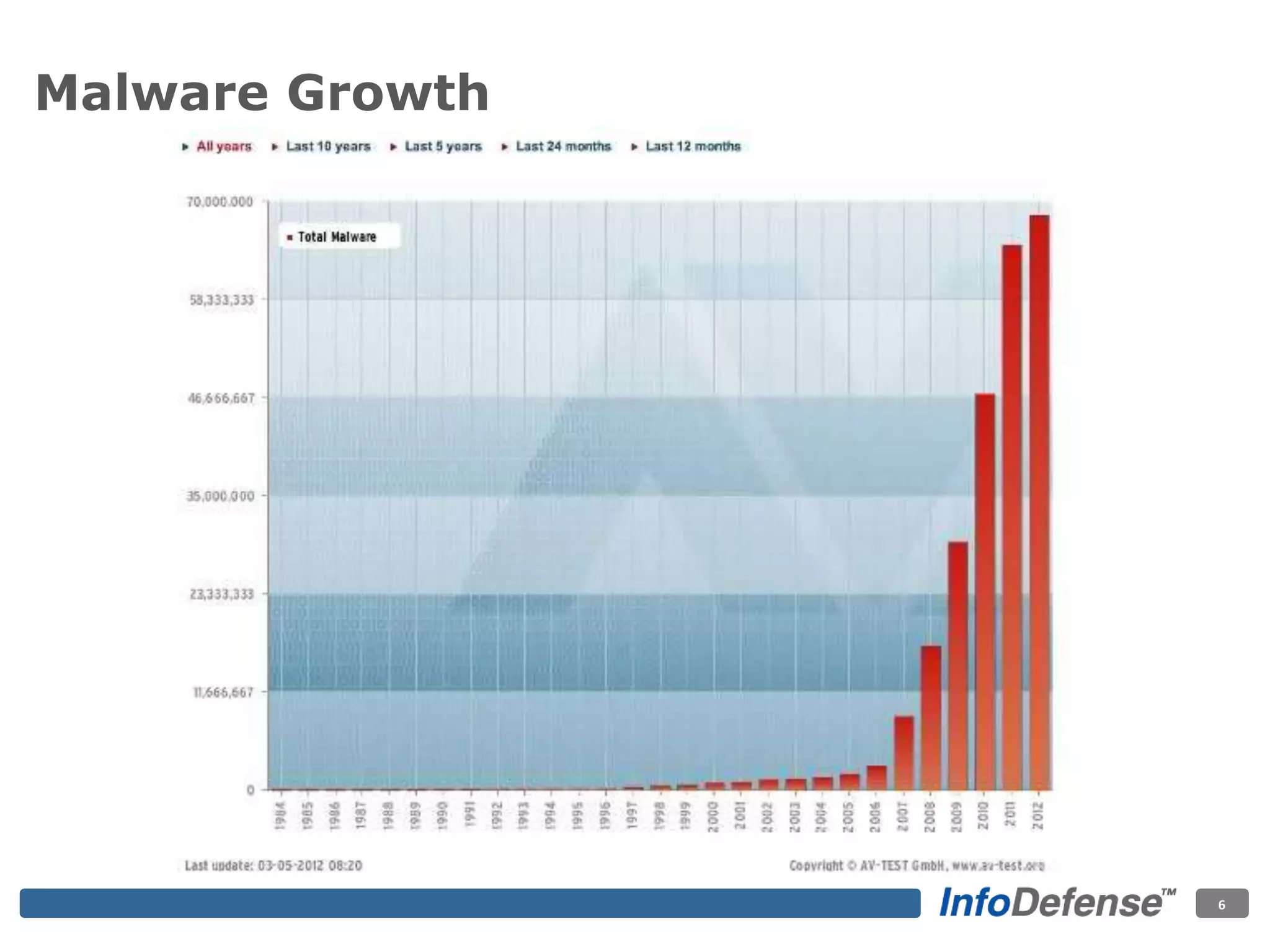
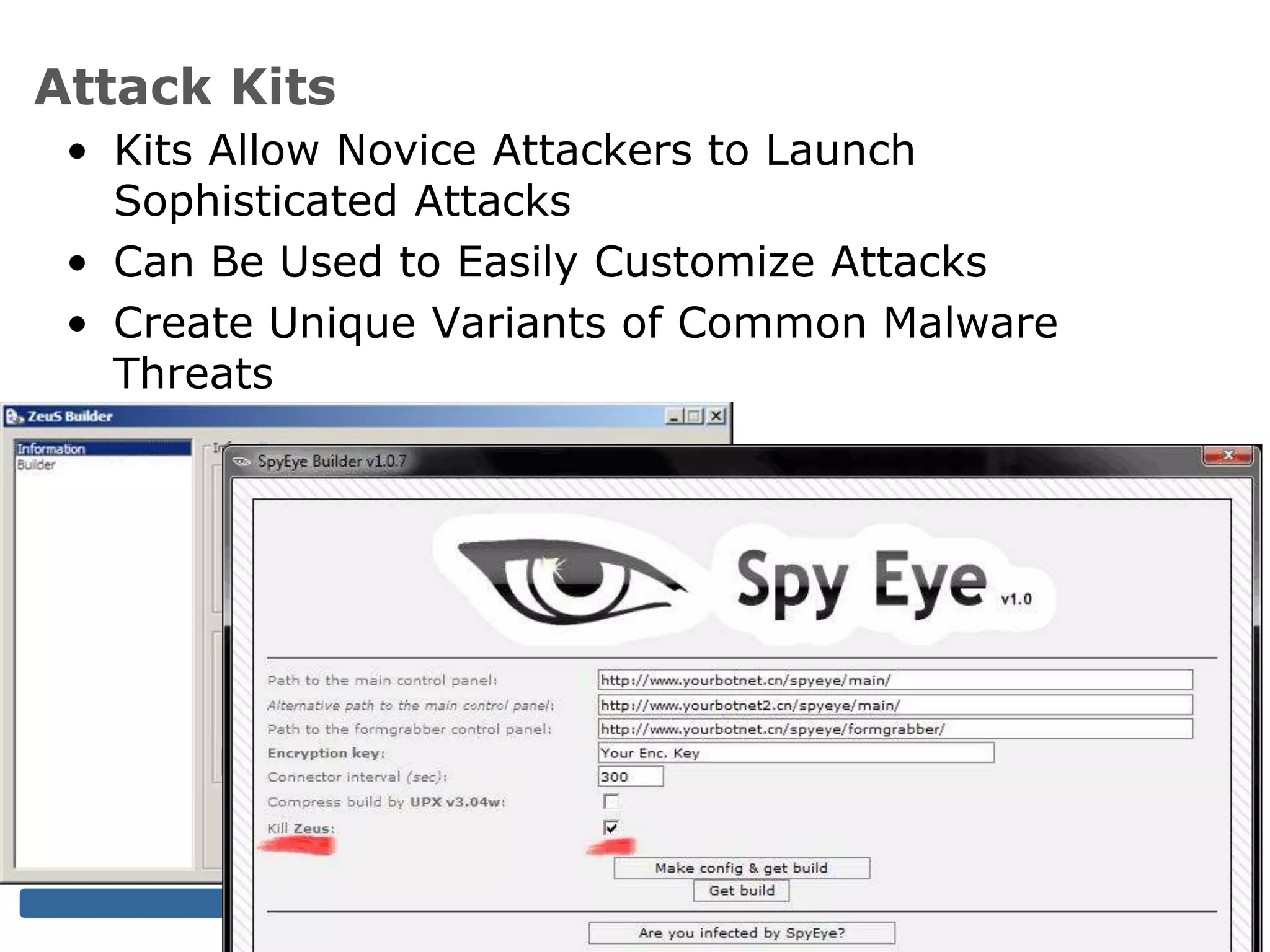
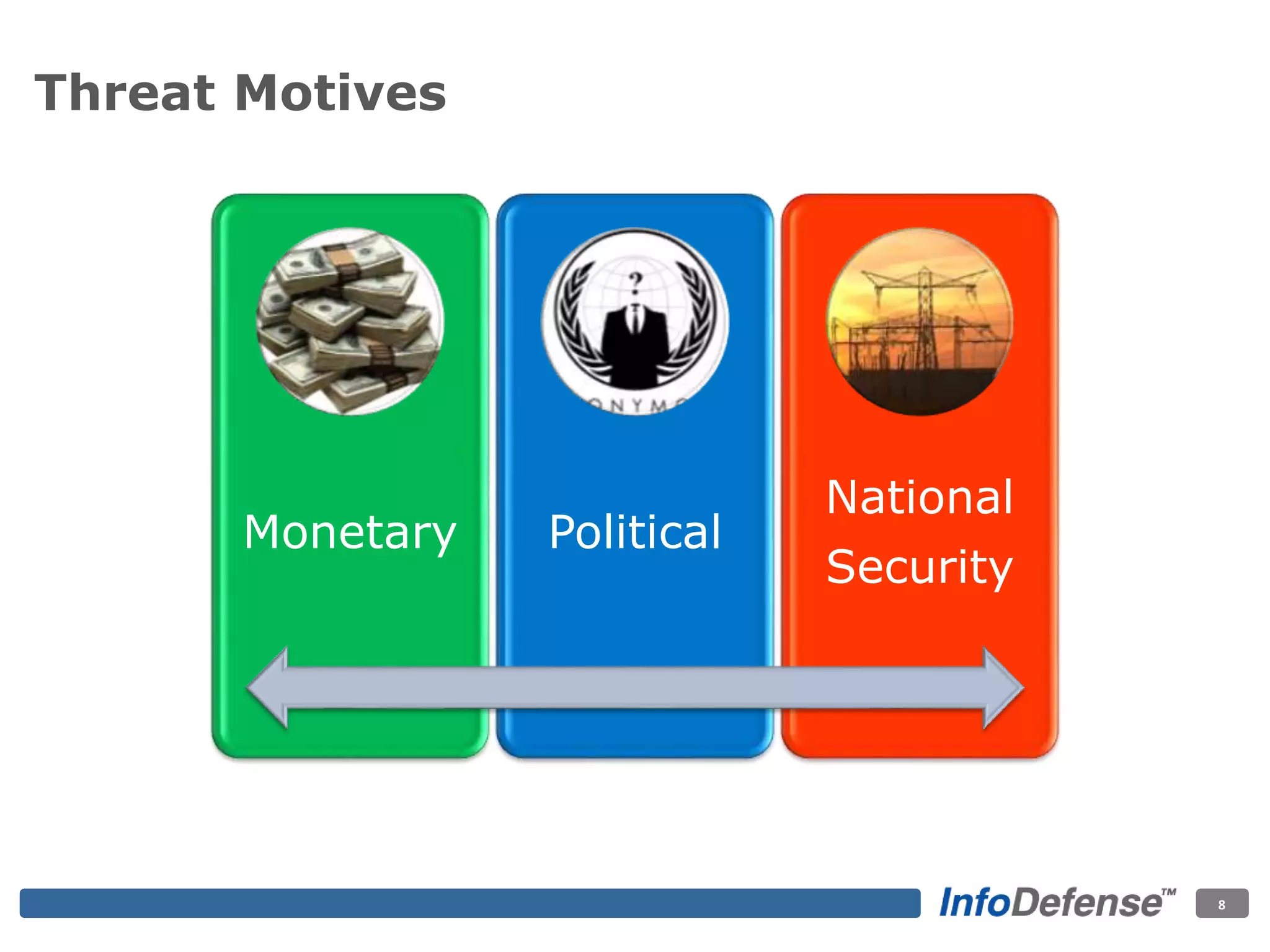
