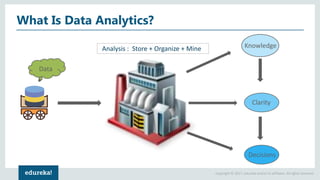
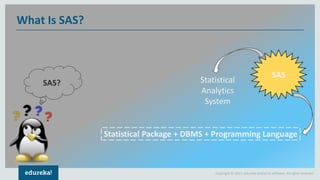
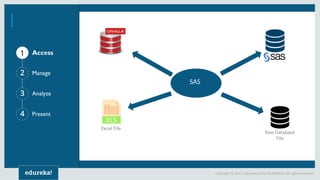
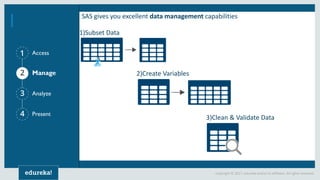
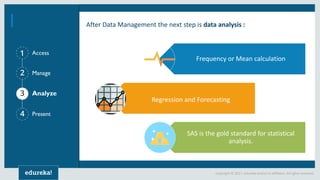
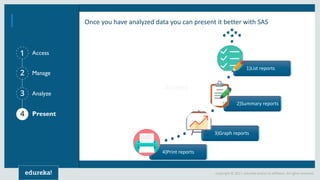
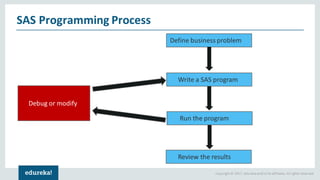
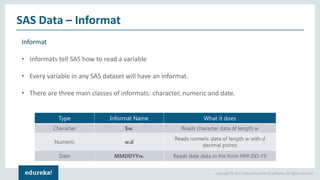
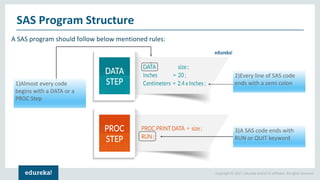
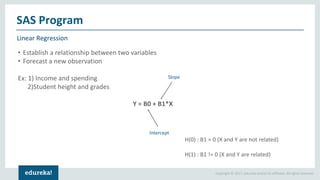
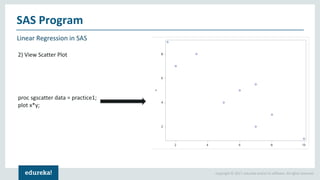
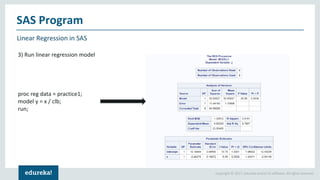
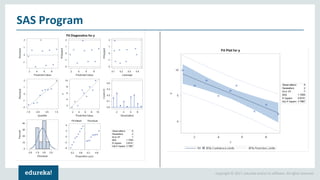
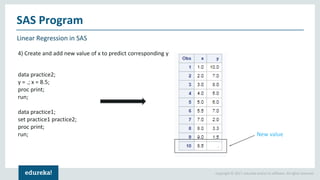
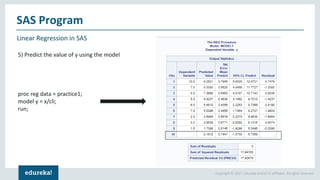
The document discusses SAS (Statistical Analytics System), a software for data management, analytics and visualization. It provides an overview of SAS framework, programming and applications. SAS allows users to access, manage and analyze data, and then present results. It discusses key SAS concepts like data sets, variables, formats and linear regression modeling using SAS procedures. Common applications of SAS mentioned are in domains like stock prediction, drug discovery, fraud detection and workflow optimization.