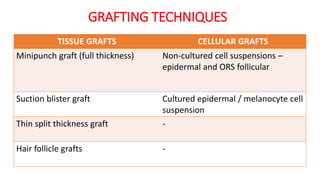
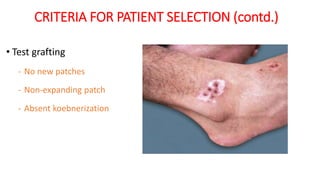
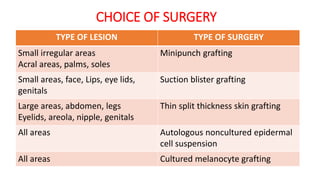
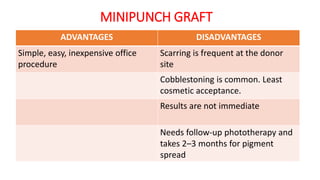
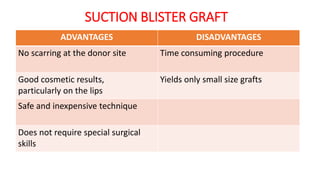
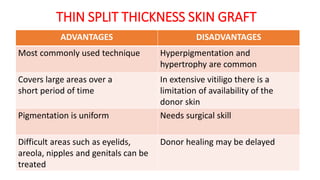
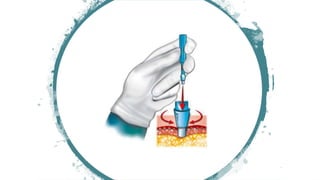
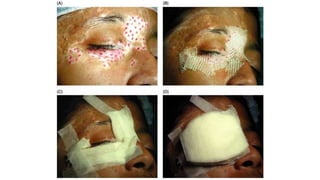
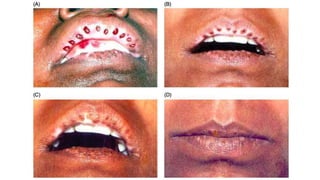
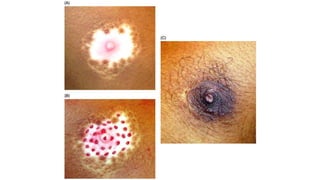
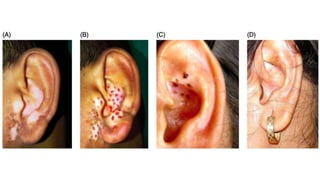
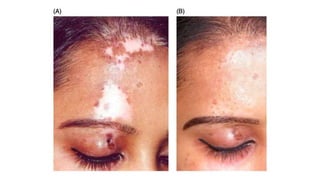
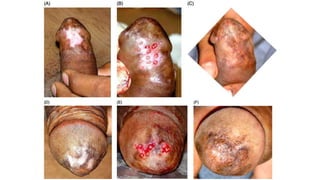
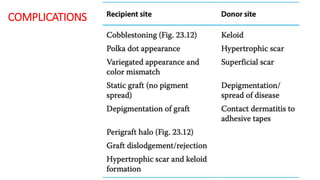
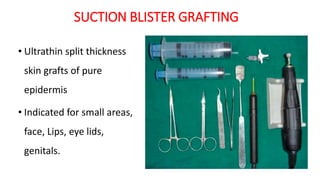
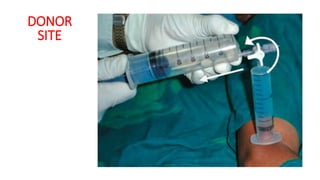
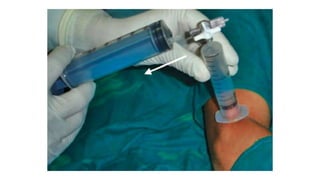
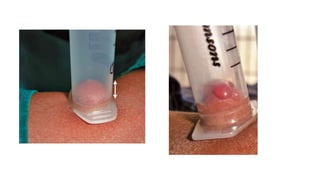
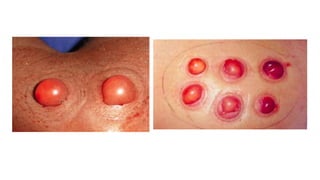
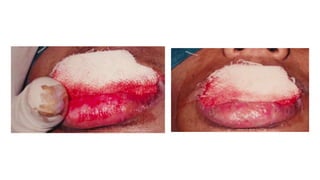
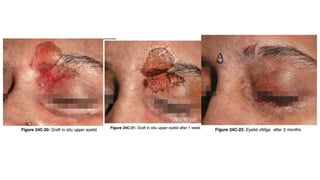
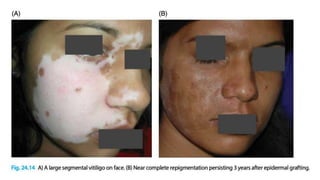
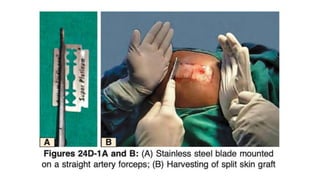
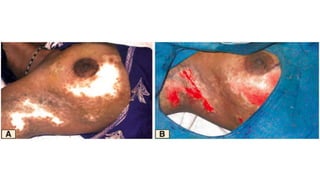
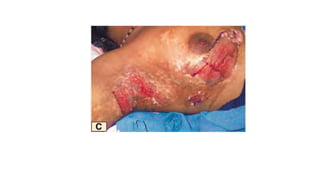
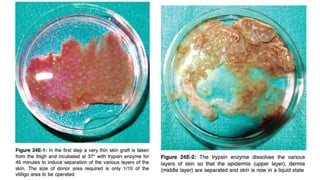
