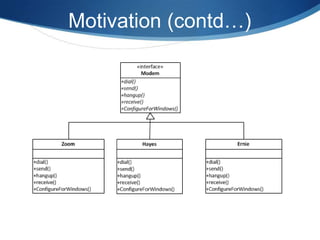
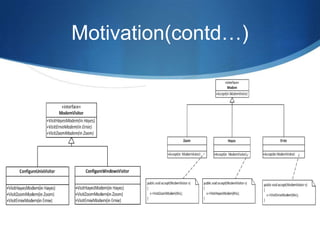
The Visitor pattern allows new operations to be added to existing object structures without modifying those structures. It separates an object structure from the operations performed on it, allowing independent extension of both. Some key aspects include:
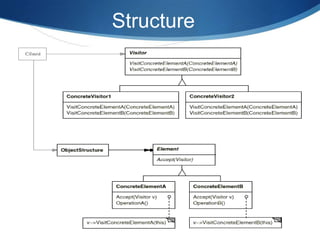
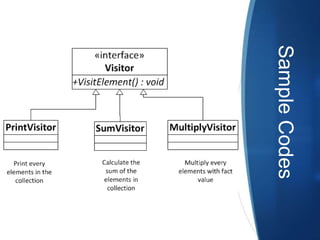
- Visitors define a visit operation for each element type in the object structure. Concrete visitors implement the operations.
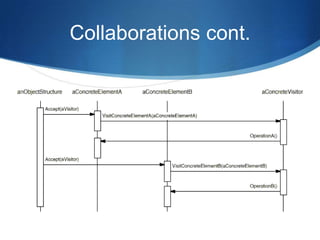
- Elements contain an accept method to accept visitor operations. Concrete elements call the appropriate visit method.
- Clients traverse the structure and pass a visitor to each element's accept method.
The pattern allows encapsulation of new operations without changing element classes, and separates unrelated operations for elements. It can apply to structures without a shared hierarchy.