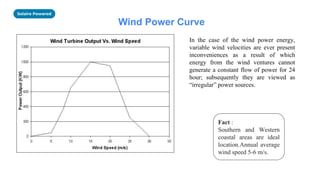
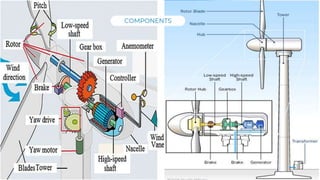
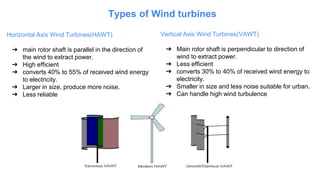
The document presents an overview of wind energy, including its history, power generation mechanisms, and types of wind turbines. It discusses the components of wind energy systems, such as horizontal and vertical axis turbines, and highlights wind energy potential and projects in Nepal. Additionally, it provides global trends in wind energy growth and its significance in climate change mitigation strategies.