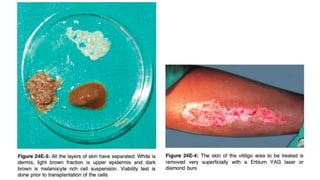
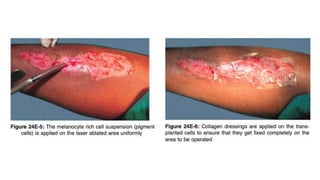
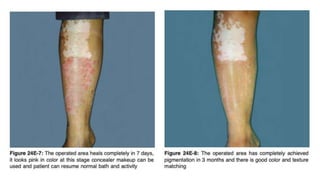
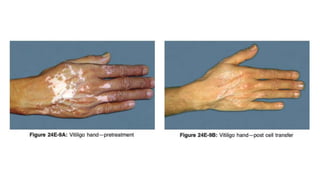
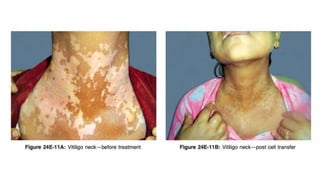
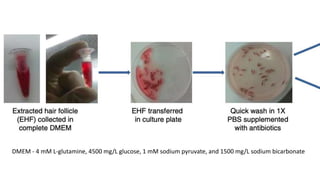
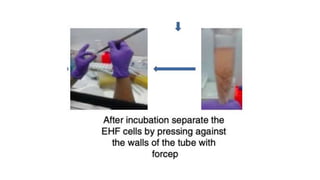
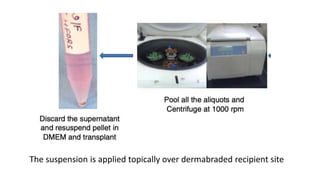
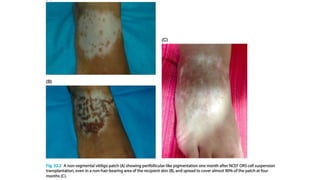
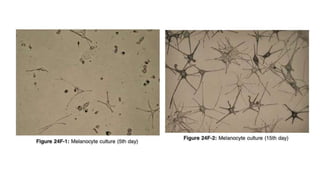
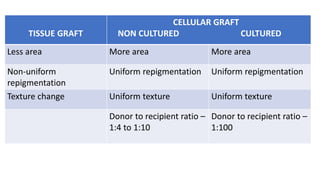
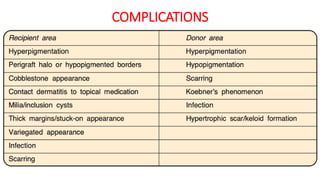
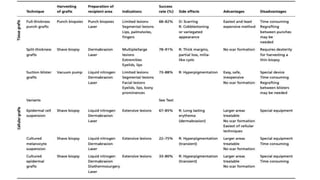
The document discusses vitiligo, an acquired depigmenting disorder, and outlines various treatment options including surgical procedures and grafting techniques aimed at achieving cosmetically acceptable repigmentation. Key factors influencing surgical choices include the type and extent of vitiligo, patient selection criteria, and the advantages and disadvantages of different grafting methods. Ultimately, effective treatments require careful patient evaluation and selection based on stability and expectations.