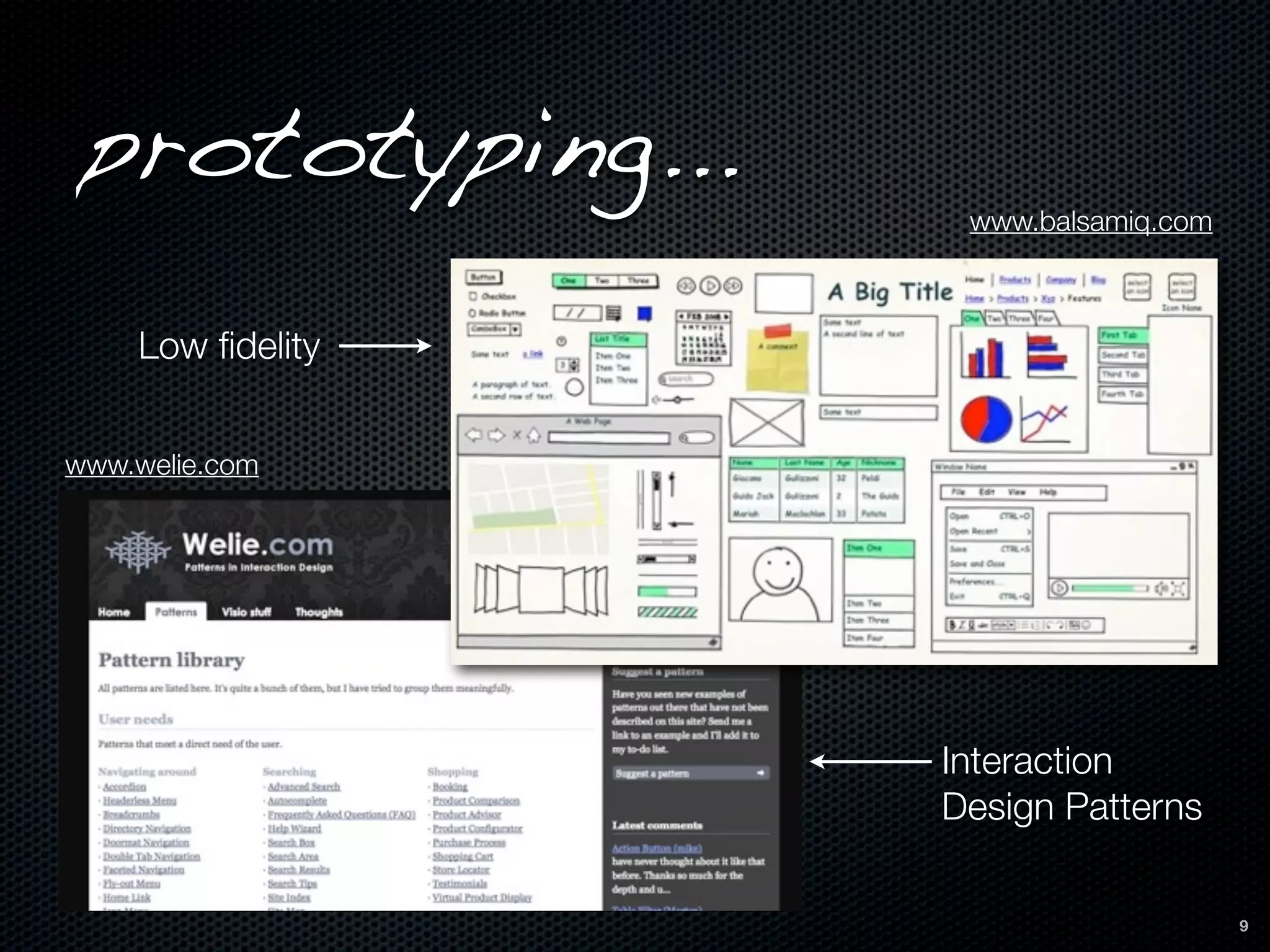
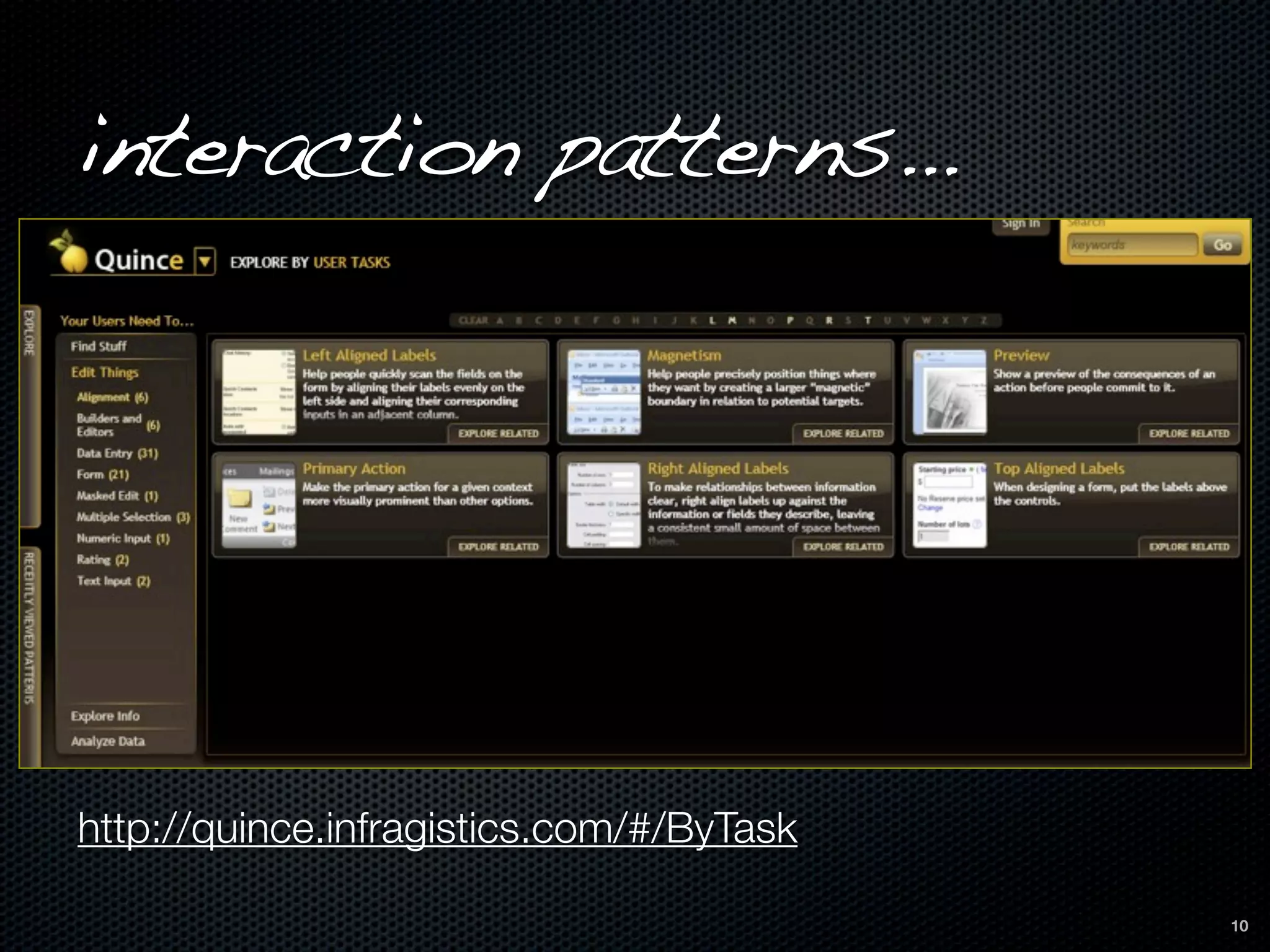
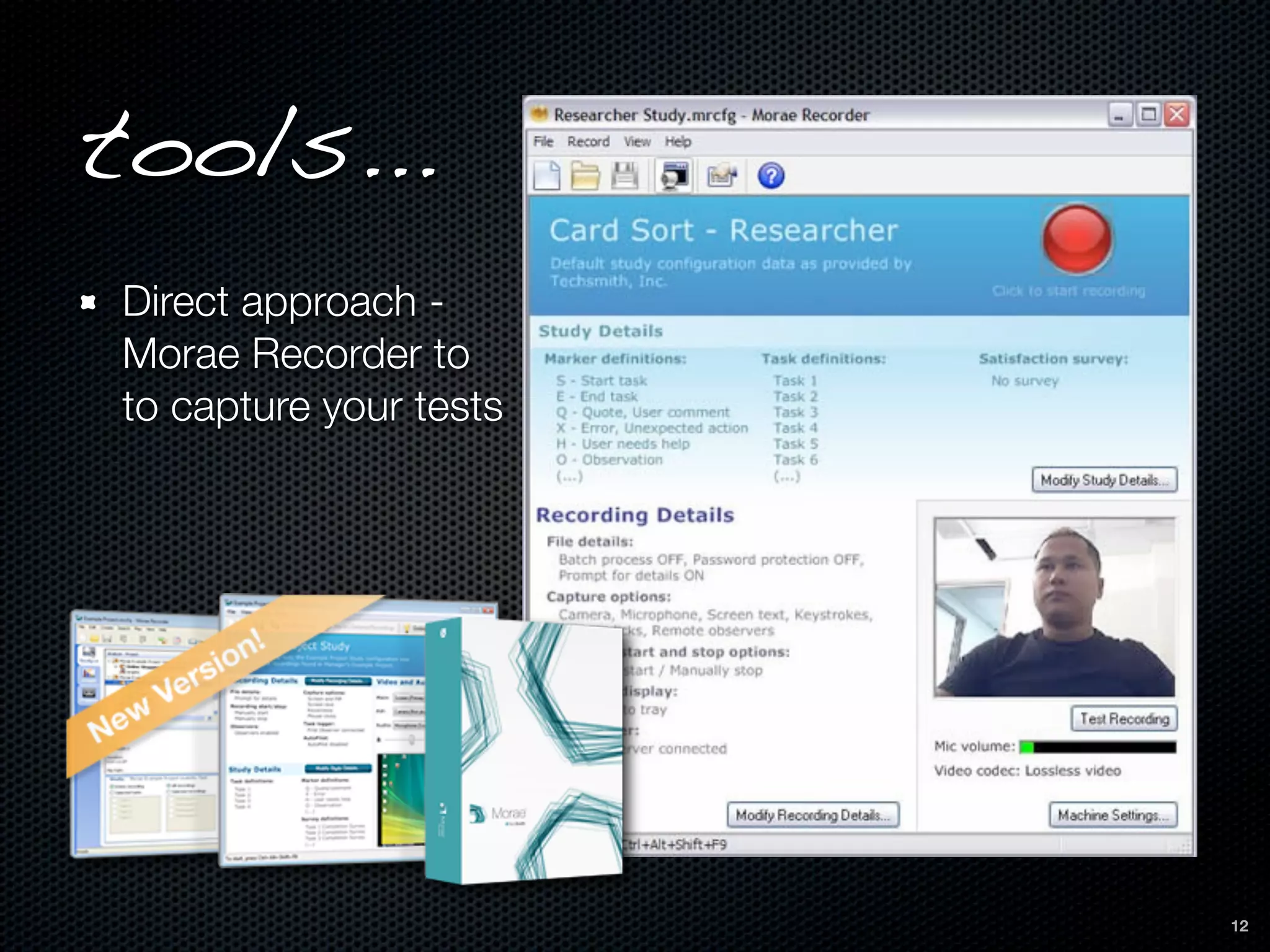
