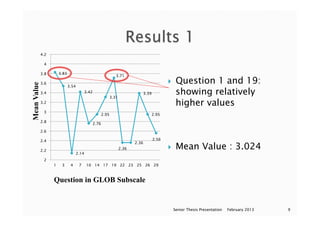
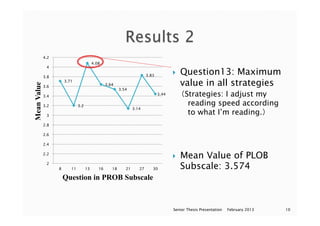
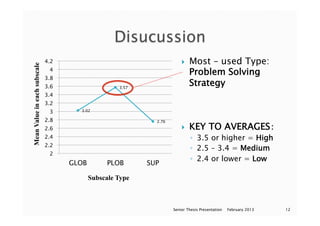
This document appears to be a series of slides from a senior thesis presentation about a study on metacognition in EFL readers. The study examined 59 EFL readers' use of metacognitive reading strategies when analyzing an English travel website about Belize. The participants completed a web analysis task and questionnaire assessing their use of global, problem-solving, and support reading strategies. Results showed problem-solving strategies had the highest mean usage. The presentation concludes by discussing using additional methods like eye tracking in future research.