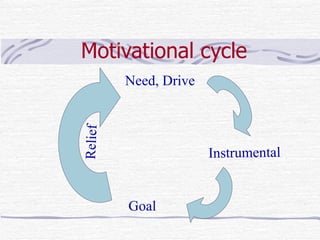
Motivation is an inferred process that causes an organism to move towards a goal. Abraham Maslow's hierarchy of needs proposes that people are motivated to fulfill basic physiological needs, safety needs, belongingness and love needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs. Self-motivation involves breaking tasks into small steps and starting action without waiting for inspiration. Effective motivational strategies include finding new skills, getting feedback, expanding abilities, and rotating work assignments. Goal-setting is important for motivation and goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, time-oriented, and tangible. Short-term goals can be achieved quickly while long-term goals take more time.