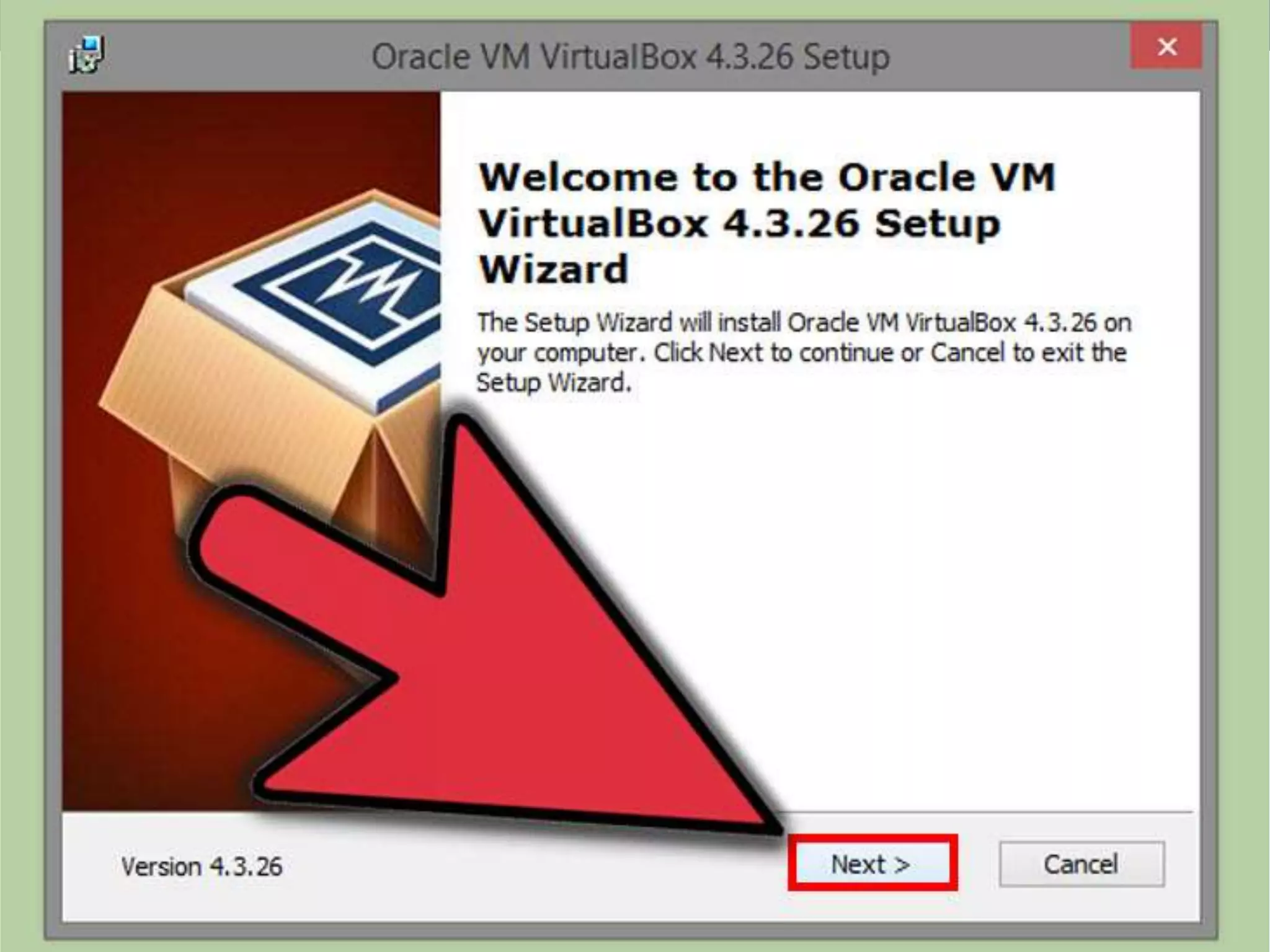
