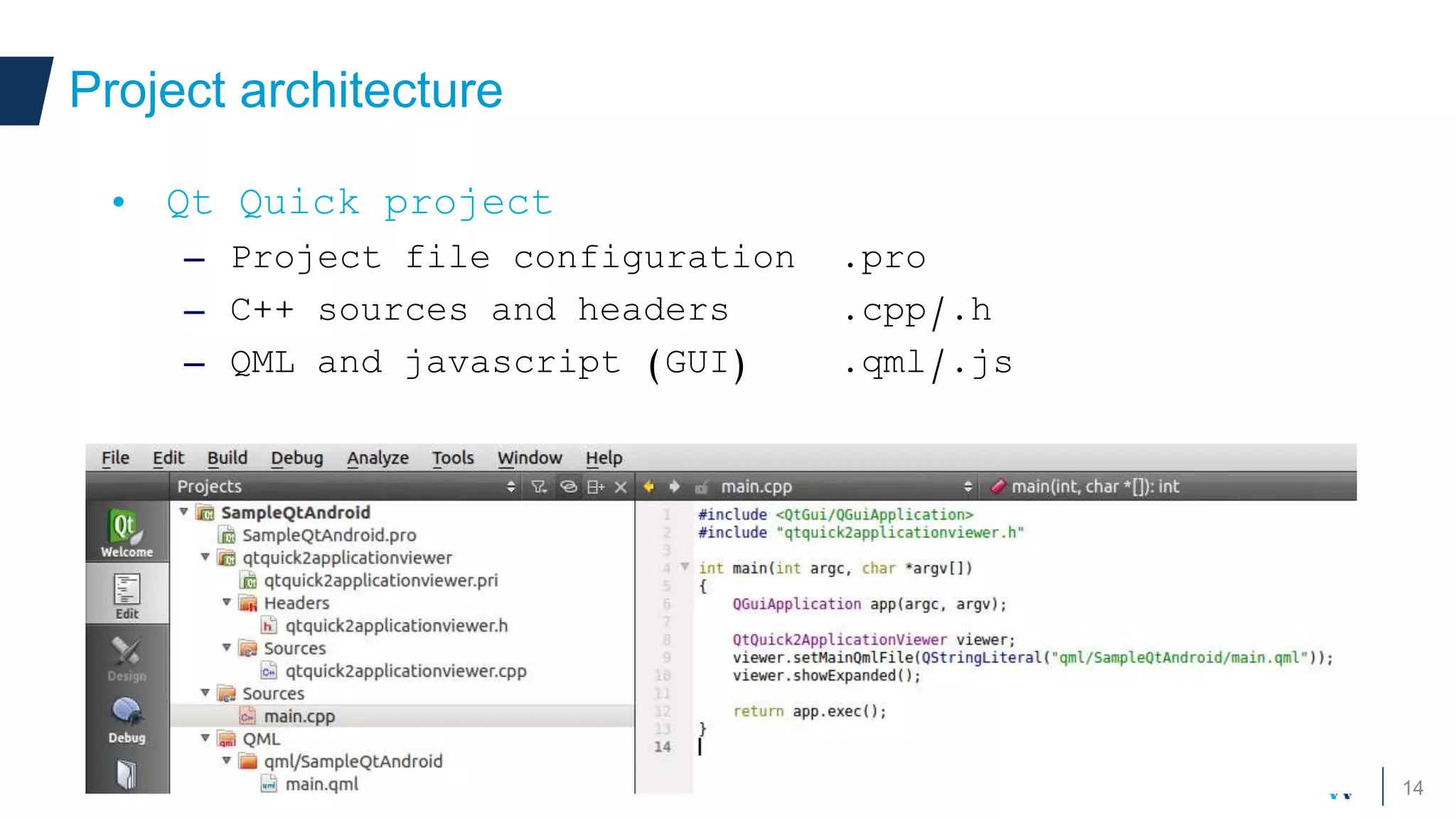
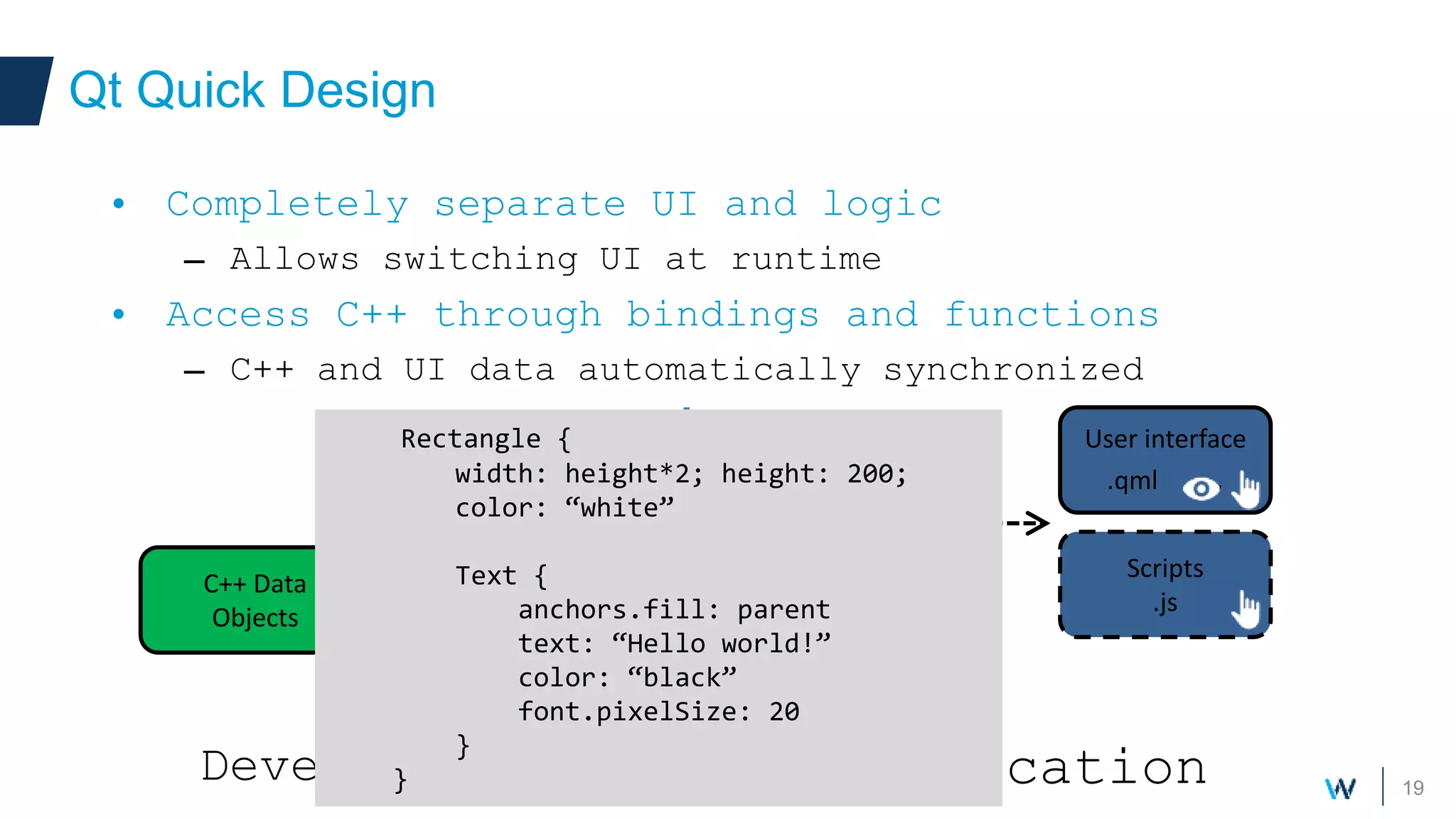
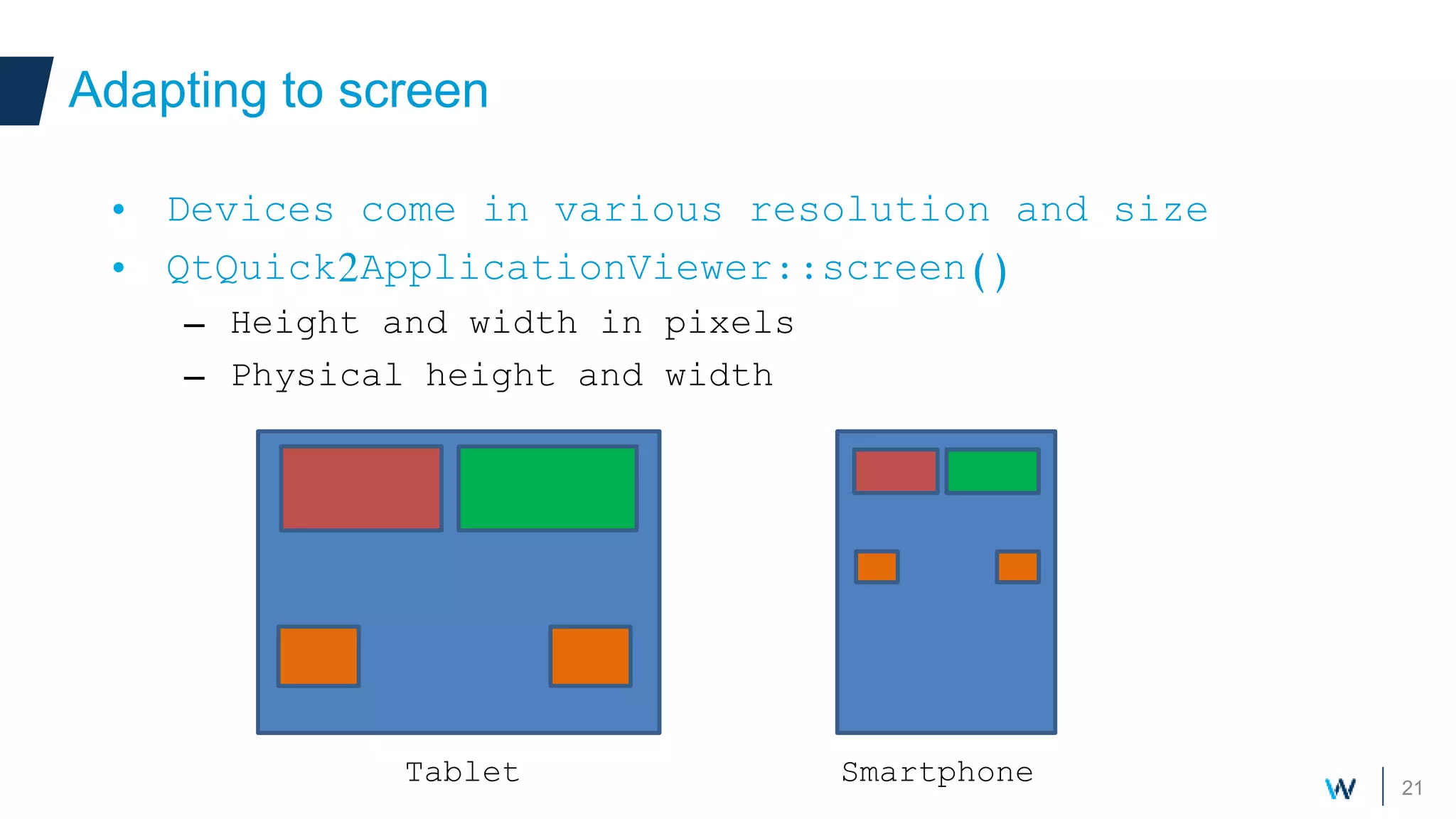
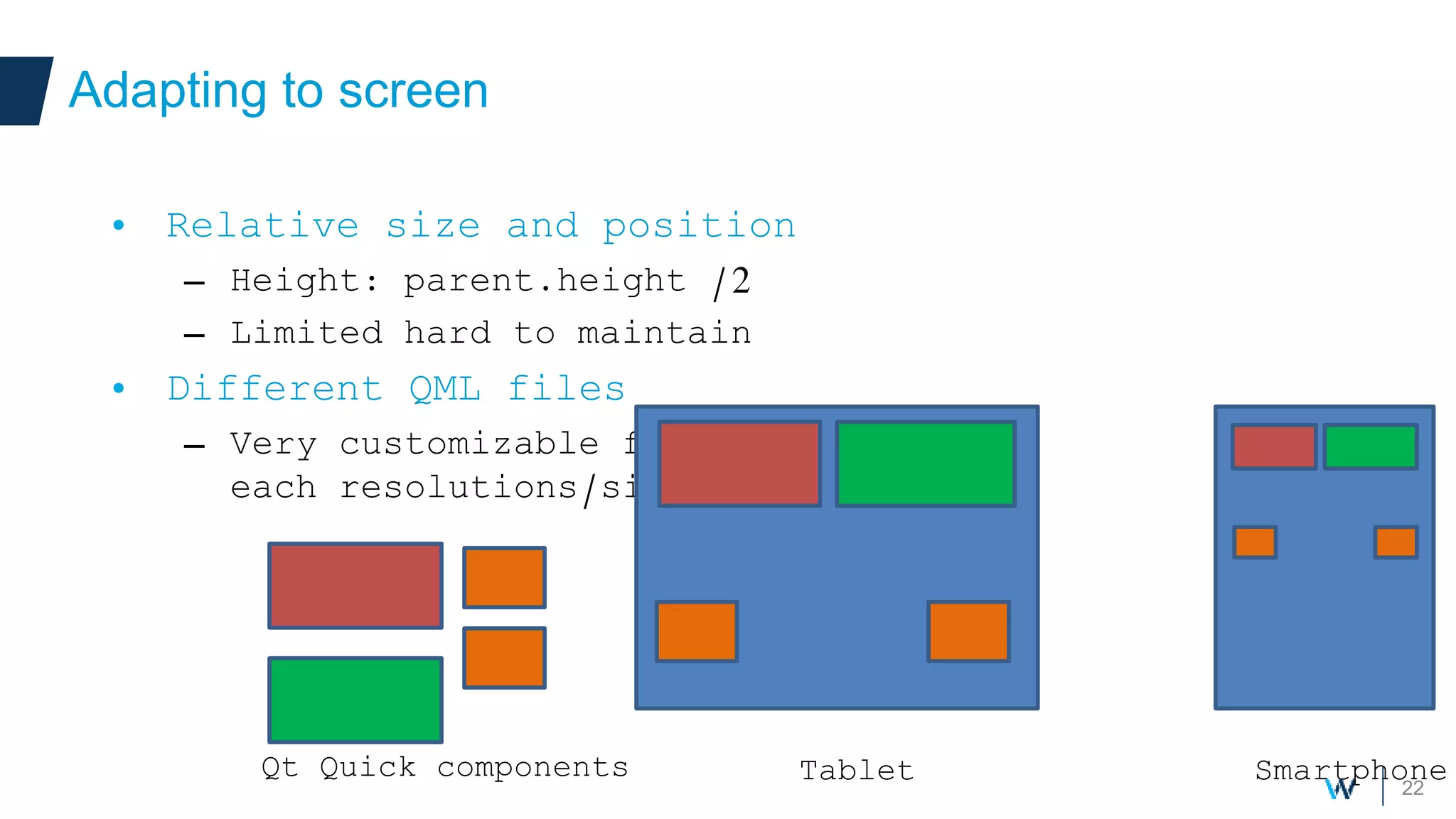
