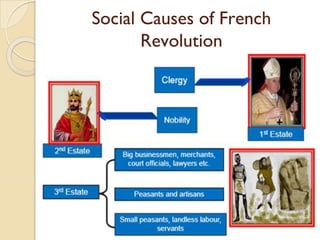
The French Revolution marked the transfer of sovereignty from monarchy to citizens, driven by political, social, and economic causes, including the financial crisis and class inequalities. The emergence of the middle class and the influence of Enlightenment philosophers played a crucial role in fostering revolutionary ideas, leading to impacts such as the abolition of censorship and the establishment of rights like freedom of speech. Napoleon Bonaparte later continued the legacy by modernizing Europe, introducing reforms such as the Napoleonic Code, which abolished feudal privileges and established equality before the law.