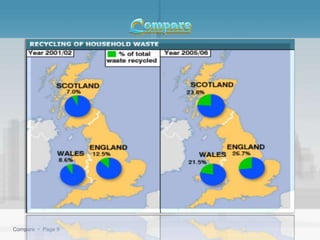
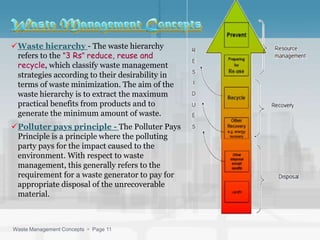
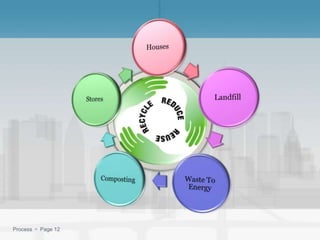
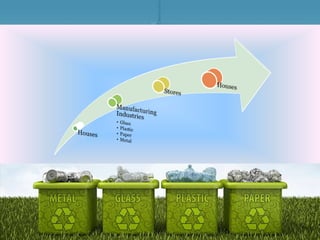
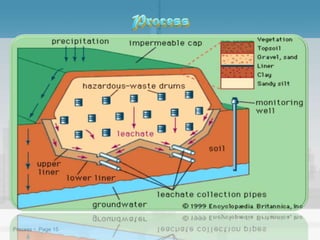
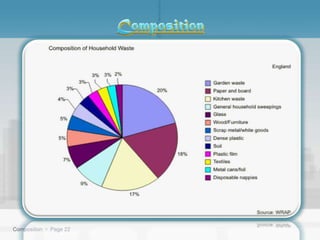
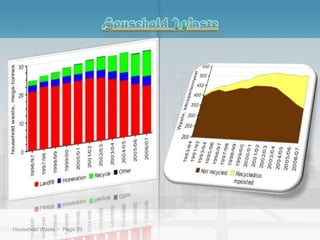
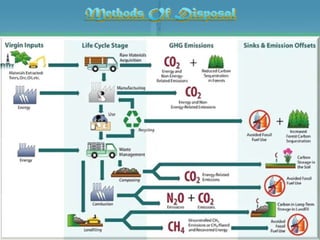
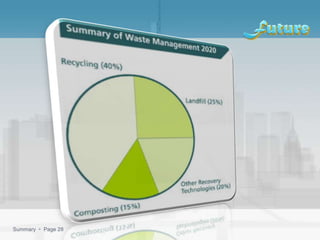
Waste management refers to the processes of collecting, transporting, processing, and disposing of waste materials produced by human activities to minimize their impact on health and the environment. It includes various types of waste such as domestic, industrial, e-waste, and agricultural waste, with differing management practices implemented in developed and developing countries. Key concepts include the waste hierarchy focusing on reducing, reusing, and recycling, and disposal methods such as landfills, incineration, and composting.