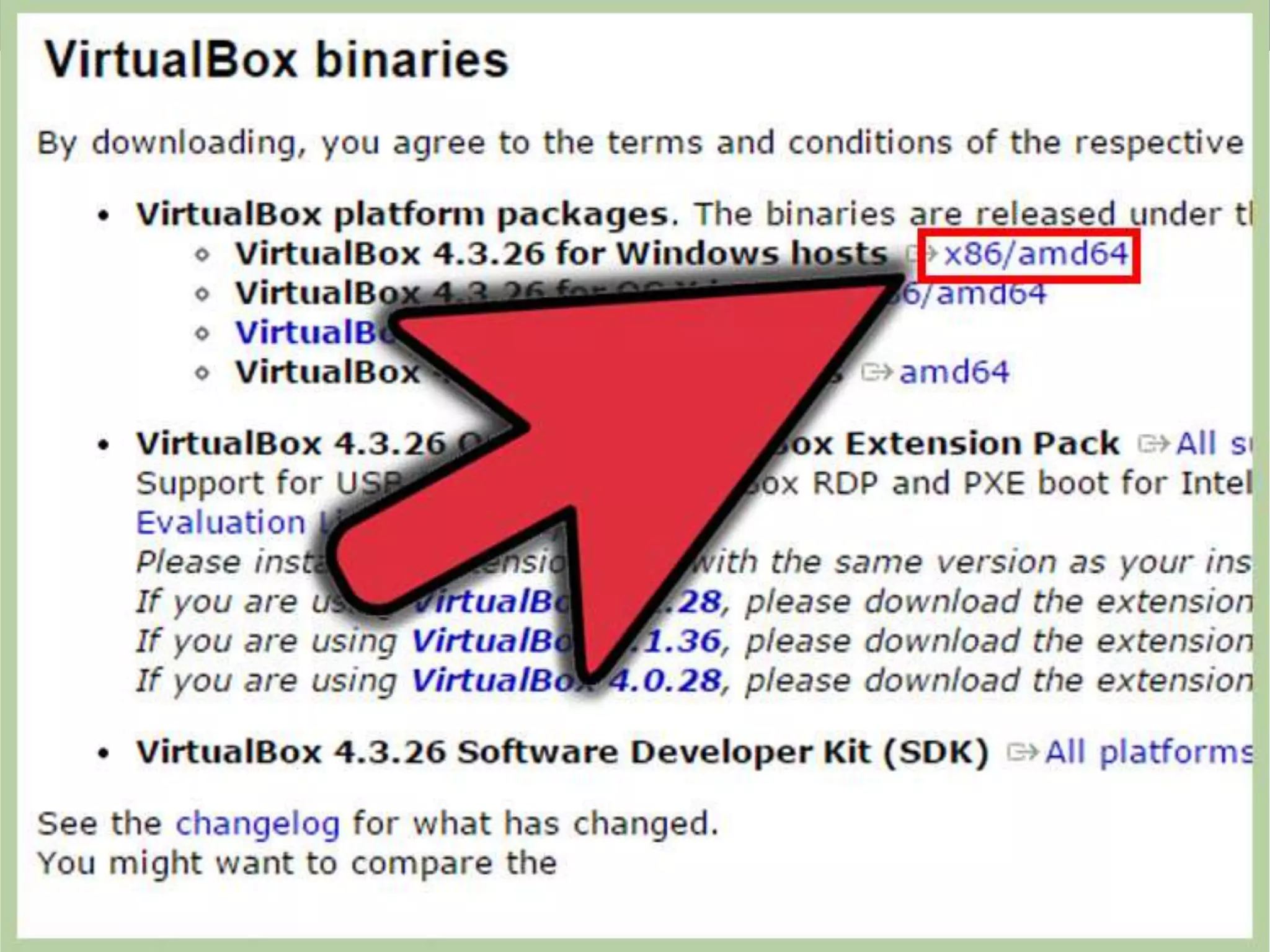
