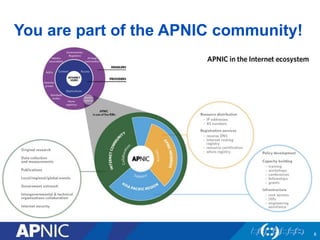
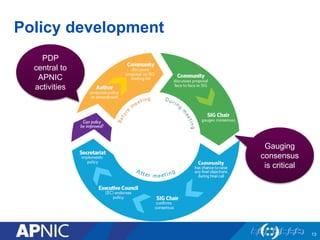
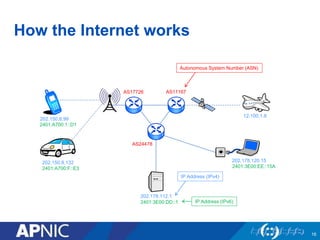
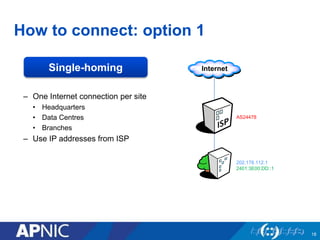
APNIC is a not-for-profit organization that provides Internet resources like IP addresses and autonomous system numbers to the Asia Pacific region. It serves 56 economies and oversees the distribution of IPv4, IPv6, and ASNs. APNIC offers services like resource distribution, DNS delegation, training programs, and facilitates policy development for the region. Becoming an APNIC member provides benefits like access to registry services, training opportunities, and participation in technical conferences.