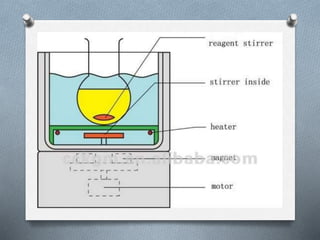
The principle used in a water bath is indirect heating. A water bath works by maintaining water at a constant temperature, which then heats other fluids placed within it through indirect contact.
The procedure for using a water bath is:
1. Fill the water bath container with clean water up to the desired level.
2. Turn the water bath on and set the thermostat to the desired temperature.
3. Allow the water to warm up until it reaches the set temperature.
4. Place the container holding the fluid you want to heat inside the water bath. The fluid will then be heated indirectly through contact with the heated water surrounding it, maintaining a constant temperature.
5. The thermostat works to