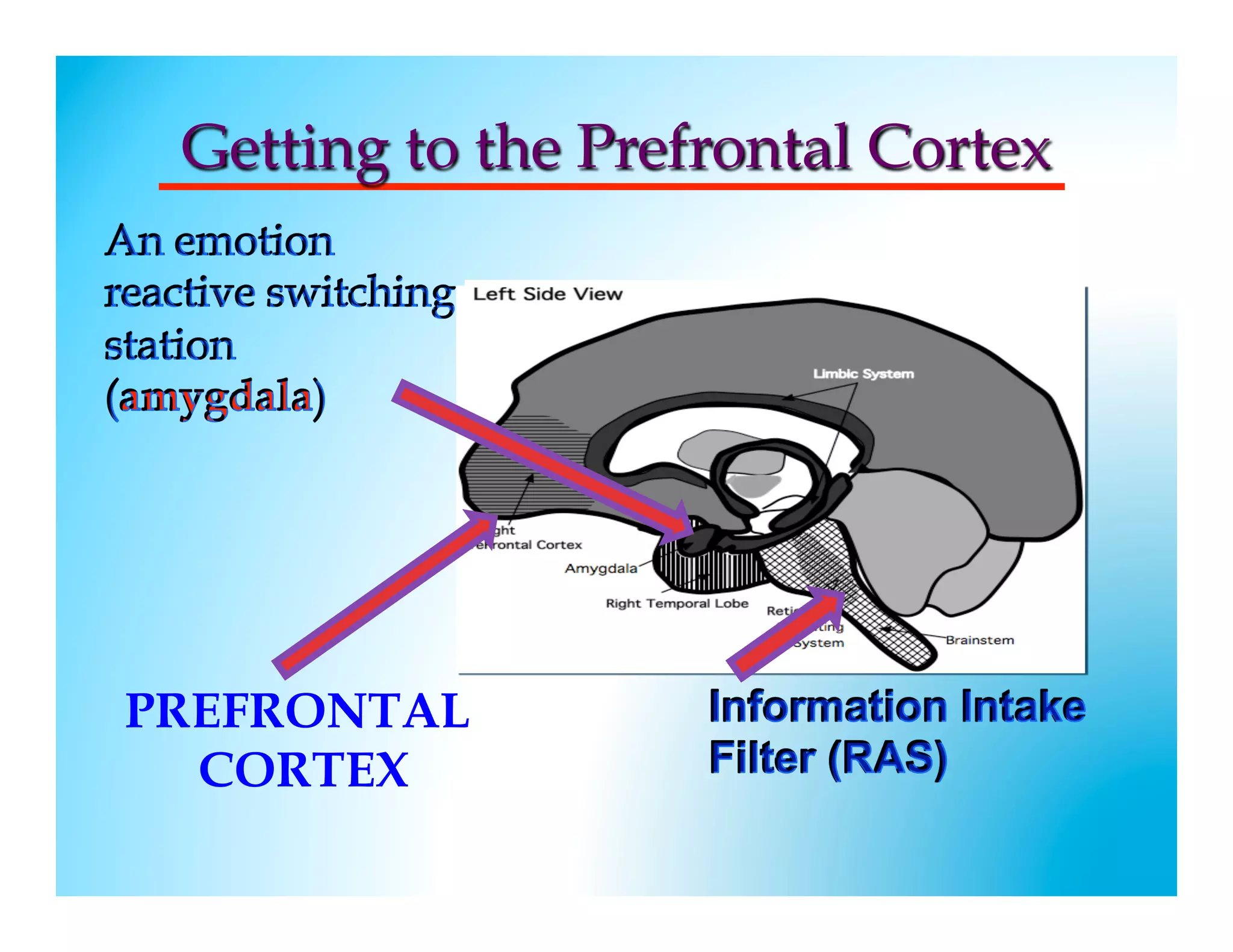
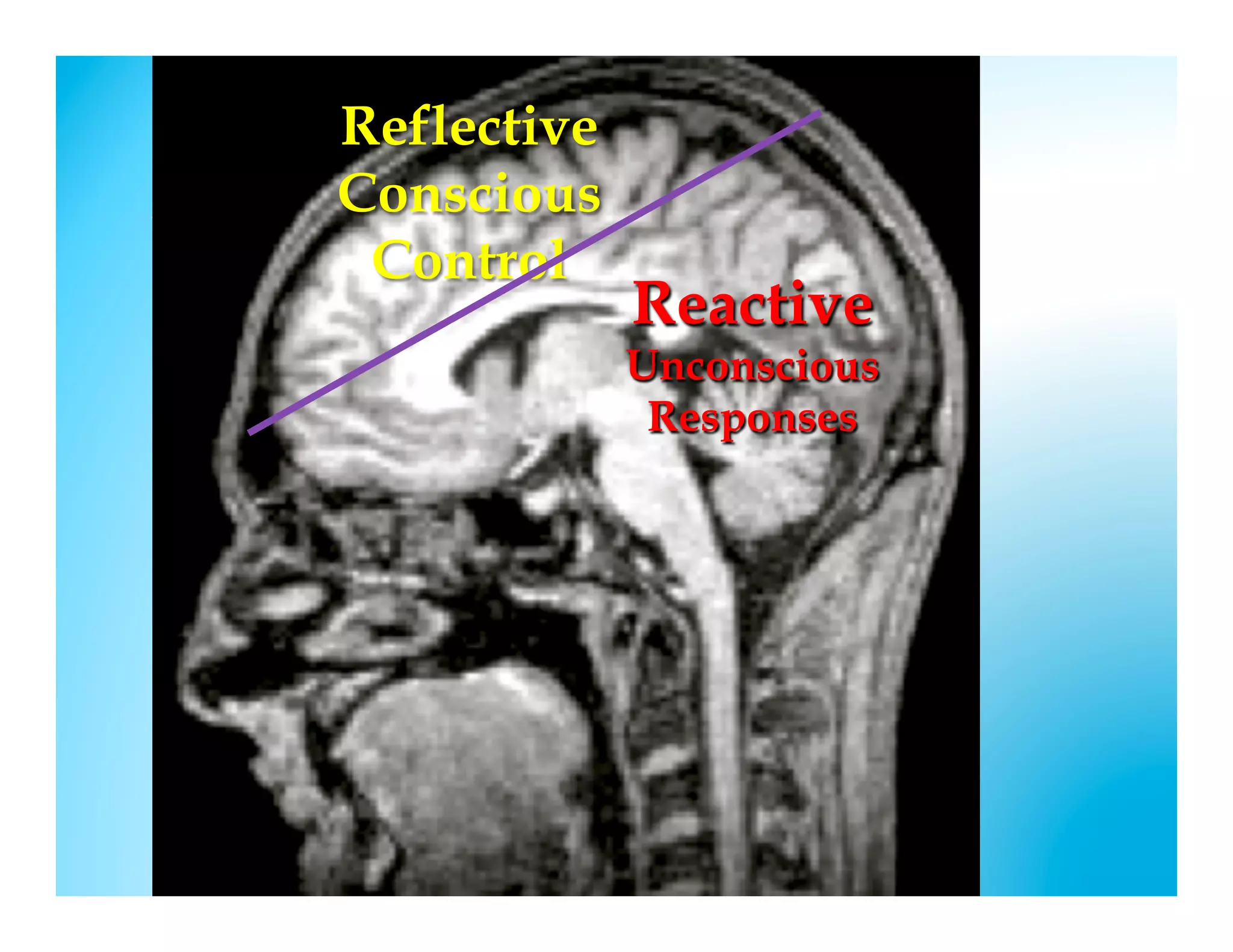
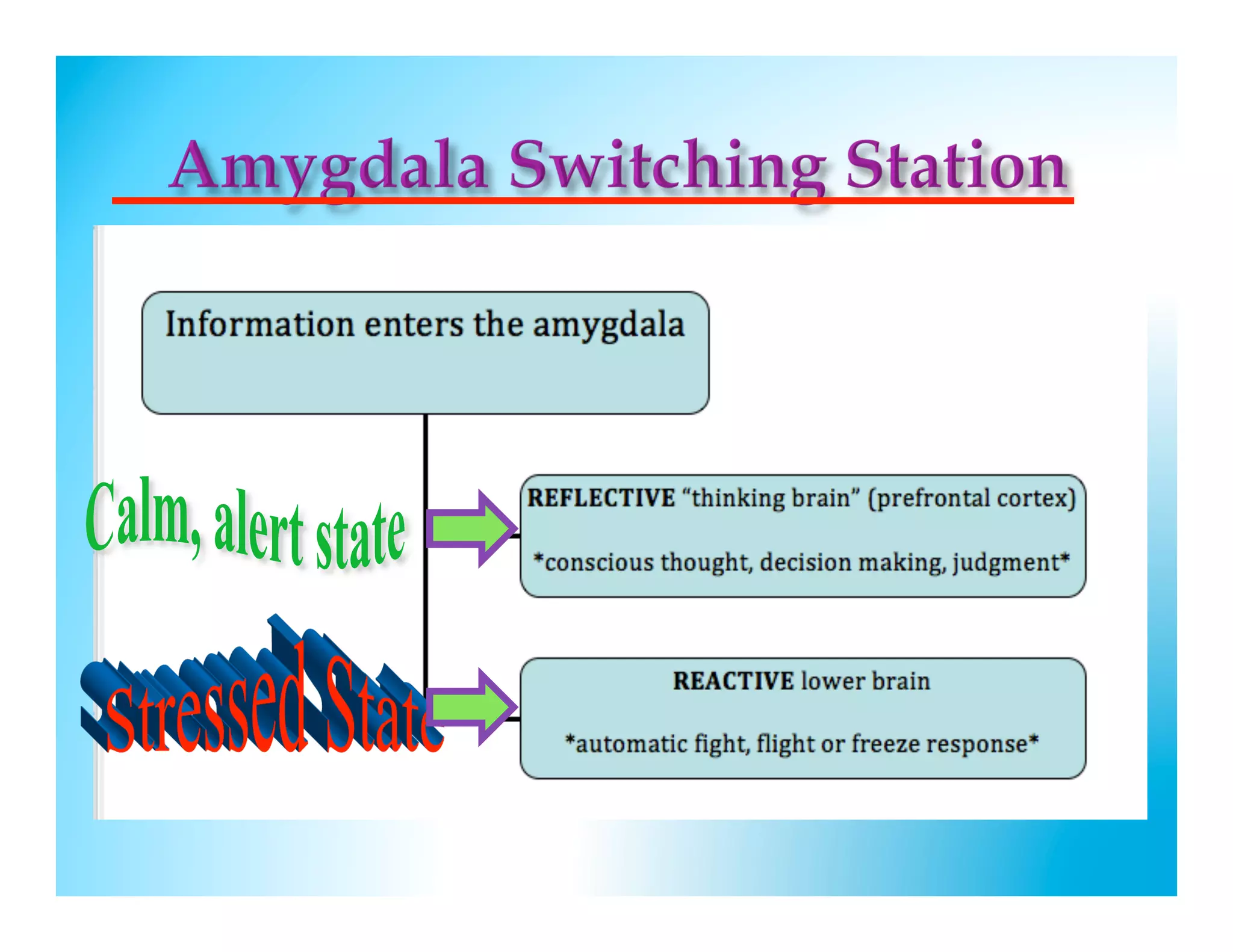
