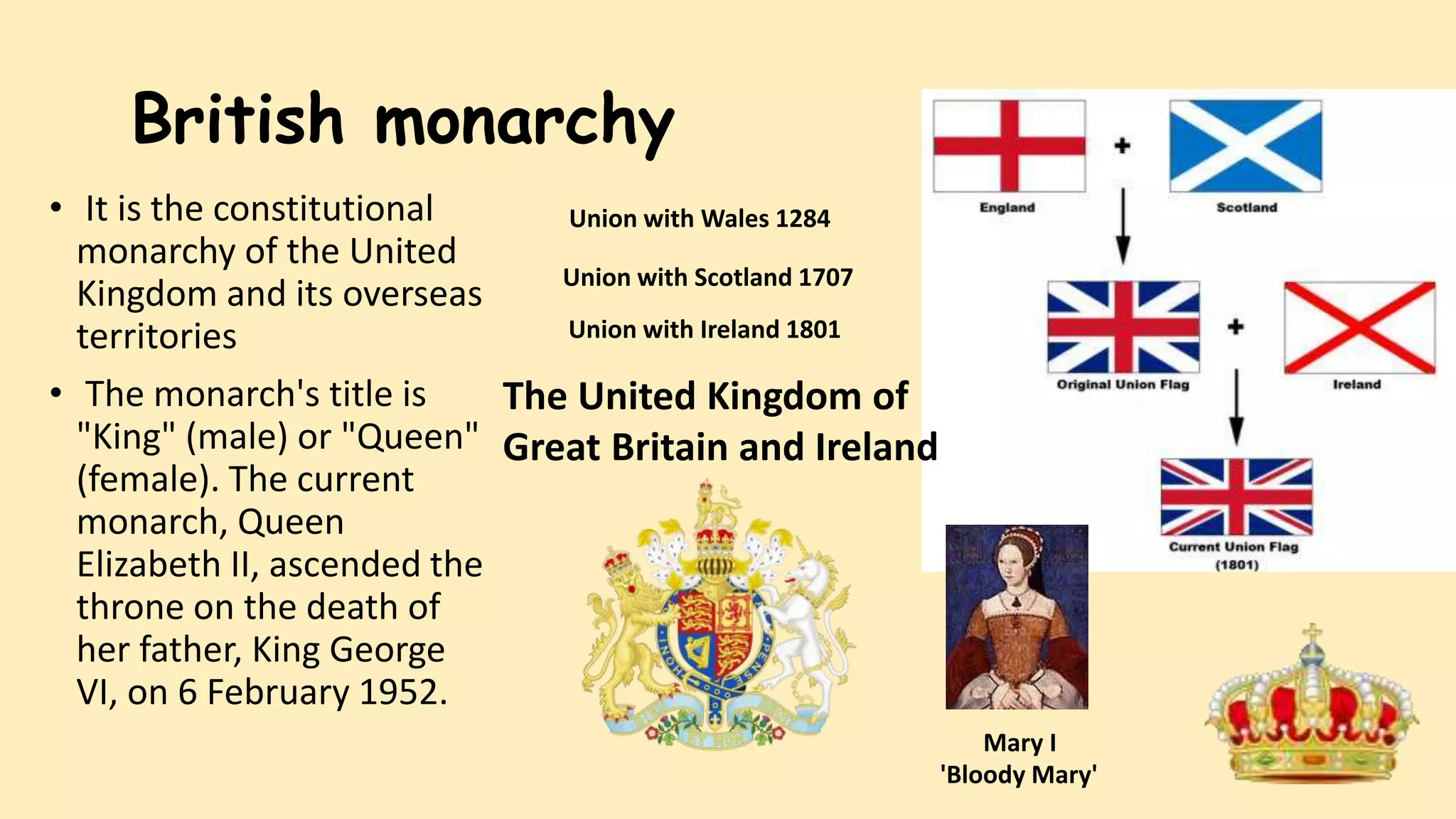
- A monarchy is a form of government in which a single person, the monarch, rules as head of state for life or until abdication. There are different types of monarchy based on the monarch's level of power and method of selection.
- Characteristics of monarchies include hereditary rule through dynasties, as well as titles like king, queen, prince, and emperor. Monarchies originated from early societies where family leaders inherited power through knowledge, skills, and land ownership.
