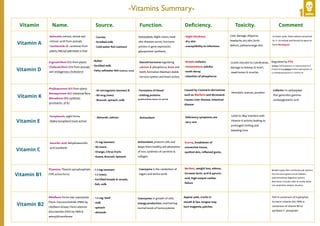
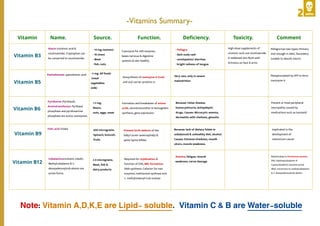
- The document summarizes key vitamins, their sources, functions, deficiency symptoms, and toxicity. It describes Vitamins A, D, E, K, C, B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B9, and B12. Vitamin A supports vision, skin health, and gene expression. Vitamin D regulates calcium and phosphorus for bone and teeth formation. Vitamin K is a cofactor for blood clotting. The B vitamins function as coenzymes in energy production and metabolism.