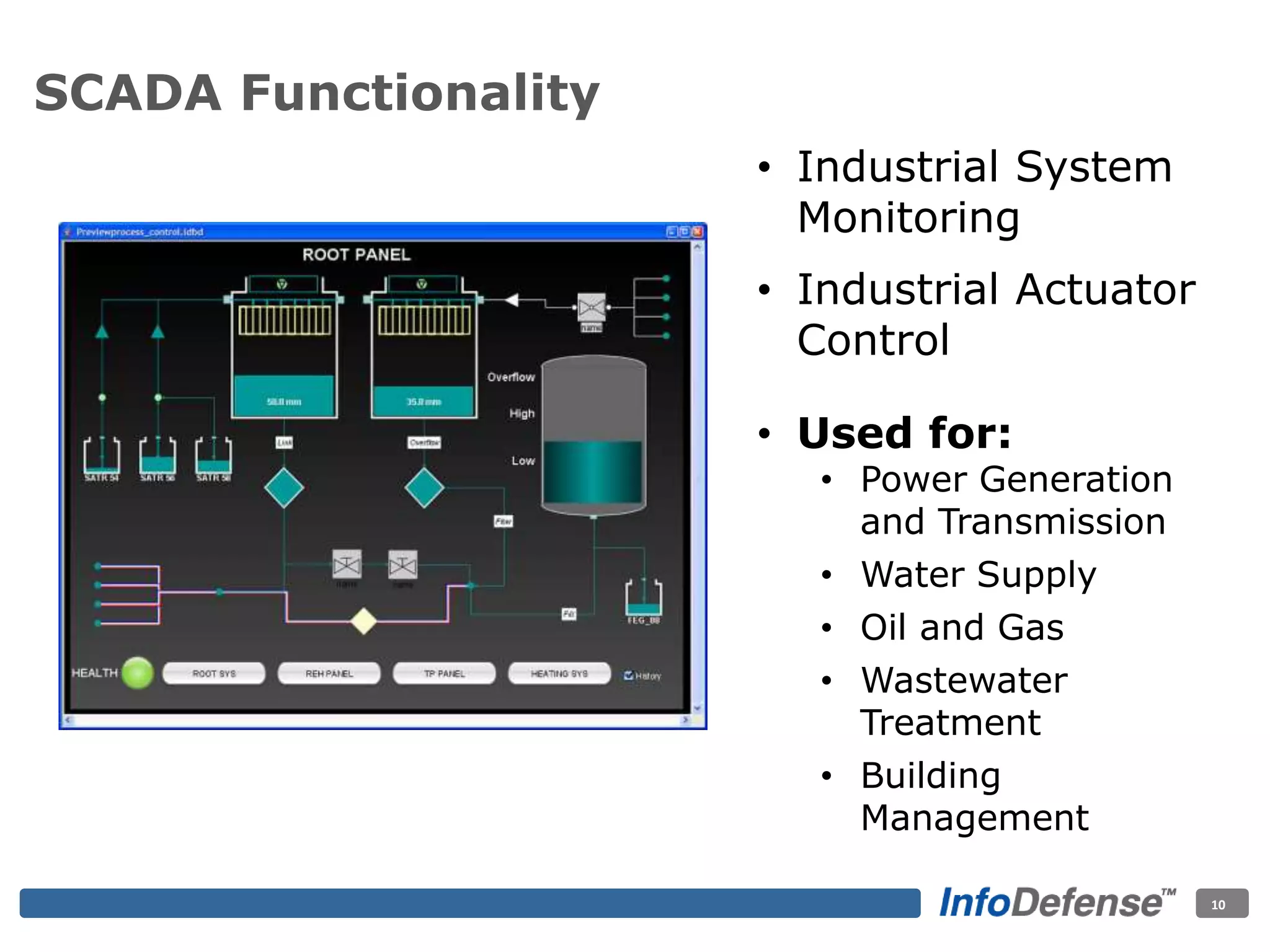
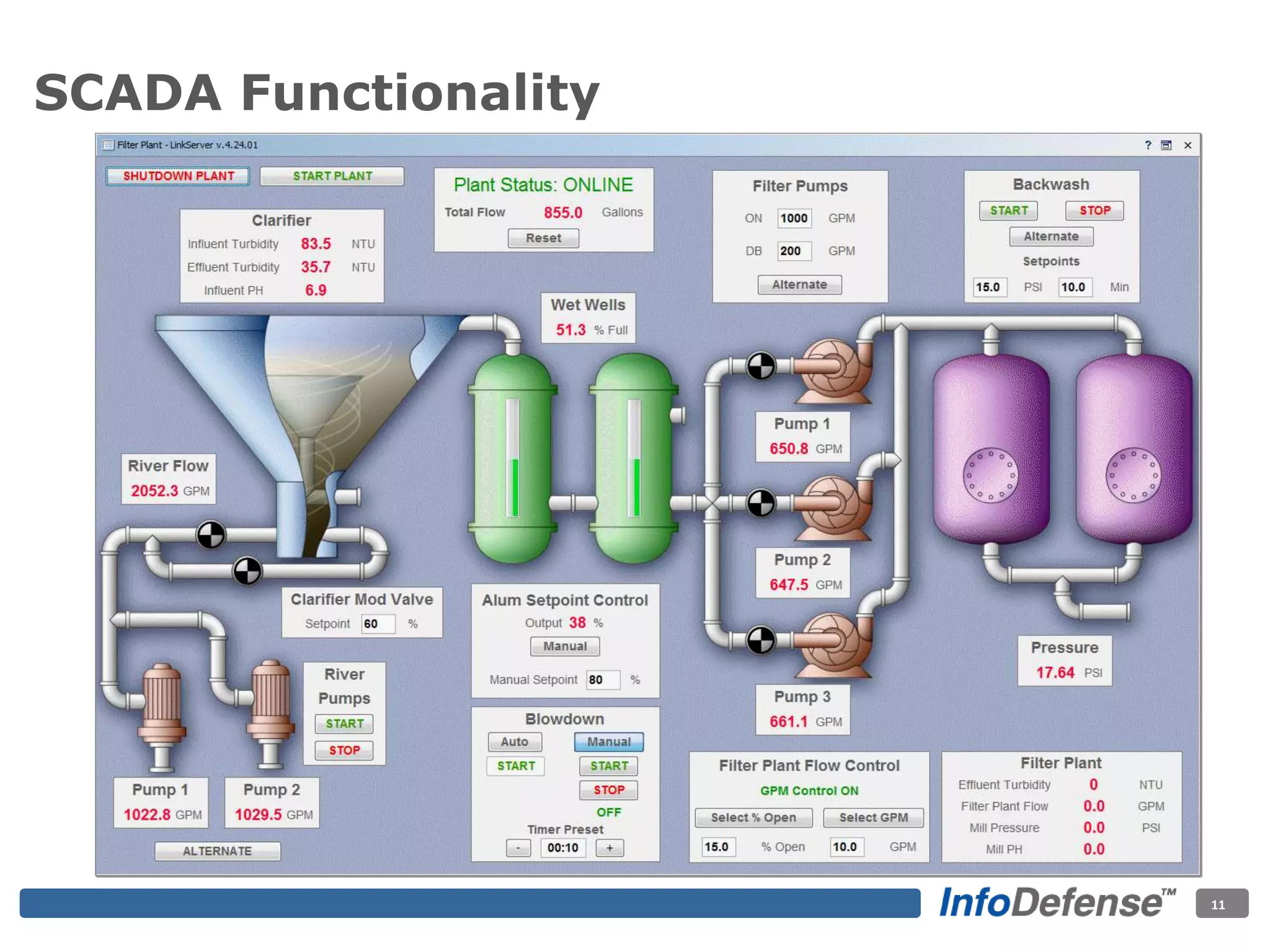
