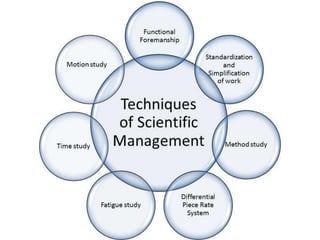
This document discusses different types of groups and organizations. It defines social groups as collections of people who interact regularly and depend on each other, distinguishing them from aggregates and categories. Groups are classified as primary (smaller and intimate) or secondary (larger and goal-oriented). In-groups and out-groups are defined by members' identification. Formal organizations are described as normative, coercive, or utilitarian based on how they are joined. Bureaucracies are discussed as rationalized organizations with characteristics like division of labor and hierarchy of authority, as well as potential problems like inefficiency and alienation. Scientific management and McDonaldization are presented as applications of rationalization. The document concludes by noting potential changes like more












![Bureaucracies
• bureaucracy = organization that uses rules and top-down
authority to achieve greater efficiency, predictability,
calculability, and control.
• the iron law of oligarchy = Michels (1911) believed that
bureaucratic leadership would tend to hold on to their power
and to reproduce themselves and end up producing a continual
rule by a few.
• The “iron cage”: refers to the fact that the bureaucracy is
simultaneously efficient and enslaving.
• Weber’s ideal type (abstract model) of bureaucracy specified six
characteristics [Recall Chapter 4].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7groupsorganizationsdc-190708192811/85/Week-13-Groups-and-Organizations-15-320.jpg)