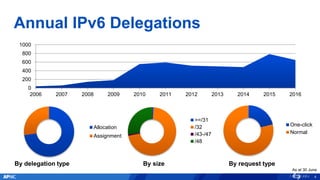
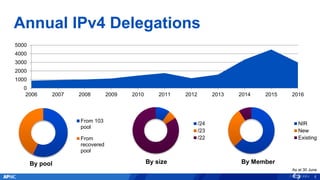
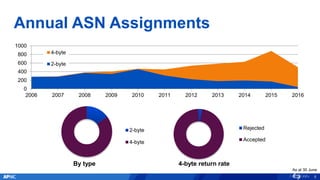
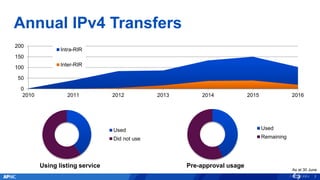
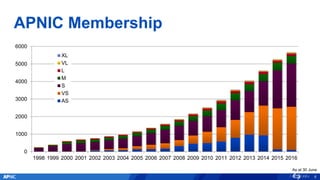
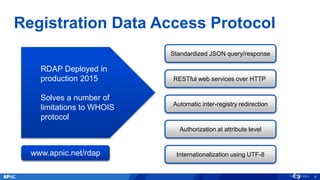
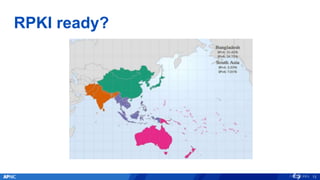
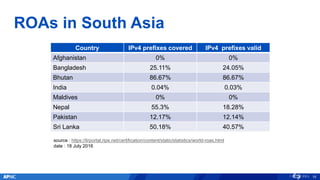
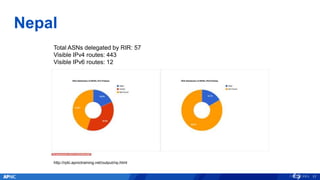
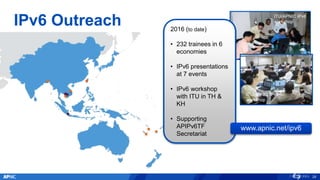
The document provides an overview of APNIC's activities and vision for a global, stable, and secure internet in the Asia Pacific community. It highlights annual statistics on IPv4 and IPv6 delegations, as well as RPki adoption efforts and the growth of APNIC membership. It also discusses improvements in the myAPNIC platform, training initiatives, and upcoming APNIC conferences.