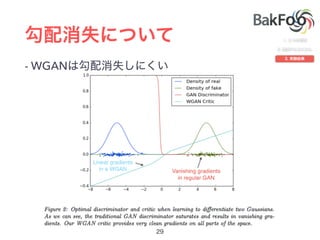
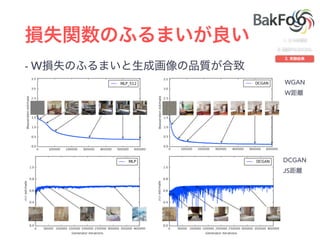
1. The document discusses Wasserstein GAN (WGAN), a type of generative adversarial network (GAN) that uses the Wasserstein distance rather than Jensen-Shannon divergence. WGAN has improved stability during training over traditional GANs.
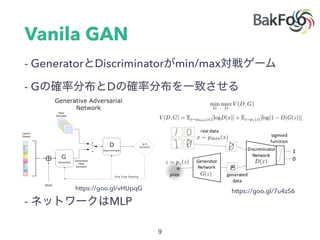
2. WGAN trains the discriminator/critic to estimate the Wasserstein distance between real and generated distributions rather than classify samples. The gradient of the Wasserstein distance can be used to train the generator.
3. WGAN allows for using techniques like minibatch discrimination and batch normalization that previously caused issues with GAN training stability. WGAN has better theoretical properties and often produces higher quality samples than alternatives like DCGAN.

















![4
- W
- JS
- KL
- TV
KL(P0kP✓) = KL(P✓kP0) =
(
+1 if ✓ 6= 0 ,
0 if ✓ = 0 ,
(P0, P✓) =
(
1 if ✓ 6= 0 ,
0 if ✓ = 0 .
JS(P0, P✓) =
(
log 2 if ✓ 6= 0 ,
0 if ✓ = 0 ,
W(P0, P✓) = |✓|
U[0, 1]
https://goo.gl/40eCbR](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tfug2017-07-12-170713011723/85/Wasserstein-GAN-Tfug2017-07-12-19-320.jpg)

![3 2
3: Kantorovich-Rubinstein
- W
- W
max
w2W
Ex⇠Pr
[fw(x)] Ex⇠P✓
[fw(x)] sup
kfkLK
Ex⇠Pr
[f(x)] Ex⇠P✓
[f(x)]
= K · W(Pr, P✓)
r✓W(Pr, P✓) = r✓(Ex⇠Pr
[fw(x)] Ez⇠Z[fw(g✓(z))])
= Ez⇠Z[r✓fw(g✓(z))]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tfug2017-07-12-170713011723/85/Wasserstein-GAN-Tfug2017-07-12-21-320.jpg)
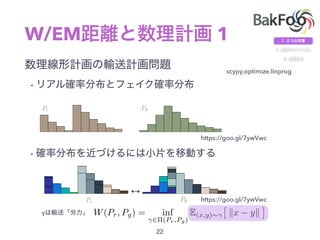
![W/EM 2
: Kantorovich-Rubinstein
-
W(Pr, Pg) = inf
2⇧(Pr,Pg)
E(x,y)⇠
⇥
kx yk
⇤
W(Pr, Pg) = sup
kfkL1
Ex⇠Pr
[f(x)] Ex⇠Pg
[f(x)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tfug2017-07-12-170713011723/85/Wasserstein-GAN-Tfug2017-07-12-23-320.jpg)
![3 2( )
3: Kantorovich-Rubinstein
- W
- W
max
w2W
Ex⇠Pr
[fw(x)] Ex⇠P✓
[fw(x)] sup
kfkLK
Ex⇠Pr
[f(x)] Ex⇠P✓
[f(x)]
= K · W(Pr, P✓)
r✓W(Pr, P✓) = r✓(Ex⇠Pr
[fw(x)] Ez⇠Z[fw(g✓(z))])
= Ez⇠Z[r✓fw(g✓(z))]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tfug2017-07-12-170713011723/85/Wasserstein-GAN-Tfug2017-07-12-24-320.jpg)

![r✓W(Pr, P✓) = r✓(Ex⇠Pr
[fw(x)] Ez⇠Z[fw(g✓(z))])
= Ez⇠Z[r✓fw(g✓(z))]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tfug2017-07-12-170713011723/85/Wasserstein-GAN-Tfug2017-07-12-26-320.jpg)