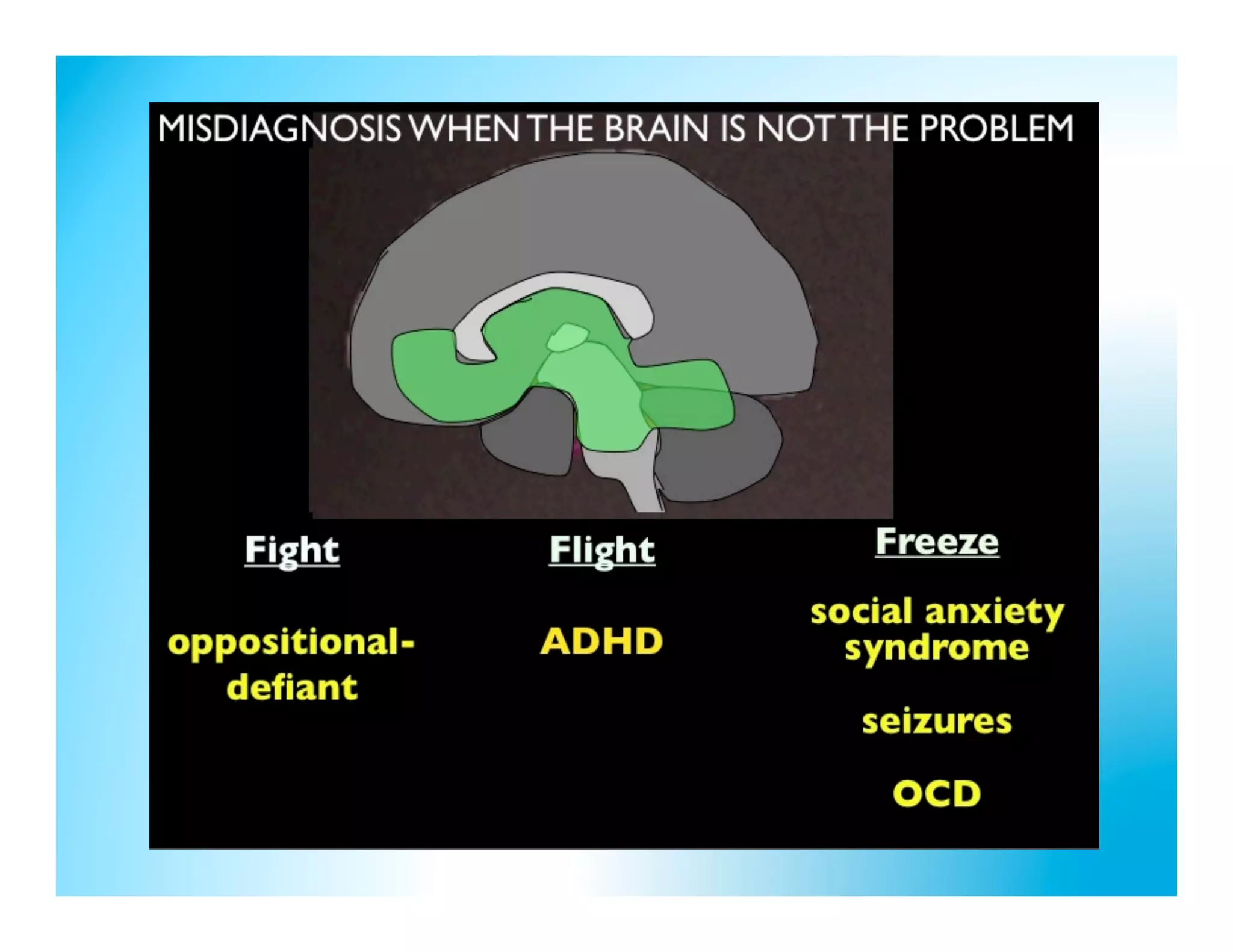
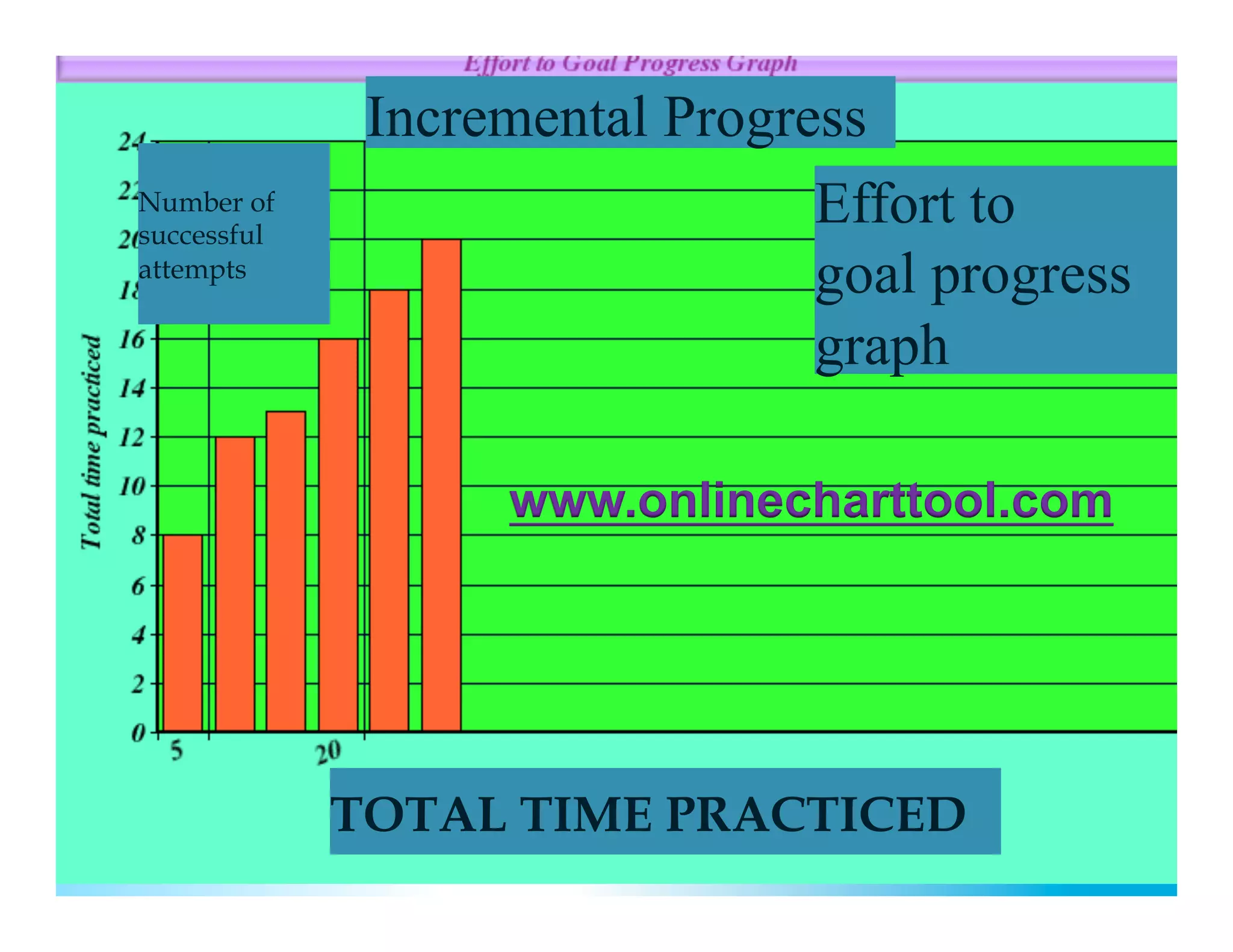
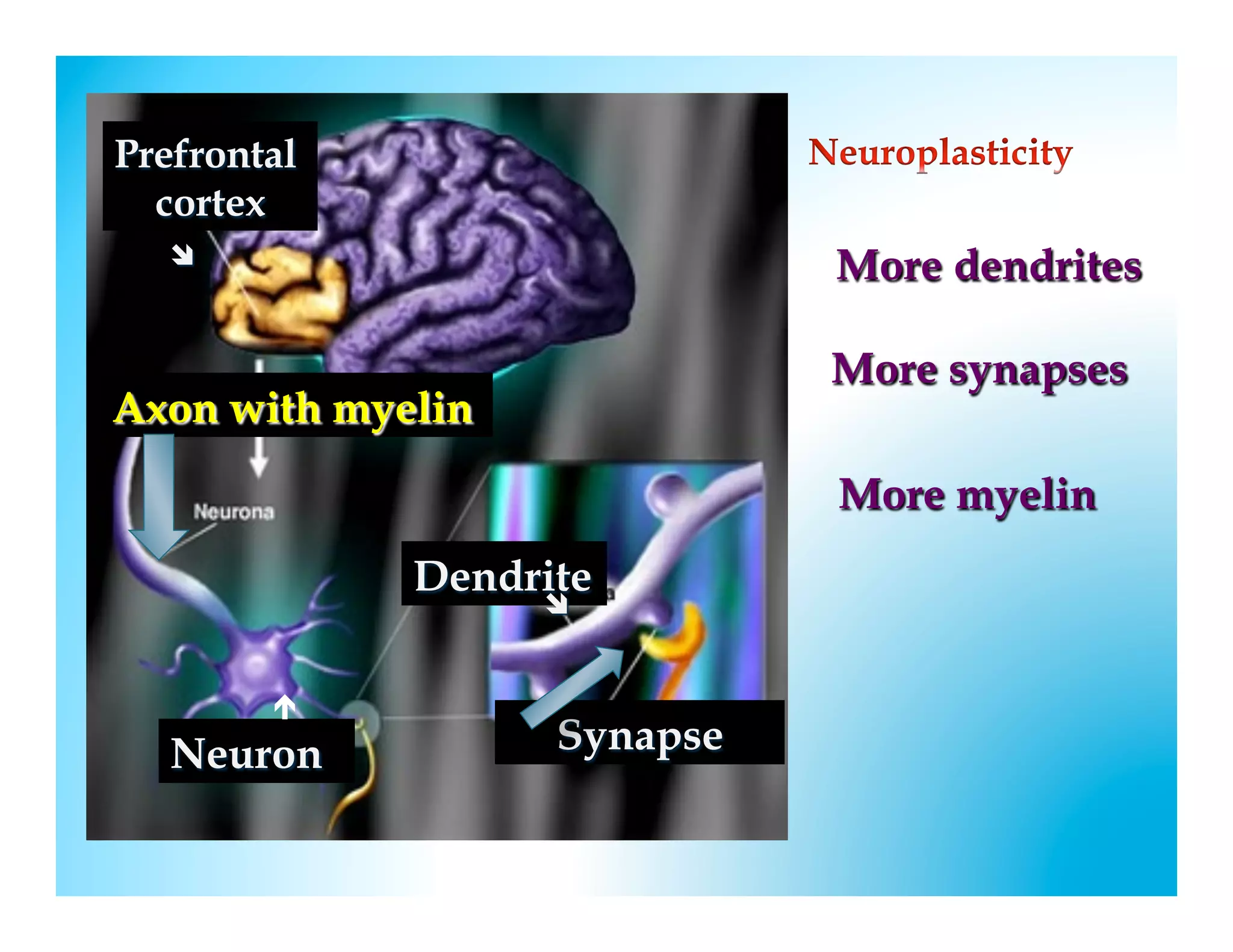
