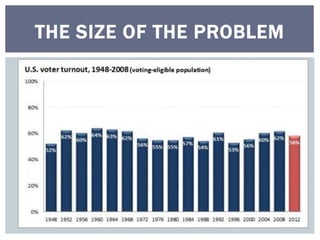
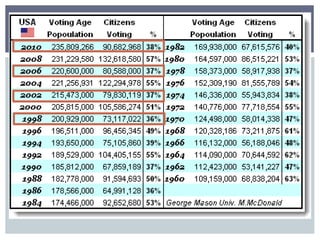
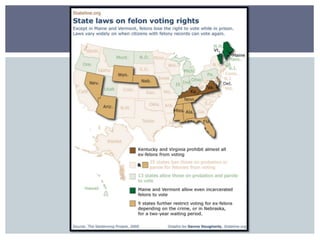
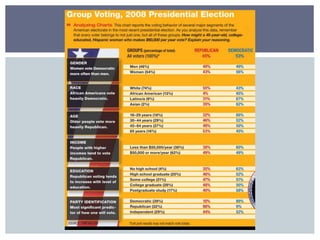
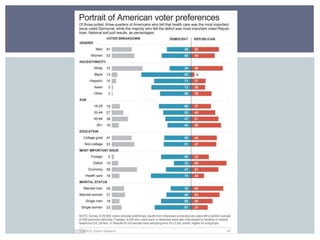
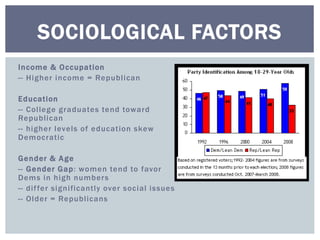
The document discusses reasons why people do and do not vote, and factors that influence how people vote. It first addresses why some people do not vote, such as being indifferent to politics or feeling alienated from the system. It then covers sociological factors that affect how people vote, such as income, education, gender, age, religion, ethnicity, and geography. Psychological factors like party identification are also discussed, noting it is a significant predictor but its influence may be weakening. The document examines both voter behavior and non-voter behavior.