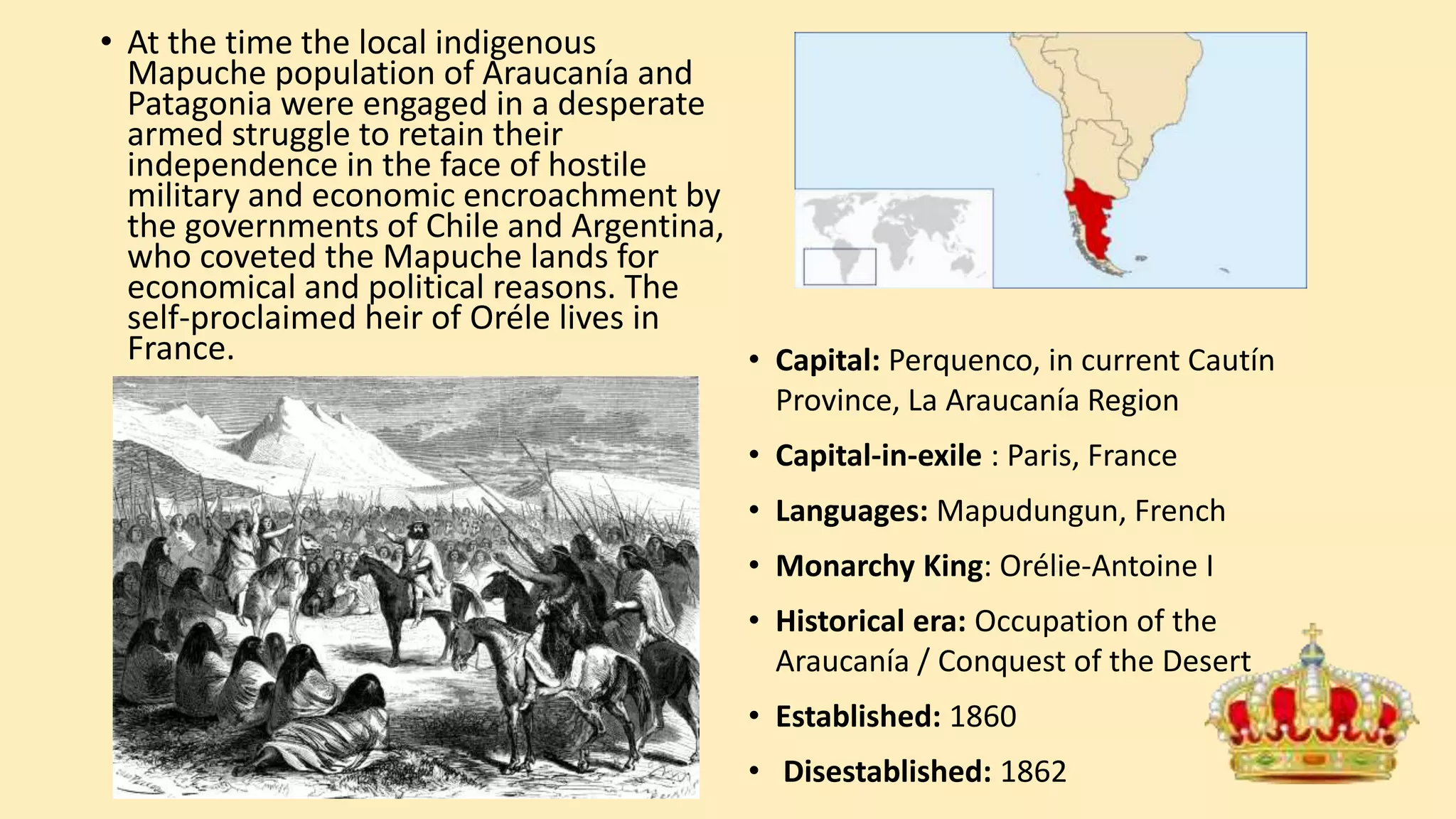
- Modern examples discussed include the constitutional monarchy of the UK, the unrecognized Kingdom of Araucanía and Patagonia created to support Mapuche independence, and the absolute monarchy of Saudi Arabia