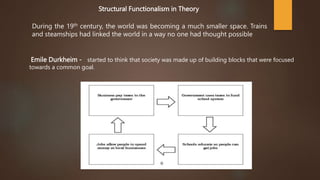
Structural functionalism views society as a complex system whose parts work together to promote solidarity and stability. It argues that social institutions like the economy and education work interdependently to maintain social order. However, it fails to account for differences between social groups and assumes they all share the same goals. It also views motivation as a zero-sum game where gains for one group mean losses for others, neglecting that groups have varying starting points and motivations. While structural functionalism emphasizes the importance of economic institutions, conflict theory highlights issues of control, alienation and problems in the workplace that functionalism overlooks.