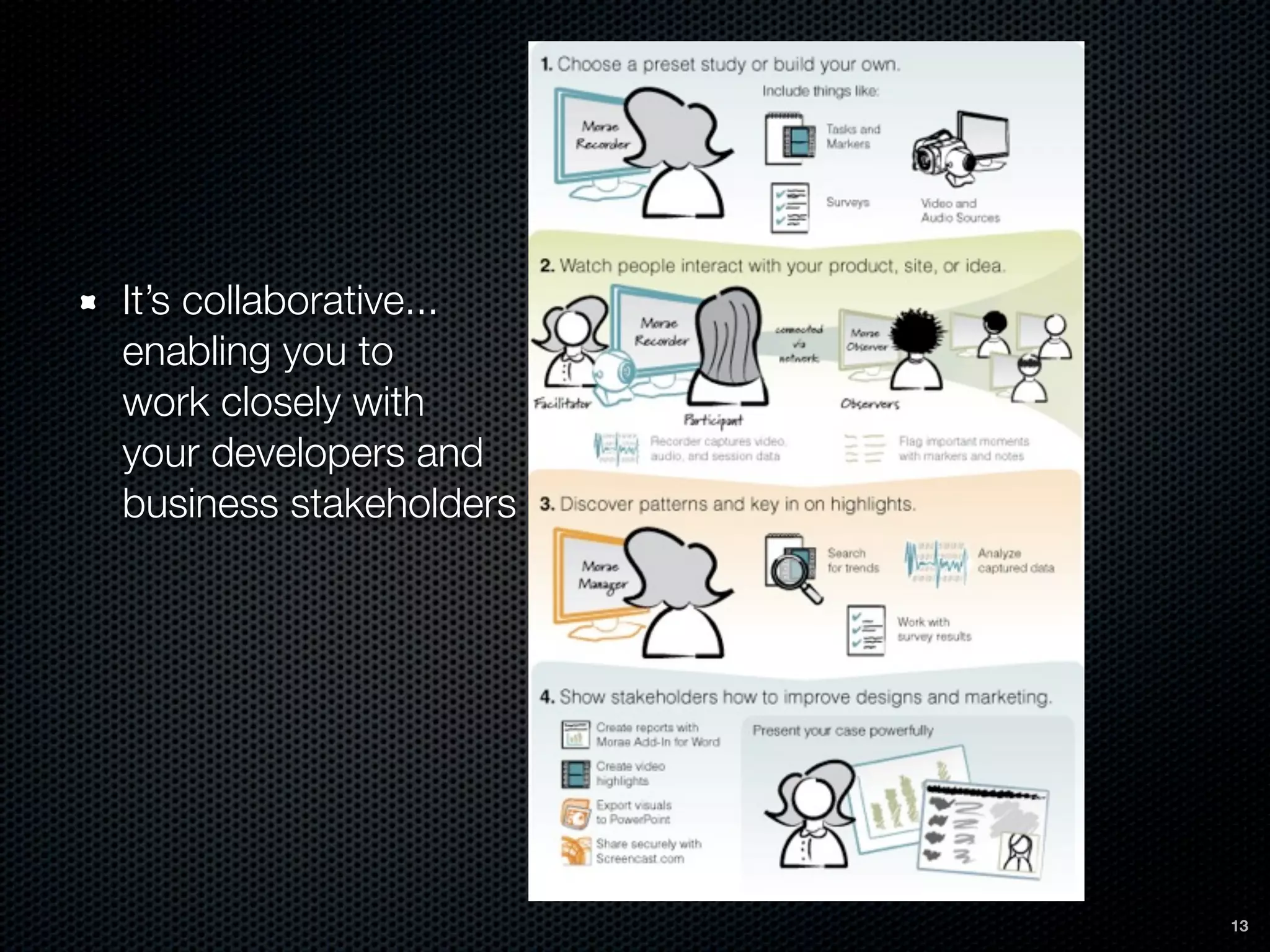
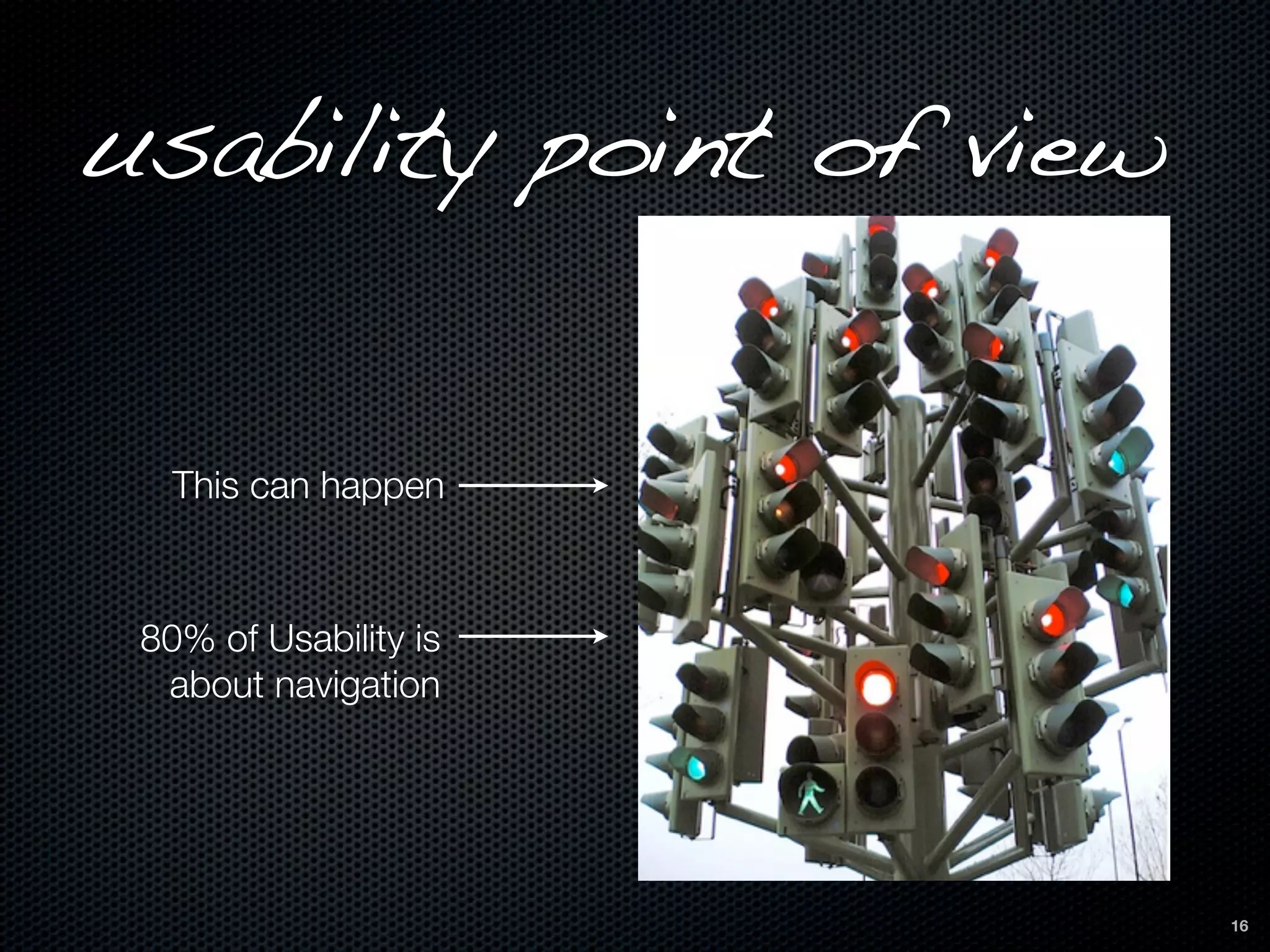
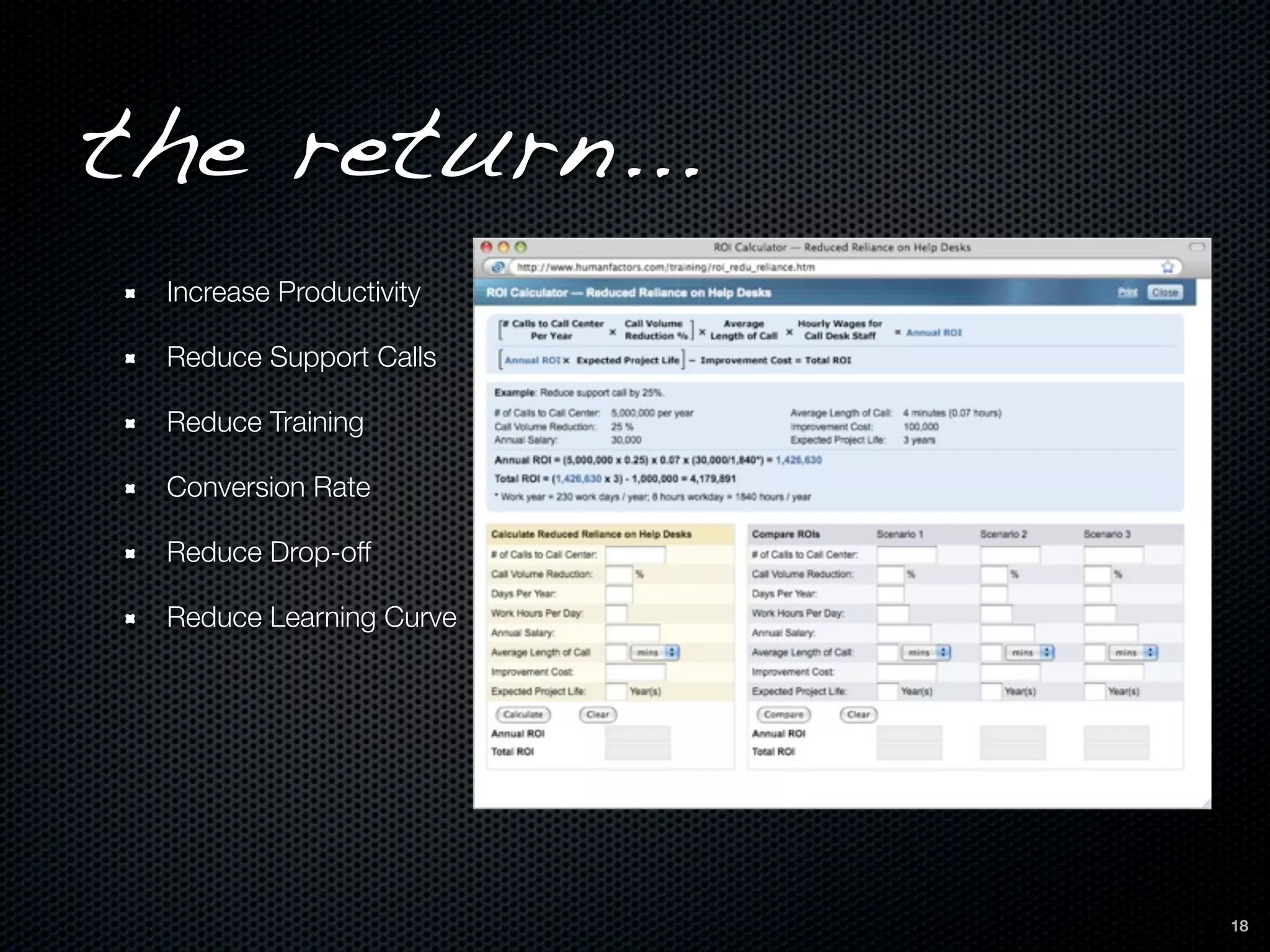
This document discusses the importance of user-centered design and usability. It defines key terms like usability, mental models, and user-centered design. It describes how user-centered design involves users throughout the development process from planning to prototyping and testing. Usability testing criteria should be established prior to testing. Tools mentioned for user research, prototyping, and usability testing include Balsamiq, Welie, Morae Recorder, and SurveyMonkey. Following user-centered design principles can increase productivity, reduce support costs, and improve conversion rates.