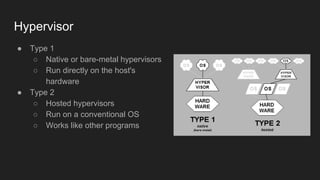
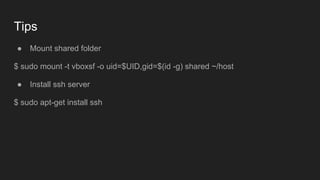
The document outlines a two-day virtualization workshop led by Davide Pelosi, covering virtualization concepts, tools like VirtualBox and Docker, and practical hands-on labs. It details different types of virtualization, including hardware and OS-level virtualization, and discusses various hypervisor types and VM products. Additionally, it provides insights into VirtualBox features, networking modes, and practical lab exercises for creating and configuring virtual machines.