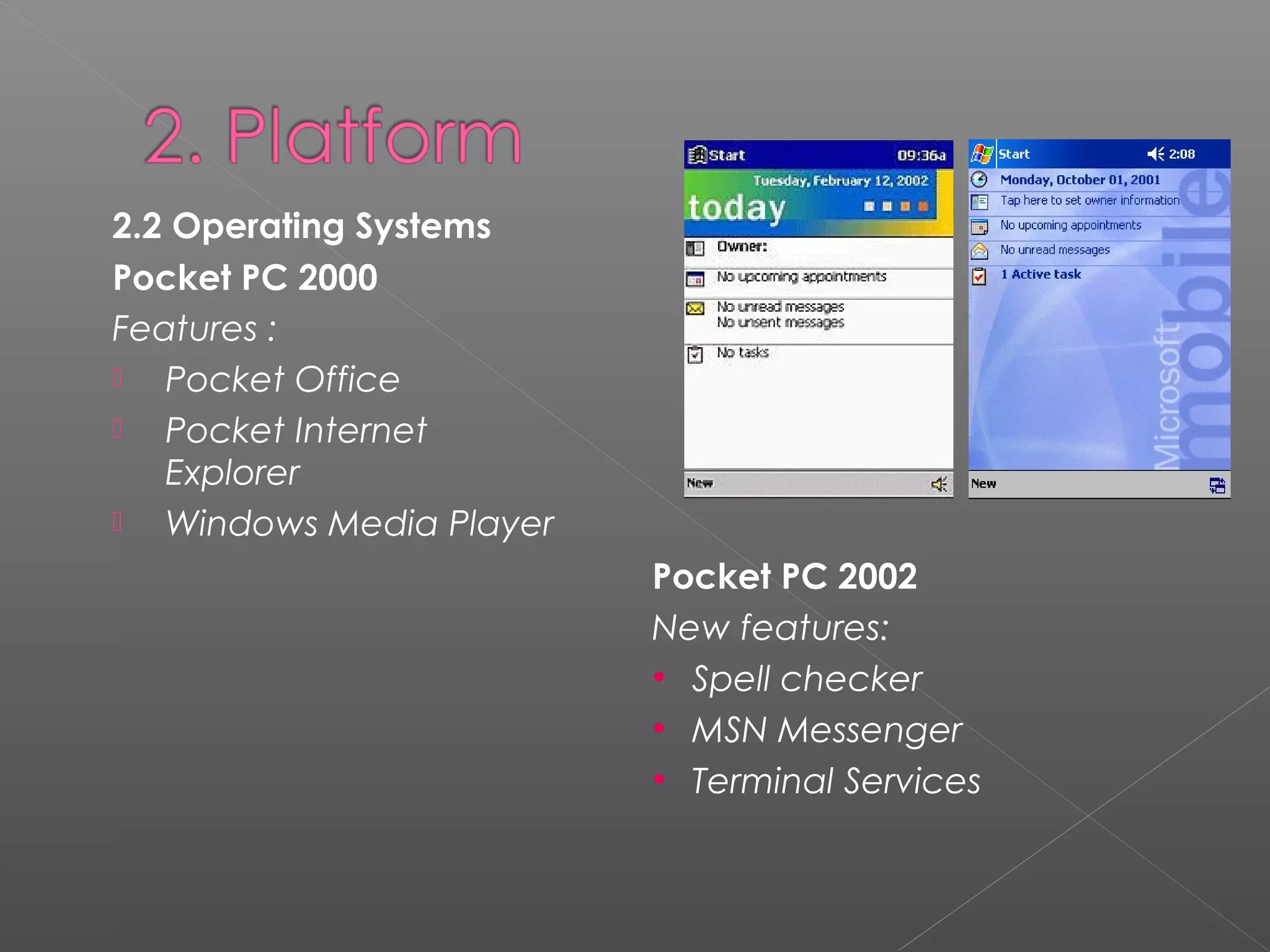
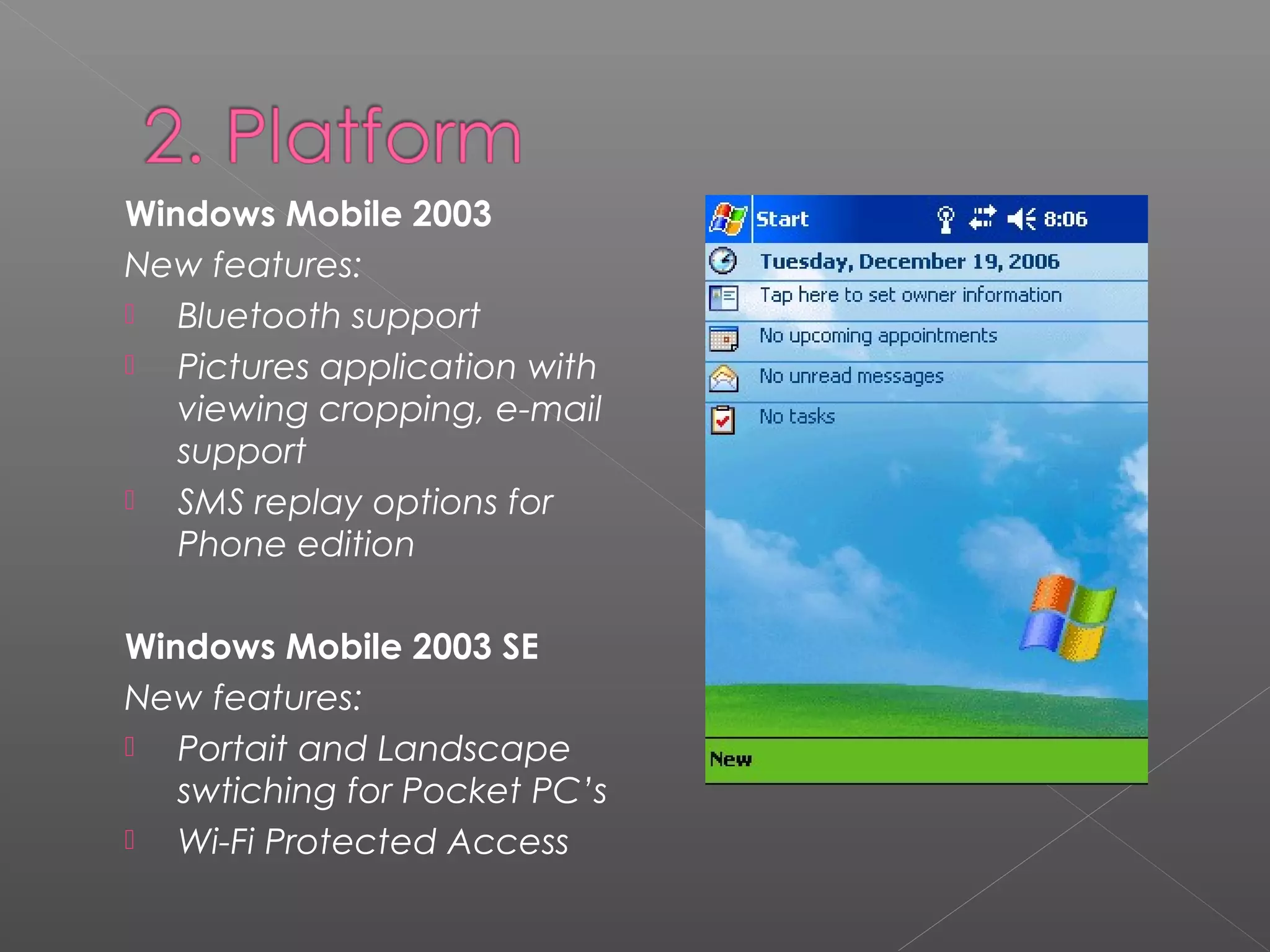
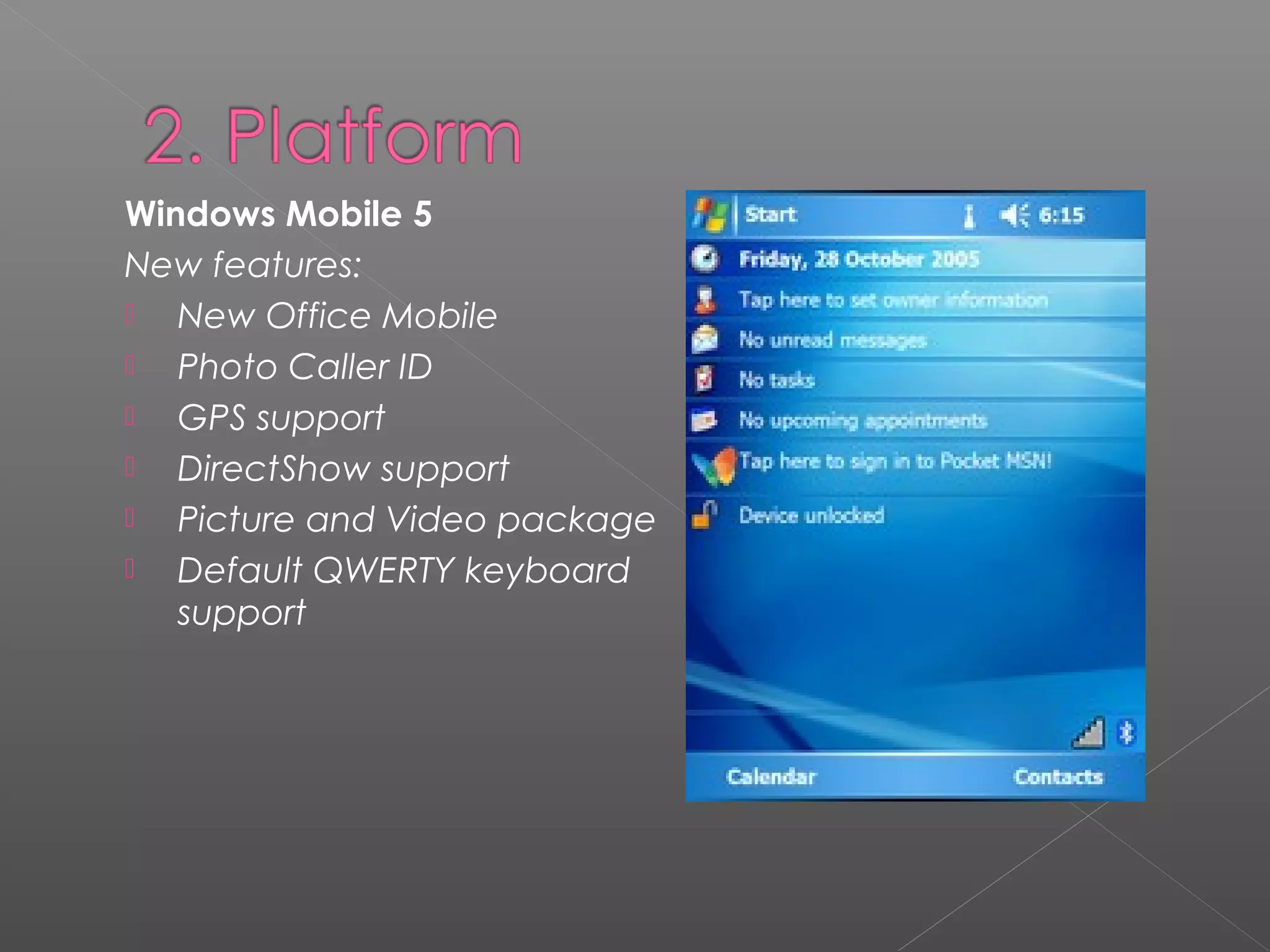
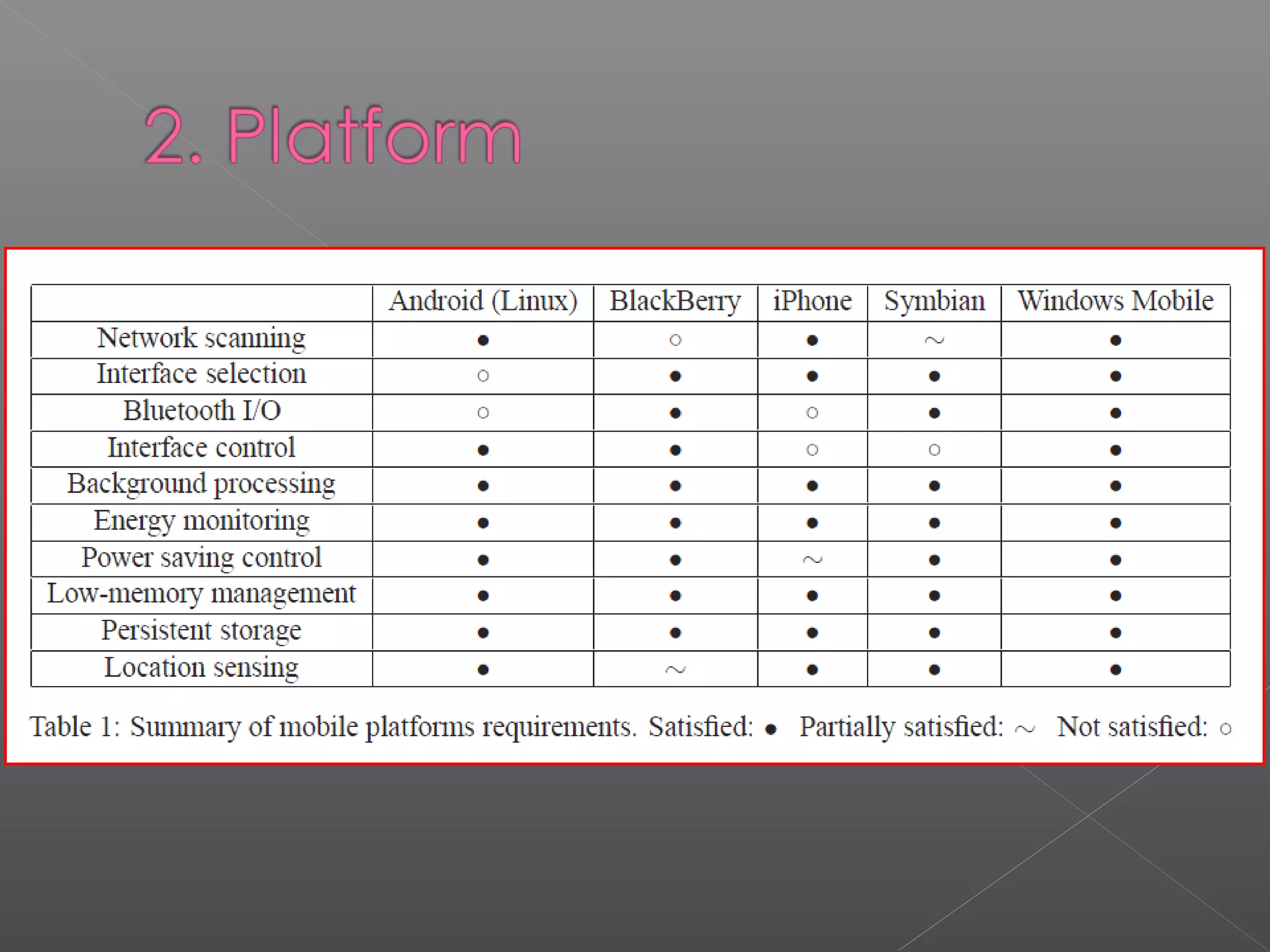
Windows Mobile is a compact operating system that runs on mobile devices like Pocket PCs, smartphones, portable media centers and automotive computers. It is designed to resemble desktop versions of Windows. Third party software can be developed for Windows Mobile using languages like C# and Visual Basic in the Visual Studio IDE. While Windows Mobile provides connectivity options and security features, its interface has been criticized for the number of steps required to perform tasks. However, Microsoft continues improving Windows Mobile.