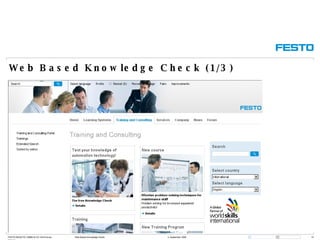
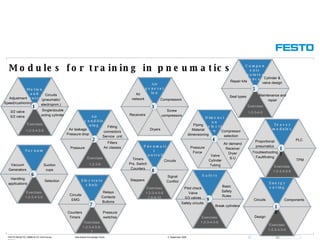
The document discusses Festo Didactic, a division of Festo Group that provides industrial automation training and consulting services. It details Festo Didactic's global presence in over 70 countries, annual turnover of around 80 million euros, and 400 employees worldwide. It also outlines Festo Didactic's training approach, which includes standardized trainings in over 50 countries and a "Train the Trainer" methodology to strengthen customers' organizations.