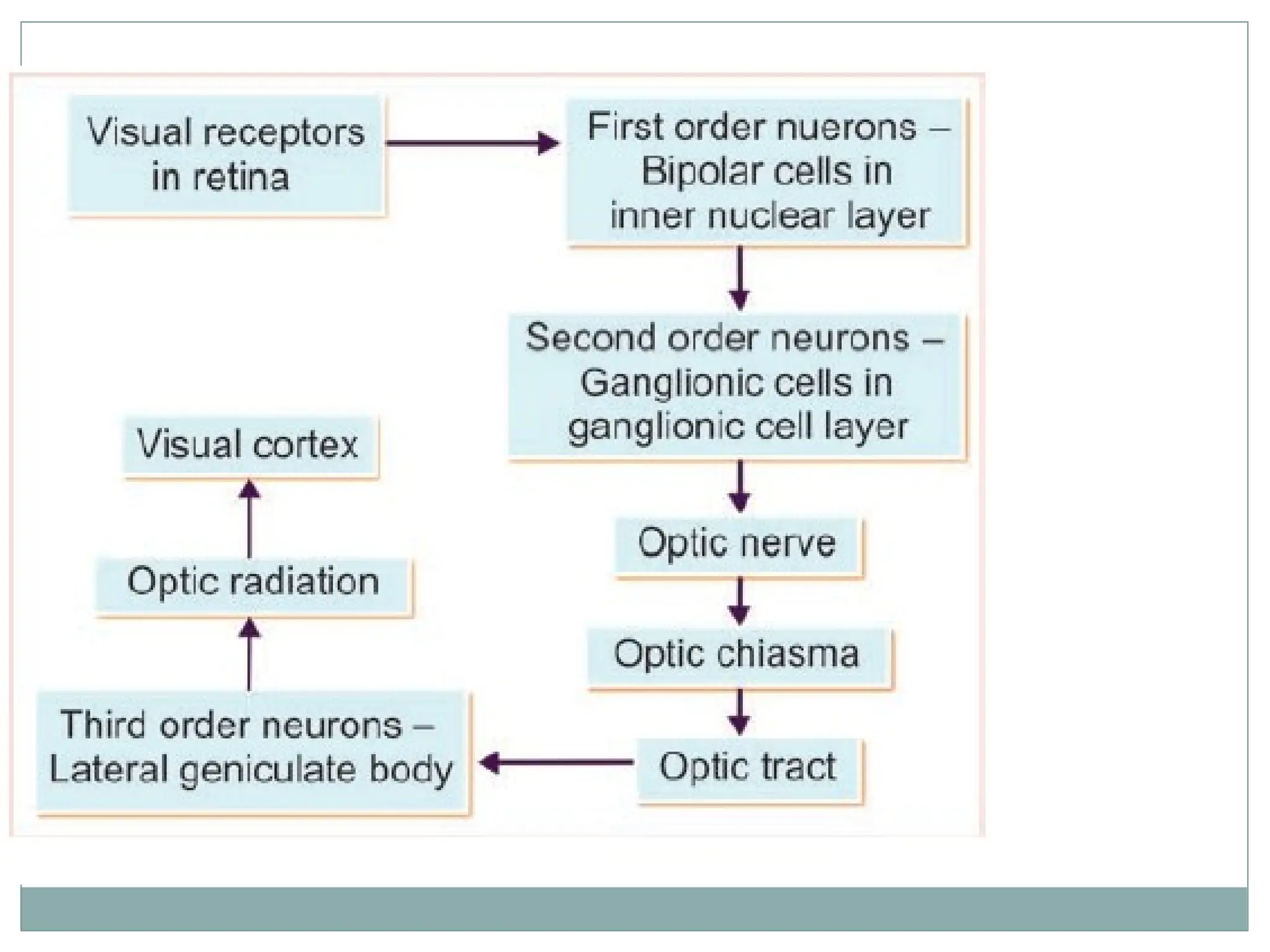
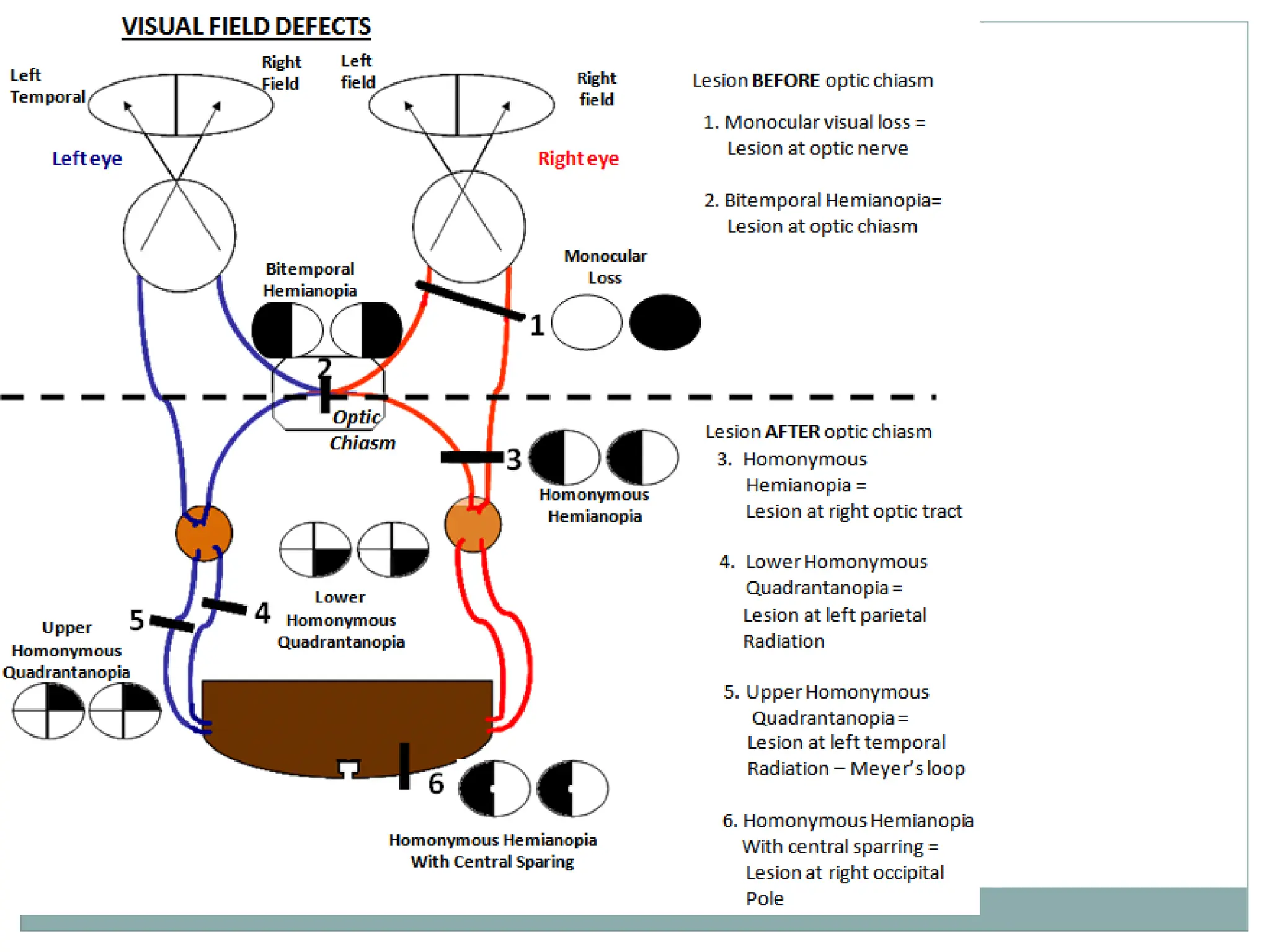
A 30-year-old patient with a history of syphilis presented with partial vision loss, suggesting a diagnosis of homonymous hemianopia due to an optic tract lesion. The visual pathway involves complex neural connections from the retina to the visual cortex, comprising multiple layers of neurons and synapses. Various causes for lesions in the visual pathway are identified, including optic nerve damage, chiasmal issues, and optic tract lesions, with corresponding diagnostic tests outlined.