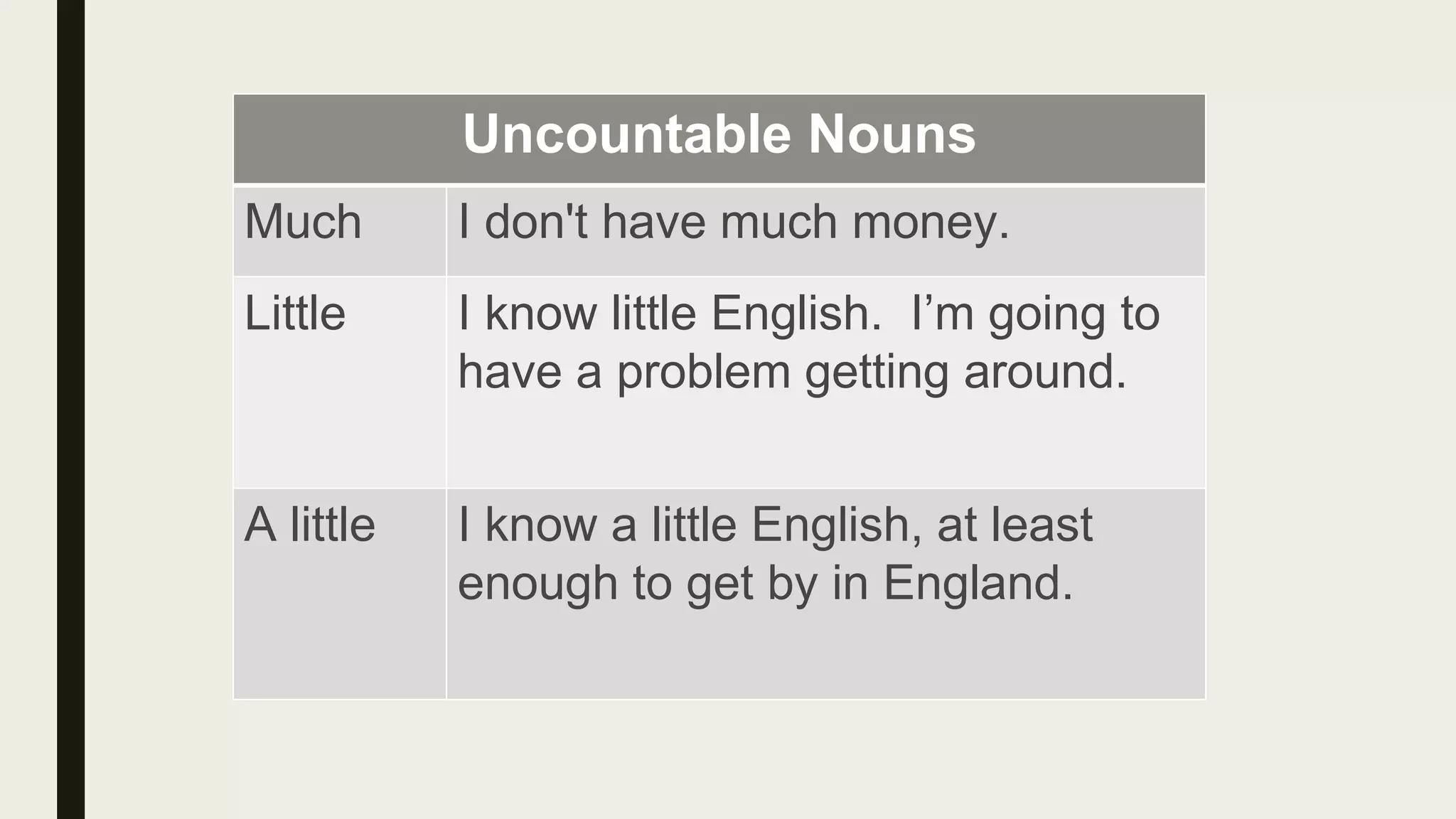
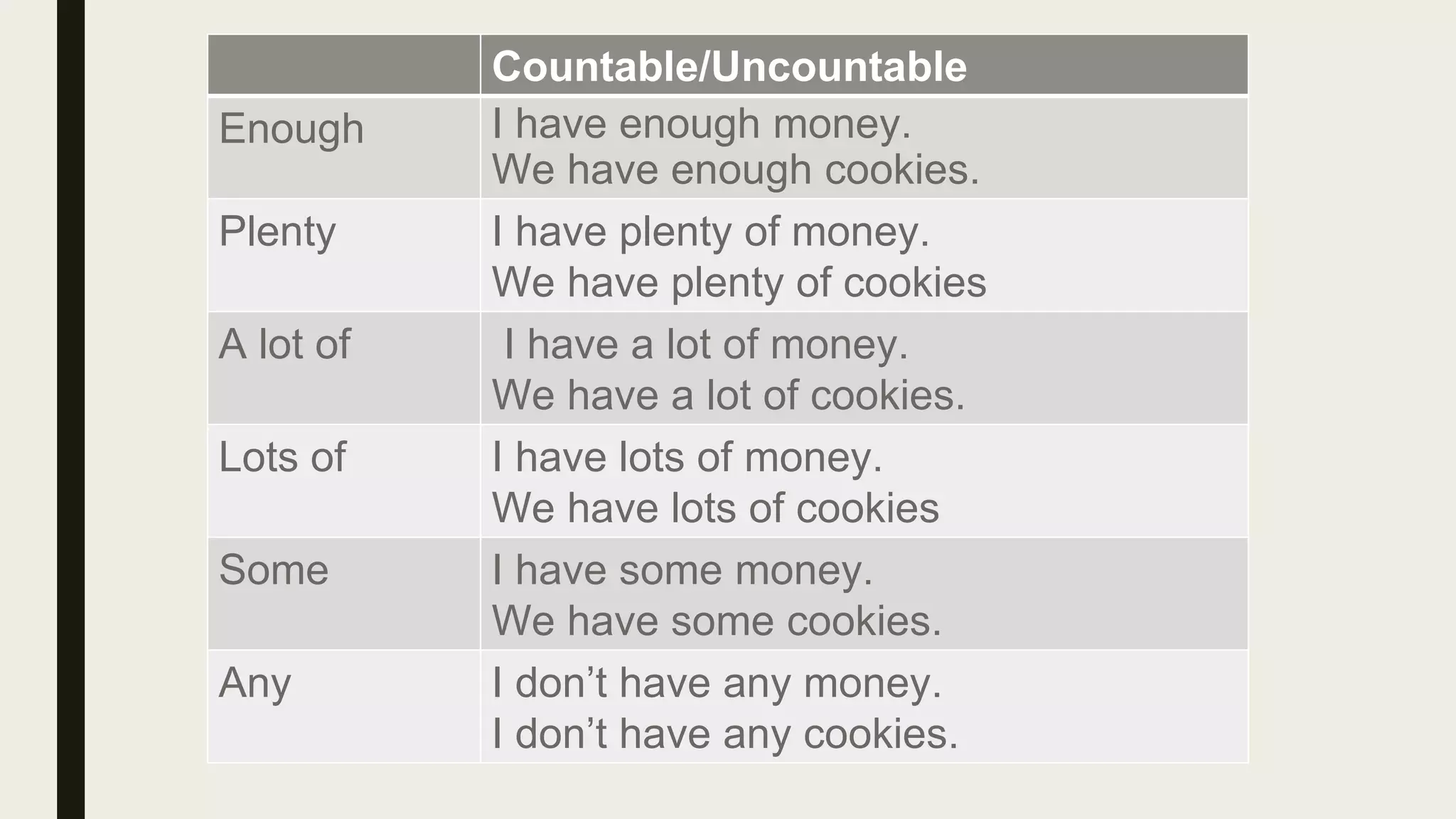
This document provides an overview of quantifiers and the words some and any. It discusses how quantifiers are used to state quantity without an exact number, and covers common quantifiers like many, few, much, little, enough, and plenty. The document also explains the differences between some and any, noting that any is used in negative sentences and questions while some is used in positive sentences and questions expecting a positive answer. Examples are given to illustrate the proper uses of quantifiers, some, and any.