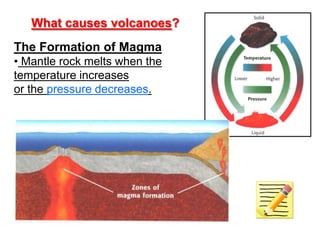
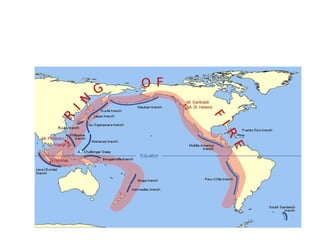
Volcanoes erupt when pressure from gases and magma built up in the volcano's magma chamber is too great. This is similar to the pressure build up in a balloon until it bursts. When the pressure is released, gases and molten rock (magma) are ejected from the volcano in explosive eruptions or flow out as lava in nonexplosive eruptions. Volcanoes form at boundaries where tectonic plates meet, especially at subduction zones, as well as at hot spots in the mantle.