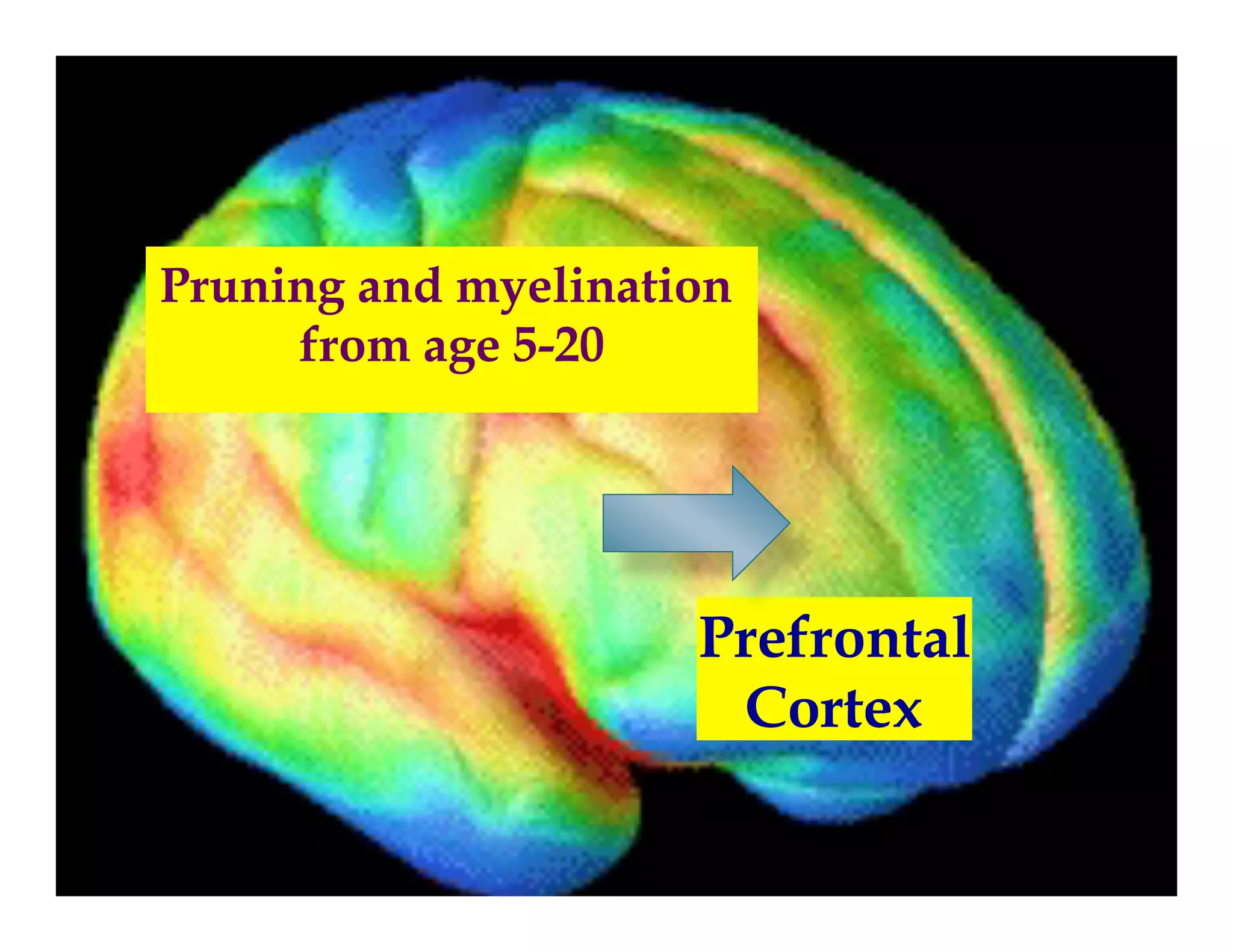
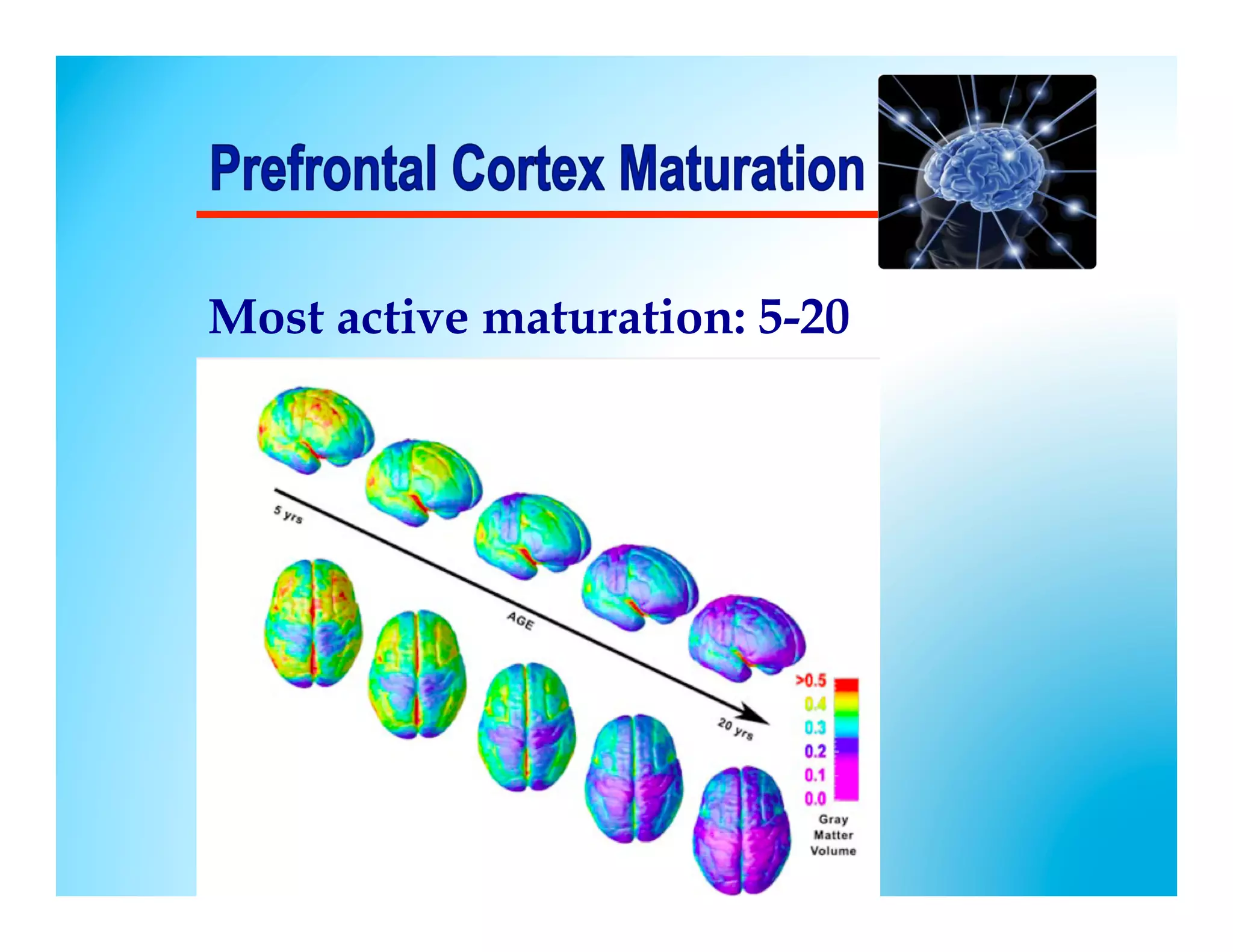
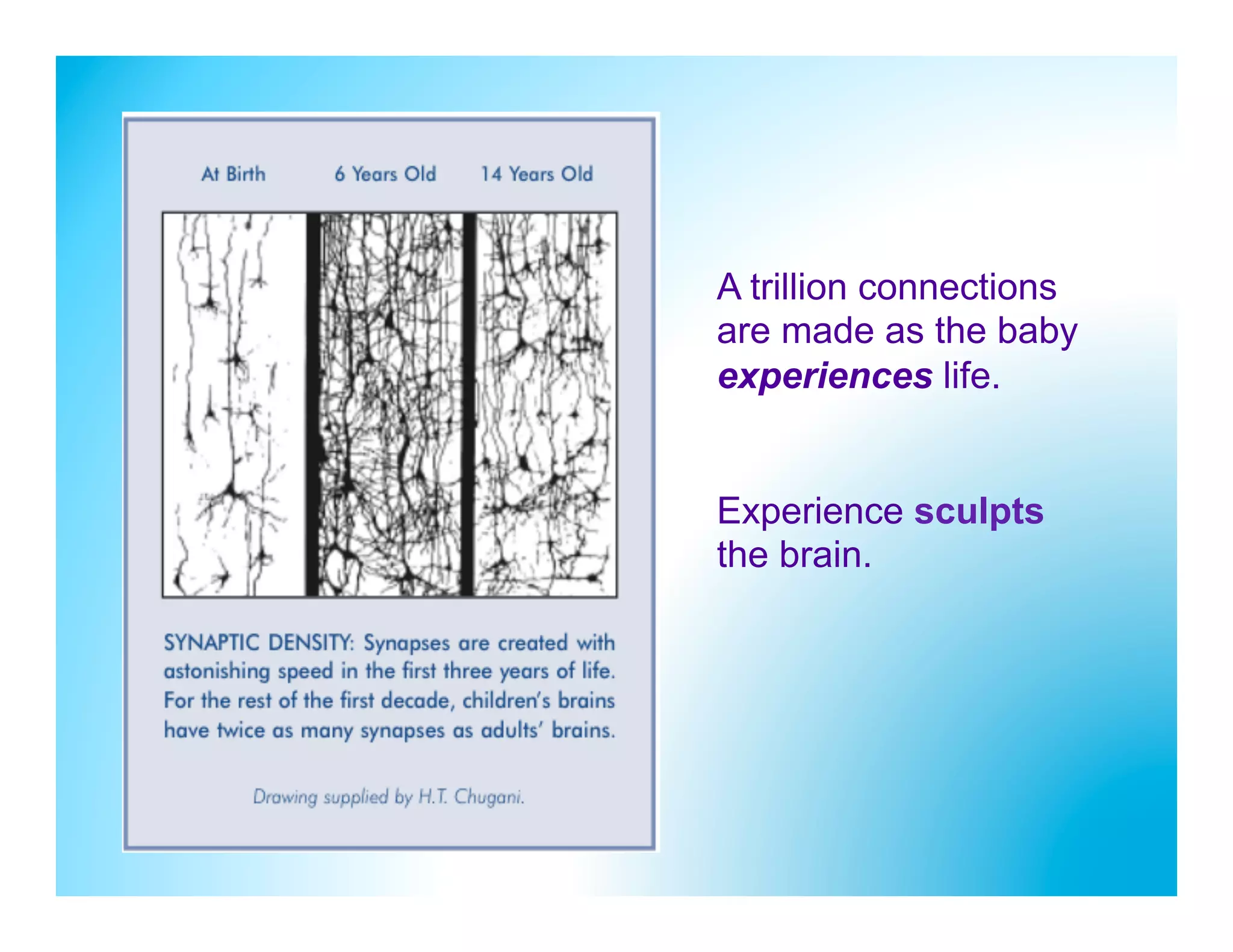
The document discusses how to develop the prefrontal cortex and executive functions in children. It explains that the prefrontal cortex, which controls executive functions like planning and decision making, develops between ages 5-20. Repeated practice of executive functions through activities that provide feedback and incremental progress can strengthen the neural connections in this brain region. Examples given include video games, which motivate players through achievable challenges and feedback. The document recommends giving children opportunities to analyze new information, consider different perspectives, and make decisions in order to exercise their executive functions.