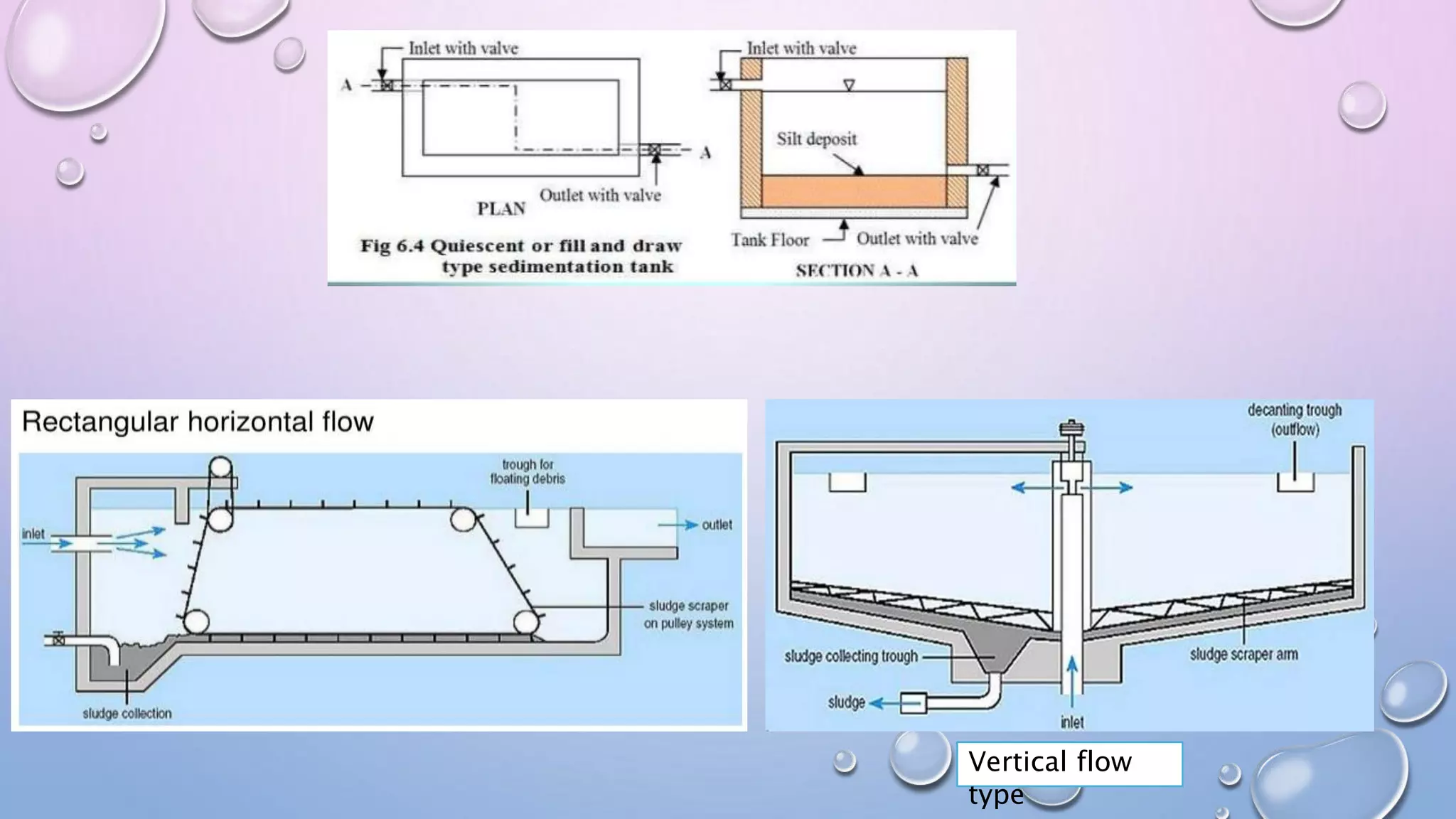
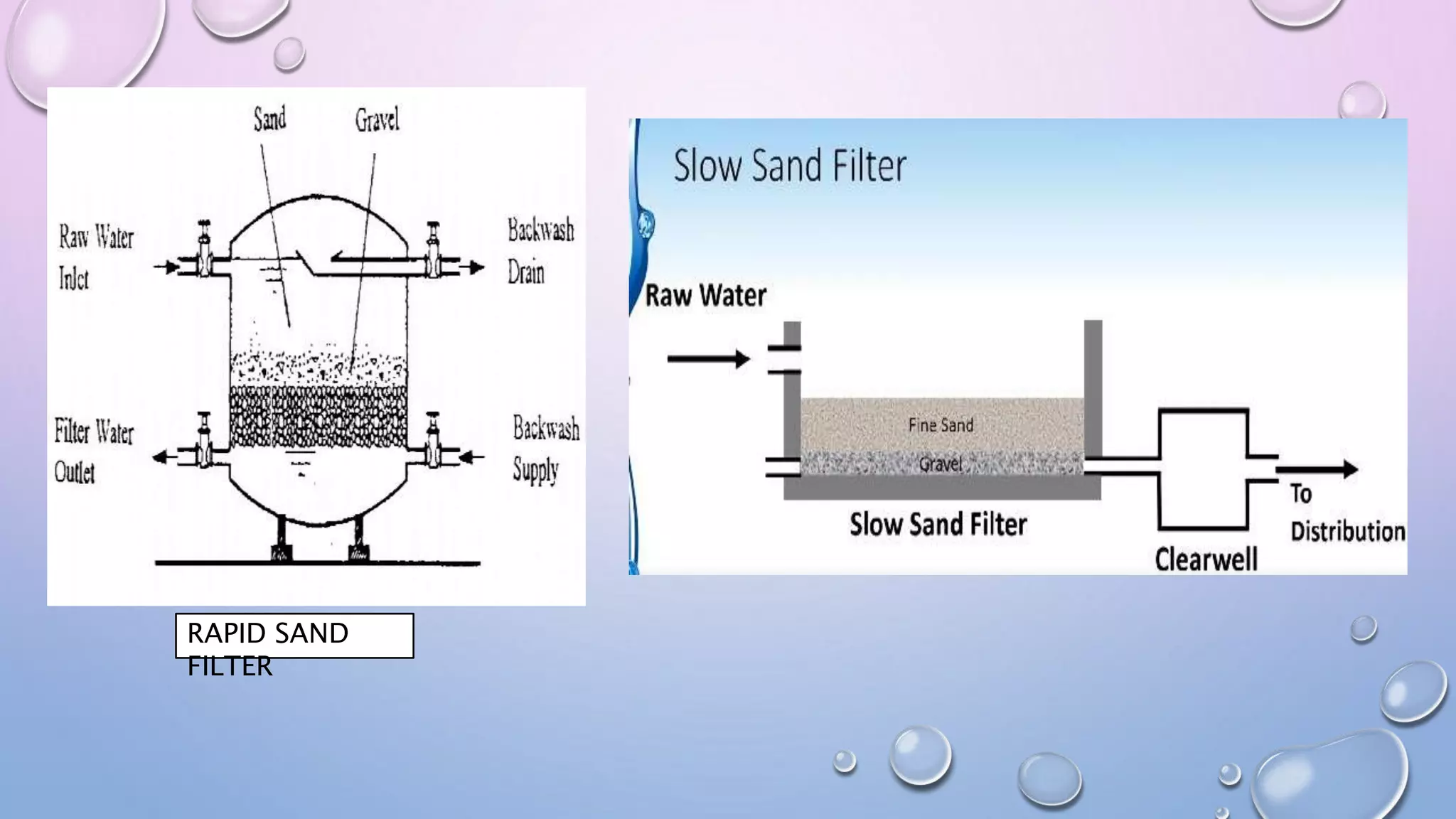
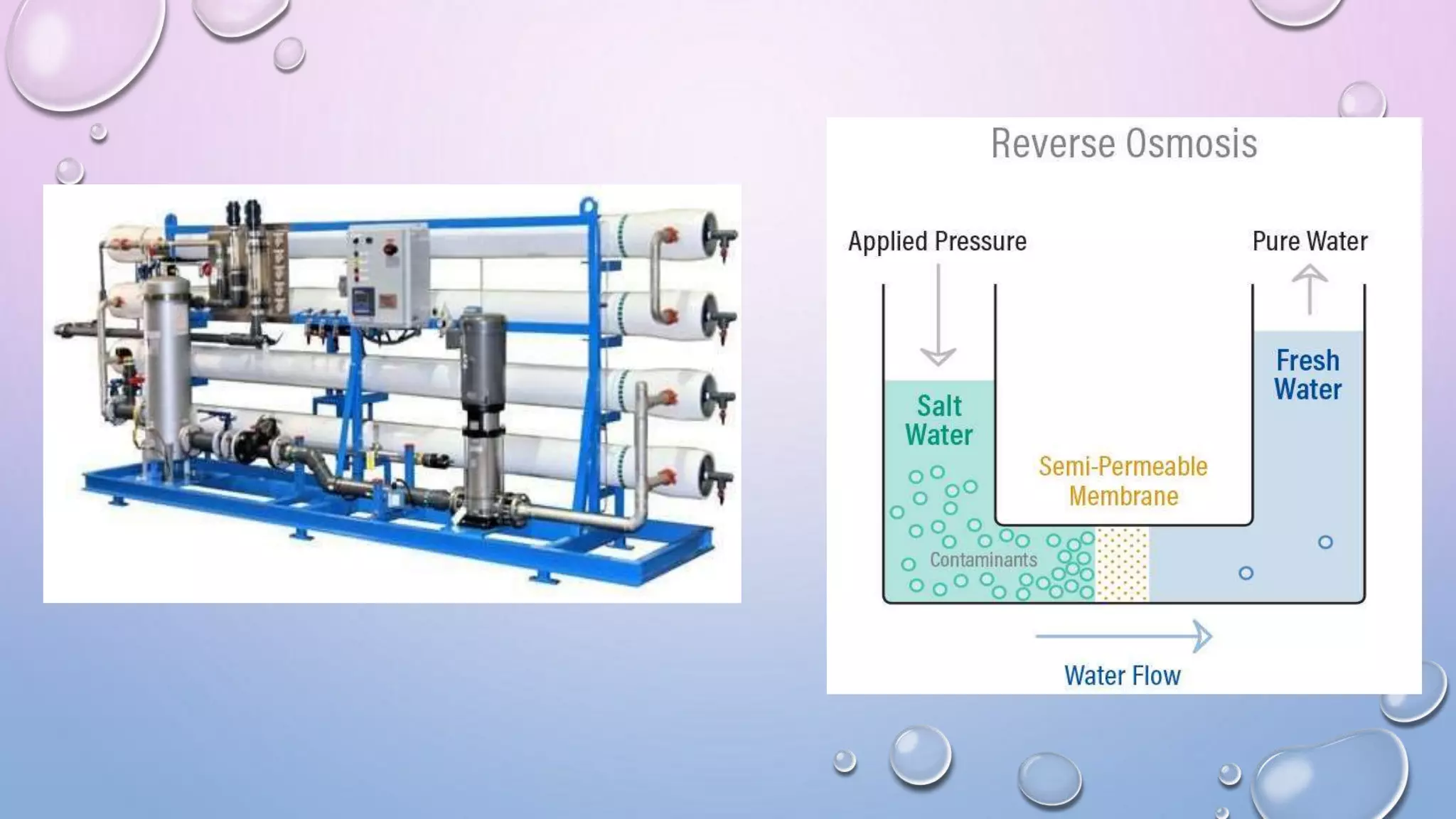
Water purification techniques can purify water on a large, medium, or small scale. On a large scale, sources like rivers and lakes undergo screening, aeration, flocculation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection to remove contaminants. Methods include using coarse or fine screens, different types of aeration, adding chemicals like alum during coagulation, settling solids via sedimentation, and using sand or membrane filters along with chlorination, ozonation, or UV radiation for disinfection. On a medium scale from wells or springs, addition of chlorinated lime is used. Small scale purification involves boiling, adding chemicals like bleach or iodine, or demineralization through processes like reverse osmosis