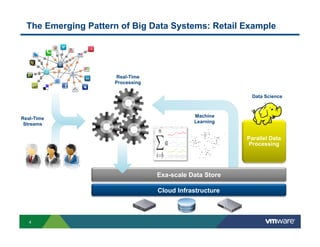
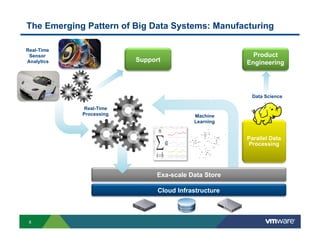
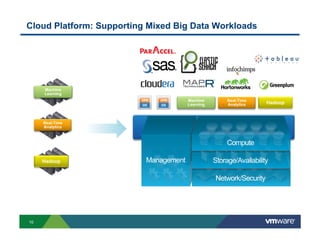
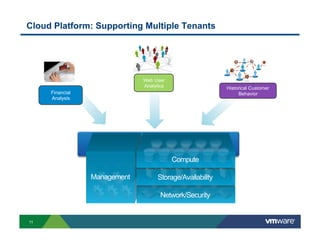
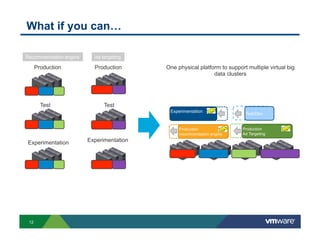
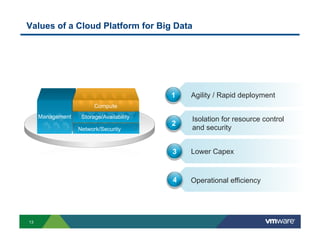
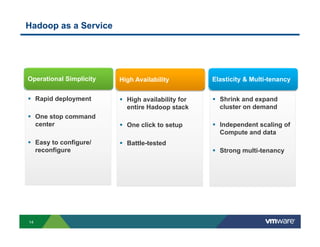
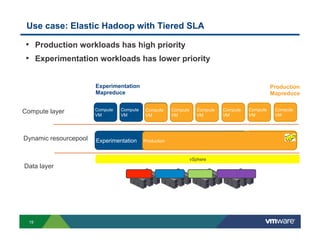
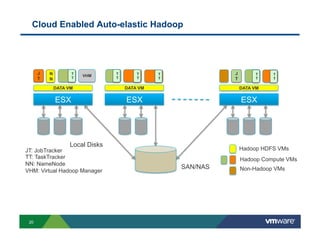
1) Cloud platforms can support big data workloads through virtualization which provides agility, isolation, lower costs, and operational efficiency.
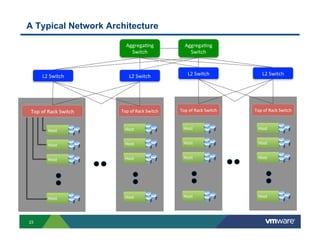
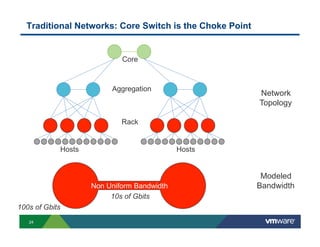
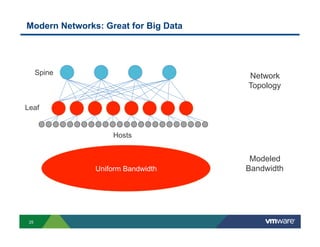
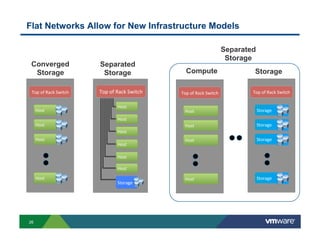
2) Modern networks with spine-leaf architectures are well-suited for big data by providing uniform high bandwidth connectivity. This allows for new converged and separated storage models.
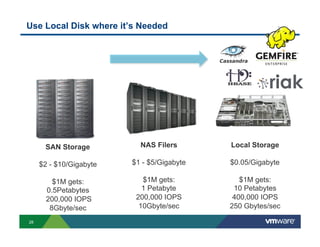
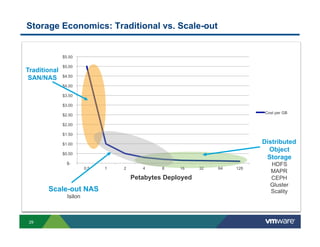
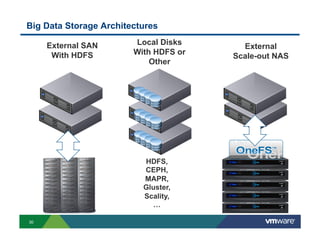
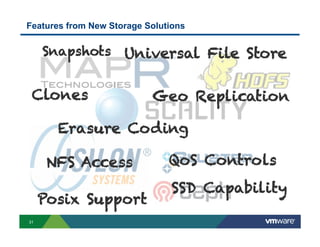
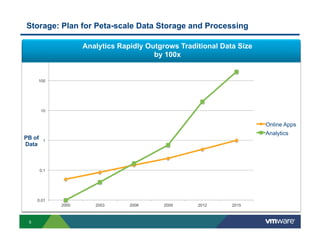
3) New distributed storage solutions like HDFS, Ceph, and scale-out NAS provide much higher capacity at lower costs than traditional SAN/NAS. They also offer features like erasure coding, snapshots, cloning and geo-replication.






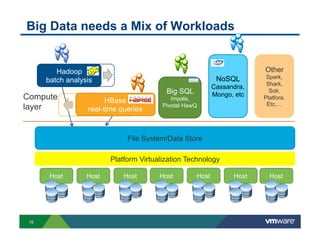

![Hadoop Performance with Virtualization
32 hosts/3.6GHz 8 cores/15K RPM 146GB SAS disks/10GbE/72-96GB RAM
(lower is better)
[http://www.vmware.com/resources/techresources/10360, Jeff Buell, Apr 2013]
21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stratanyv3-131031133024-phpapp02/85/Is-your-cloud-ready-for-Big-Data-Strata-NY-2013-21-320.jpg)