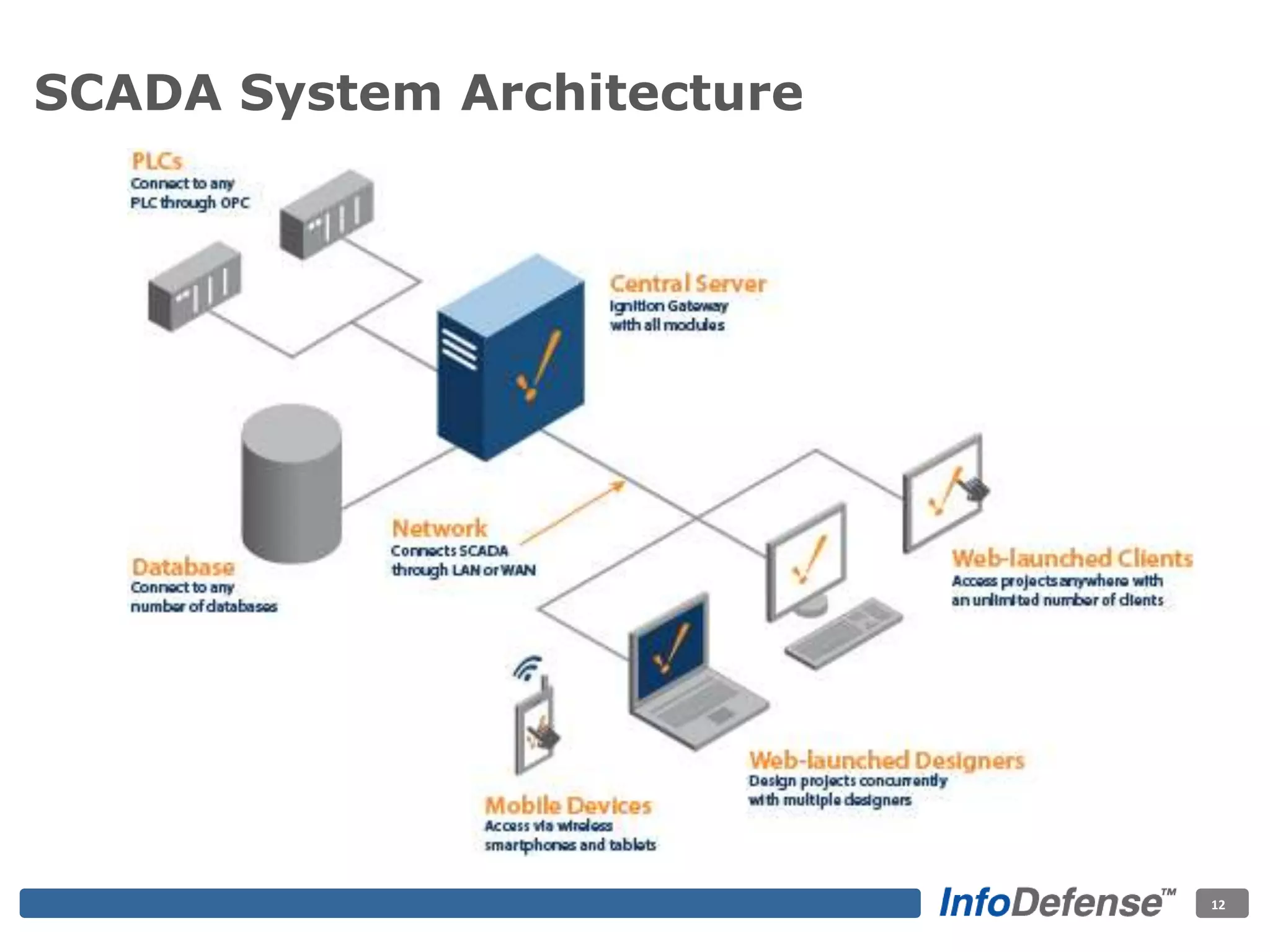
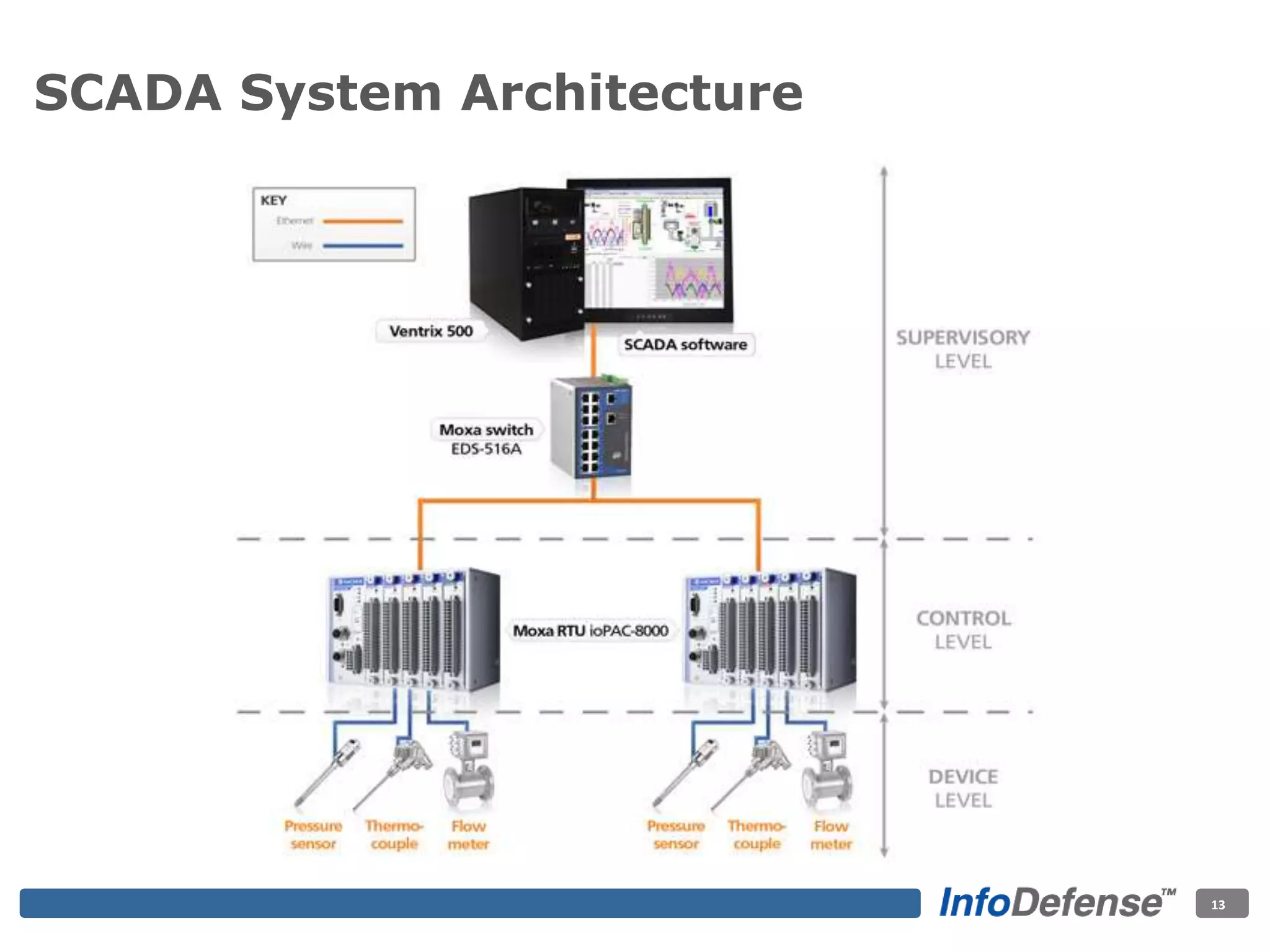
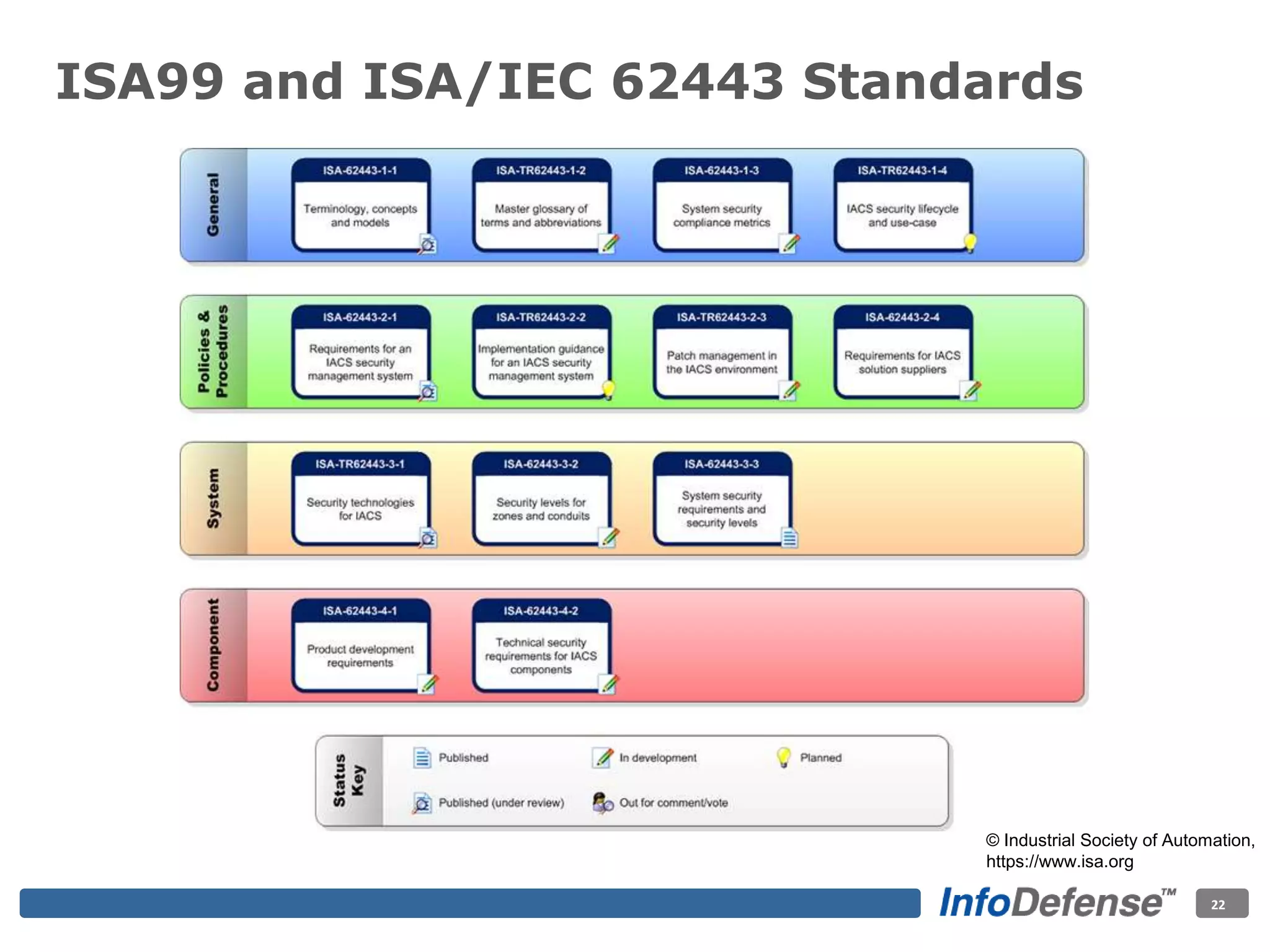
