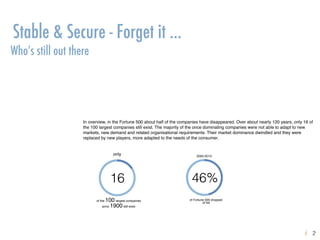
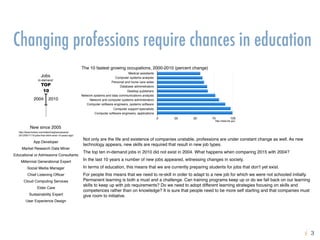
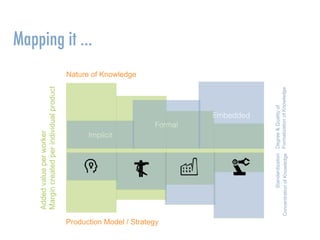
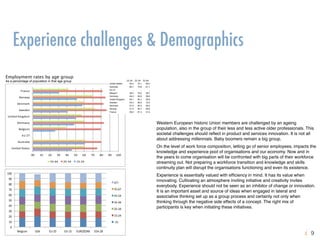
The document explores the instability of companies and professions over time, highlighting that many of the Fortune 500 companies and in-demand jobs have changed significantly since the early 2000s. It emphasizes the necessity for continuous learning and adaptation in organizational cultures to maintain competitiveness and innovation in the face of evolving market demands. Additionally, it discusses the importance of effective knowledge management strategies aligned with the nature of the workforce and the impact of demographic shifts on workforce composition and organizational knowledge continuity.