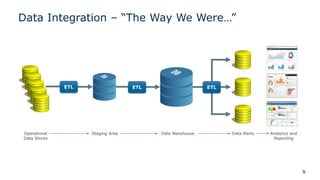
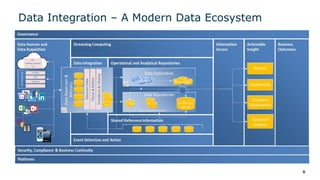
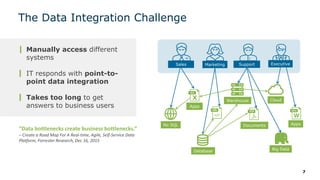
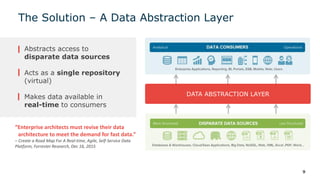
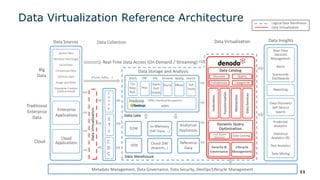
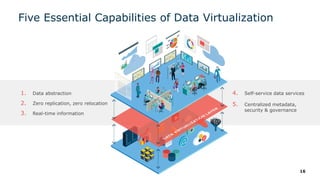
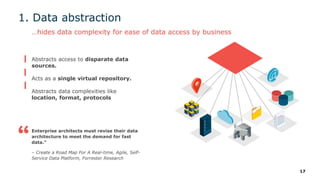
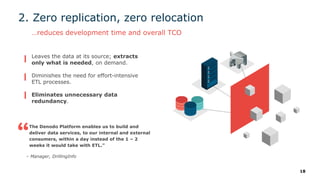
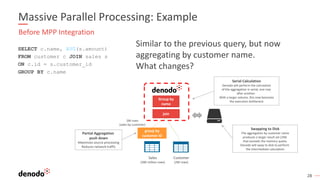
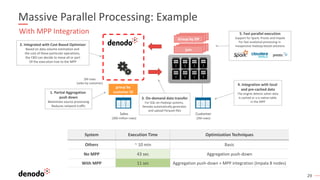
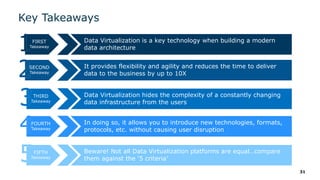
The webinar series on data virtualization, presented by Denodo experts, addresses key data integration challenges and introduces how data virtualization can streamline accessing disparate data sources in real-time. It emphasizes essential capabilities such as data abstraction, zero replication, and self-service data services to enhance analytics and decision-making. The session outlines the advantages of adopting data virtualization for modern data architecture, and the importance of considering different platforms based on specific criteria.