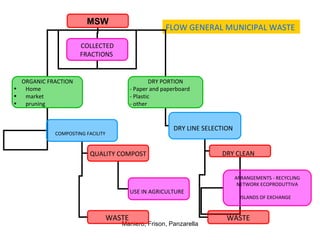
The document discusses different types of waste and the waste cycle. It notes that over 70,000 metric tons of municipal solid waste is produced per day in Italy alone, composed of 30% food waste, 30% paper, 11% plastic, and 10% glass. The document recommends ways to reduce waste such as using reusable containers and buying only what you need. It explains that recycling is the process of collecting, reprocessing, and reusing materials previously considered waste. Materials can be recycled by collecting different items like paper, glass, cans and plastic separately.