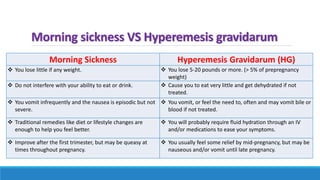
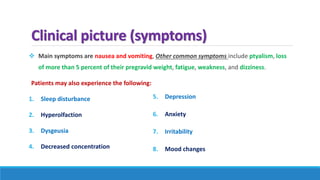
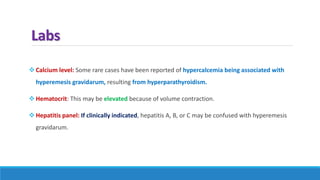
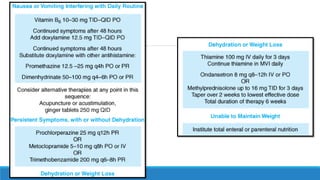
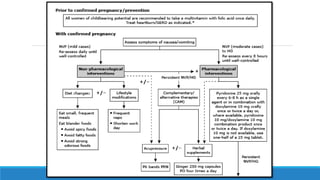
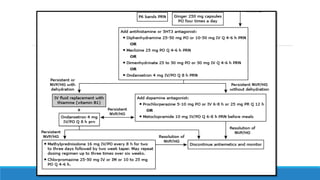
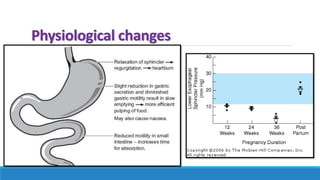
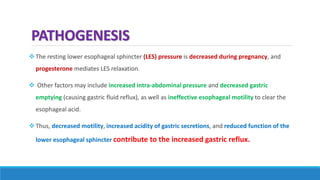
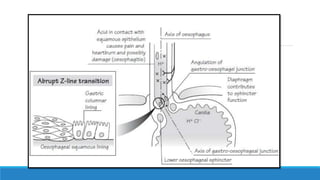
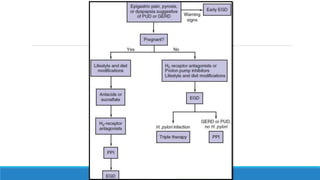
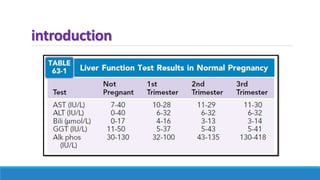
The document discusses various gastrointestinal issues during pregnancy, including nausea and vomiting, hyperemesis gravidarum, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. It details the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for each condition, emphasizing that nausea and vomiting affect a significant percentage of pregnant women while outlining the serious implications of hyperemesis gravidarum. Management strategies include dietary modifications, medication, and monitoring for potential complications.