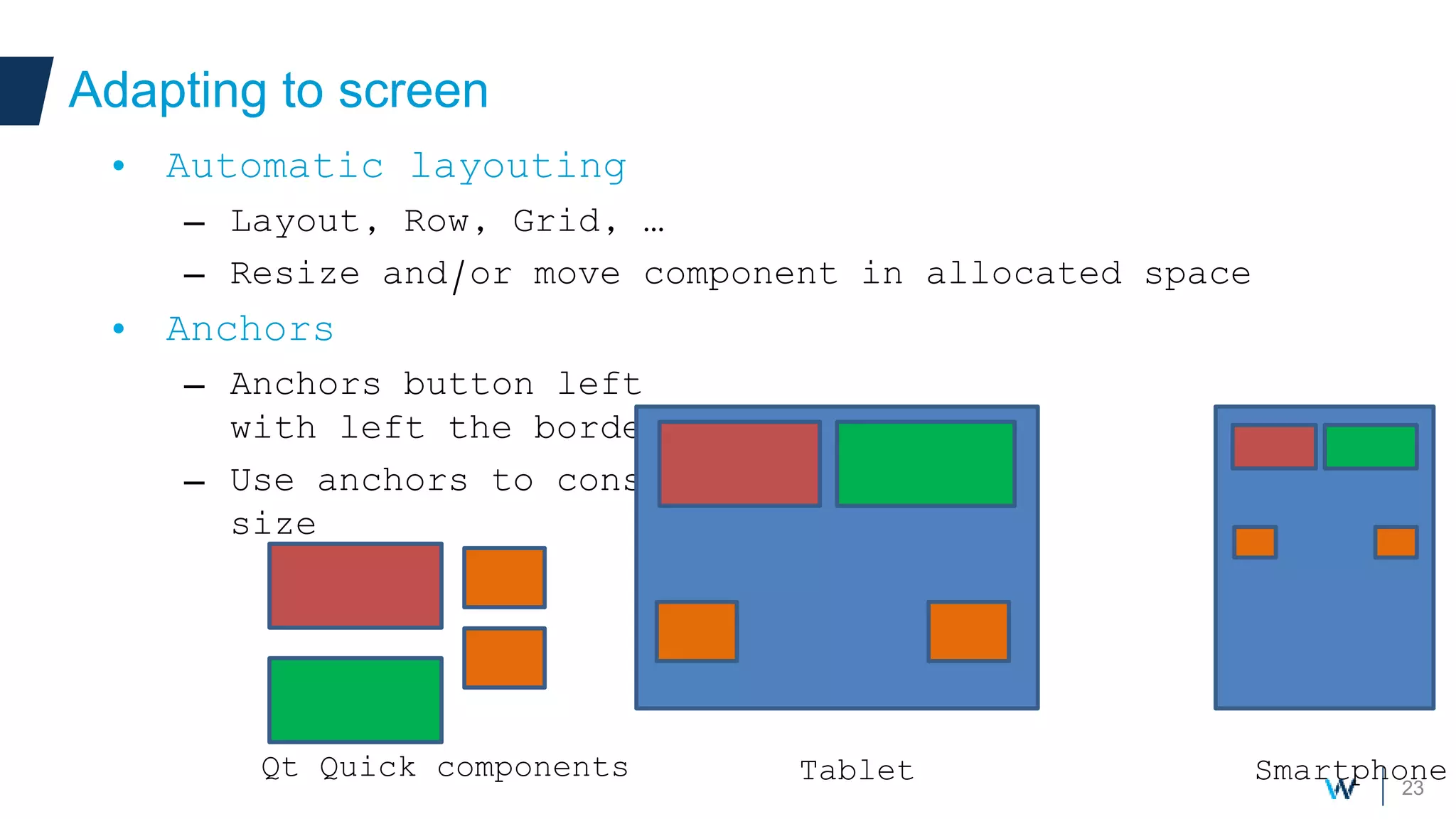
Qt allows developers to create cross-platform applications that can run on desktop, web, mobile and embedded devices like Android. There are two main ways to build Qt applications for Android - as a dedicated "boot to Qt" device or as a regular Android application within the Play Store. The talk discusses using Qt Quick for its support of gestures, animations and touch interfaces on mobile. Key Qt features like databases, networking and sensors are supported. Deployment can be to an attached device, simulator or by bundling Qt libraries into a distributable Android application package.