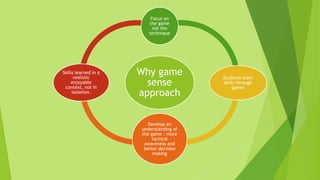
A game sense approach in PE focuses on teaching skills through games rather than in isolation. It emphasizes developing students' decision making, problem solving, and tactical awareness within a game context. The approach aims to make skills learning enjoyable and help students understand how to apply their abilities across different situations. It also encourages active participation and values students' prior experiences. For these reasons, the discussed school adopted a game sense approach over a traditional skills-drill method in their PE lessons.