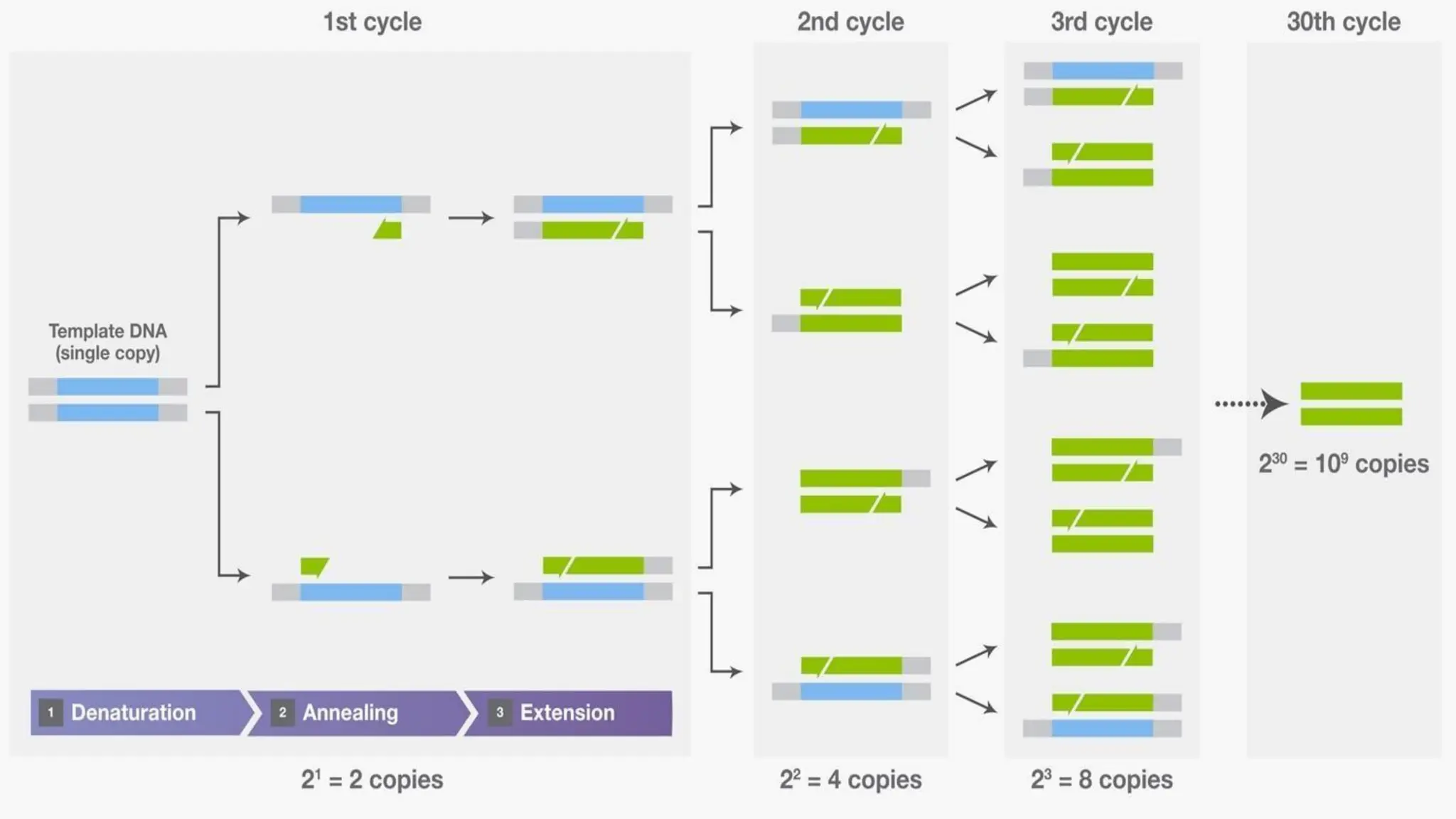
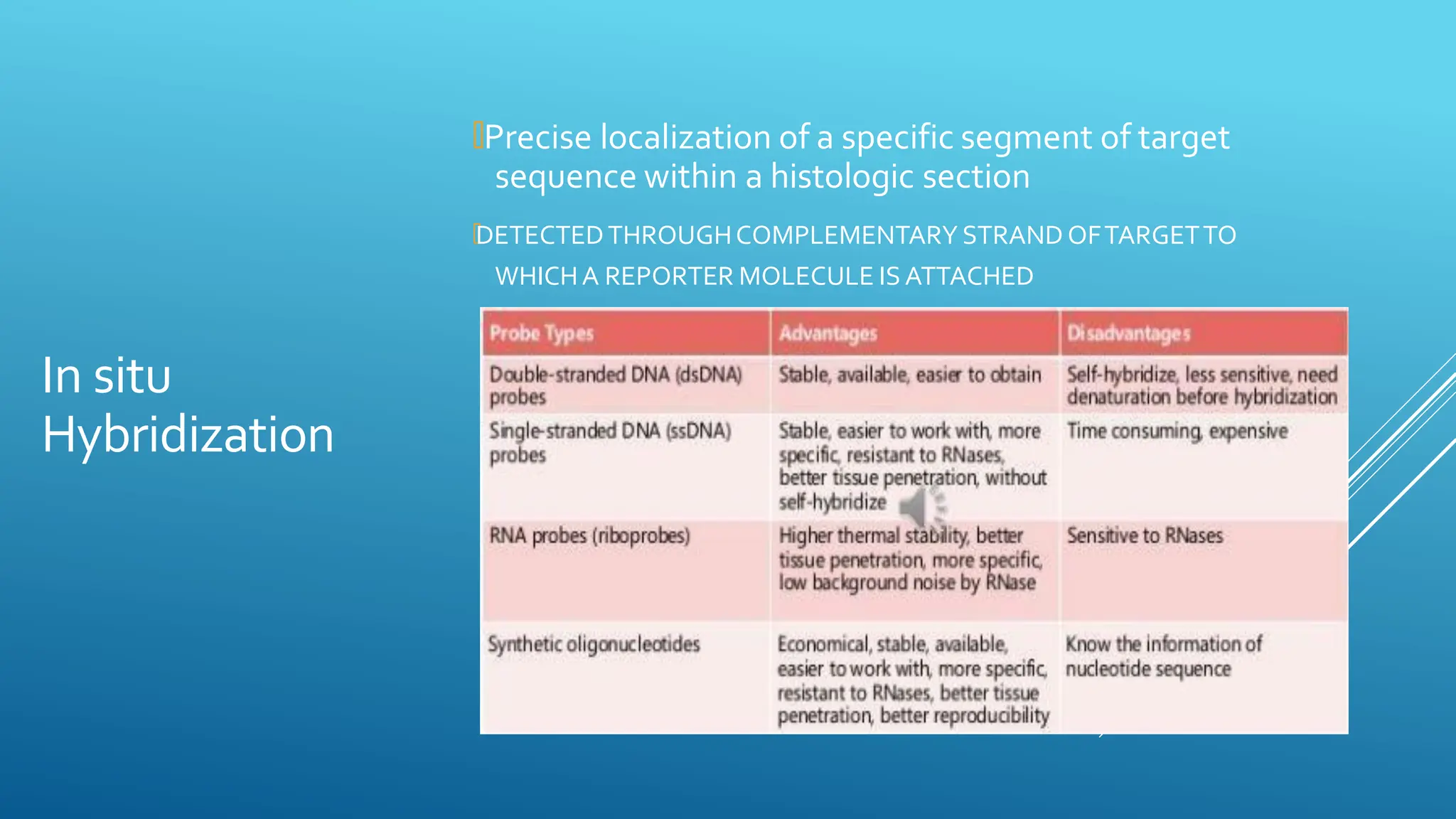
Molecular diagnostic techniques allow for the accurate analysis of DNA, RNA, and proteins involved in various medical conditions like cancers, infections, and genetic disorders. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is commonly used to amplify DNA sequences of interest. Real-time PCR detects amplification as it occurs using fluorescent reporters. Blotting techniques like Southern blotting identify DNA, Northern blotting analyzes RNA, and Western blotting examines proteins. Hybridization methods involve binding of a probe to a complementary DNA or RNA sequence, as seen in in situ hybridization and microarrays. These molecular tools provide high sensitivity and specificity for disease investigation and diagnosis.