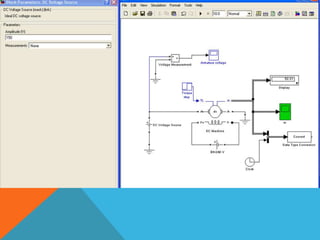
The document discusses direct current (DC) motors. It explains that a DC motor converts electrical energy to mechanical energy when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, causing a torque. The direction of rotation reverses if the current direction is reversed. Factors like the number of poles and flux per pole affect the motor's speed. The document also describes methods of controlling the speed of a DC motor, including armature control and voltage control.