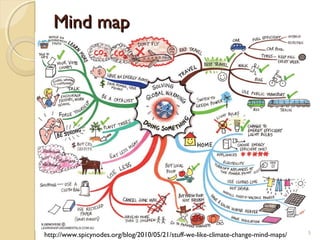
This document describes a project to represent textual information from documents in a graphical mind map format. Key points include using phrases to represent semantic information hierarchically, extracting relevant phrases from documents using heuristics and tools like the Stanford Parser and Tregex, and generating a mind map from the extracted phrases. The approach was evaluated using precision and recall metrics in a survey where participants answered questions about documents using the mind maps. The mind maps were able to extract information accurately but had low recall and some phrases needed refinement. Future work could focus on machine learning to select important keywords and patterns for phrase extraction.