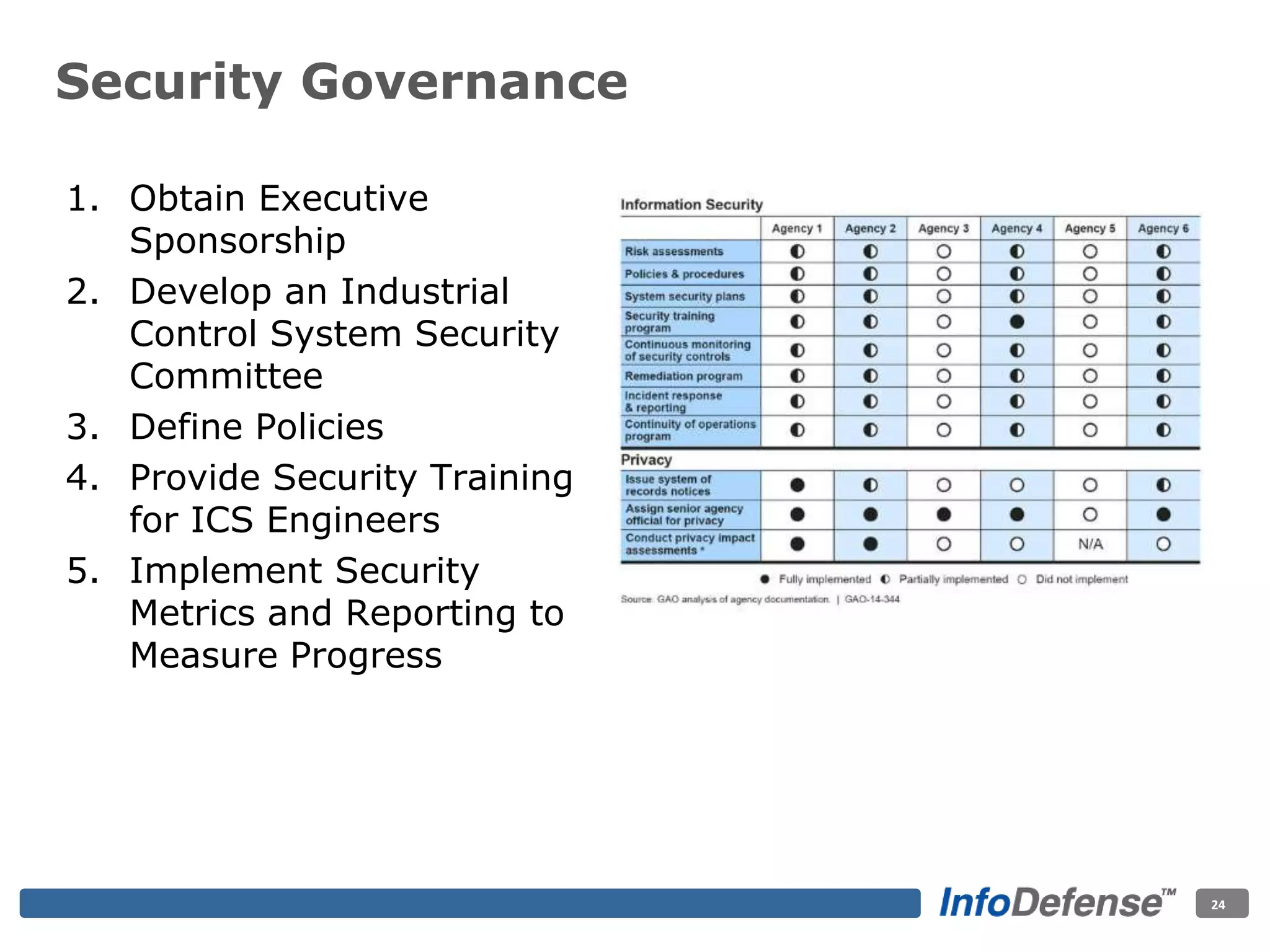
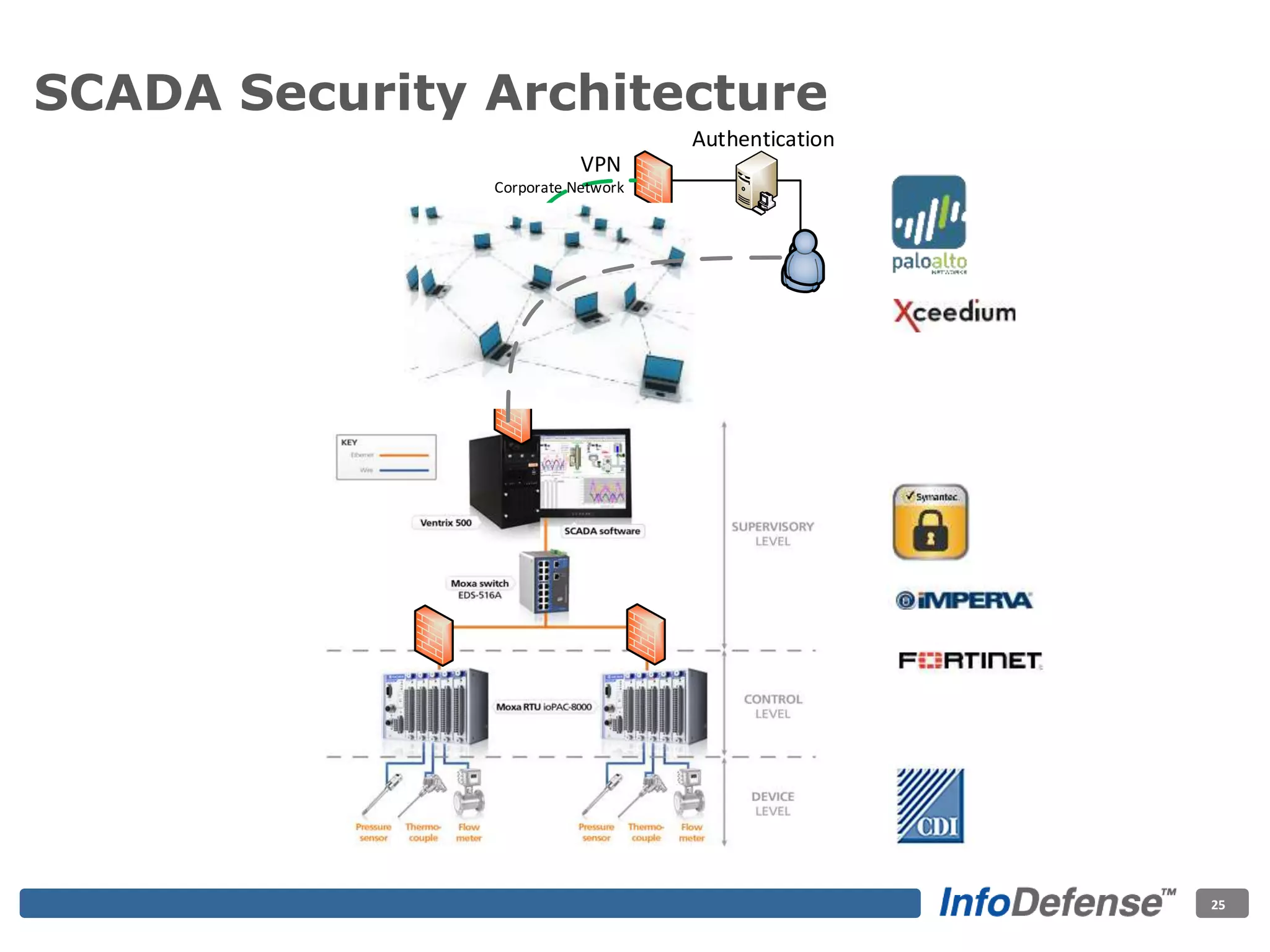
The document discusses the evolving threat landscape for industrial control systems (ICS), highlighting the rise in cyber-terrorism and nation-state threats. It reviews specific case studies, such as the Stuxnet worm and attacks on SCADA systems, which illustrate the vulnerabilities and potential impacts on critical infrastructure. Recommendations are provided for enhancing security governance, threat management, and access control within ICS environments.