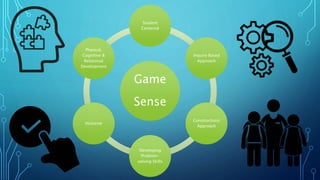
Game sense is a student-centered, inquiry-based approach to physical education that uses modified games to develop problem-solving and decision-making skills. It focuses on inclusive physical, cognitive, and social development through exploratory games. Games are modified to increase participation and challenge skills. Students work collaboratively to problem-solve modifications, promoting skills like critical thinking, communication and collaboration. This approach engages students, links to other subjects, and encourages positive behavior.