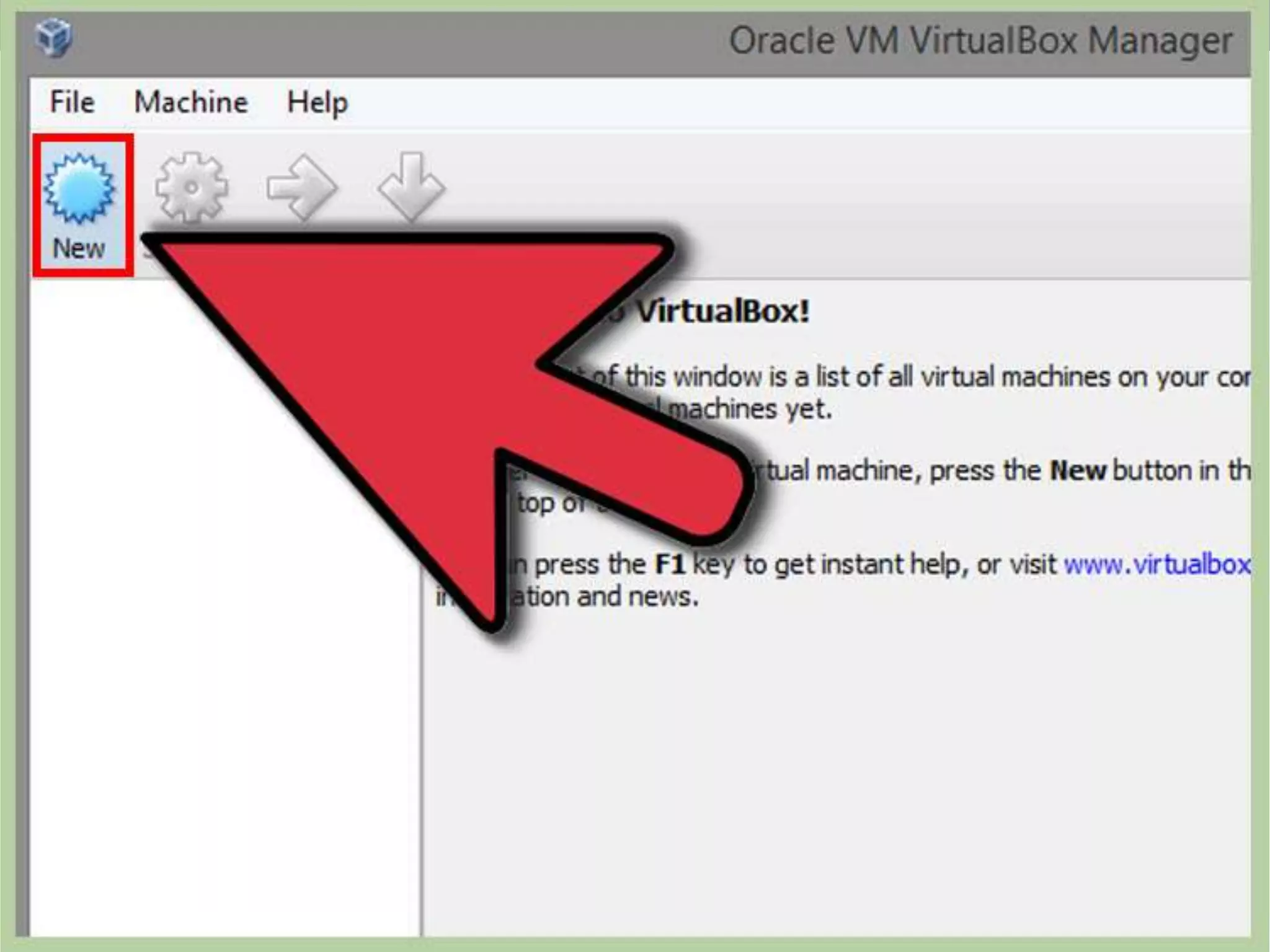
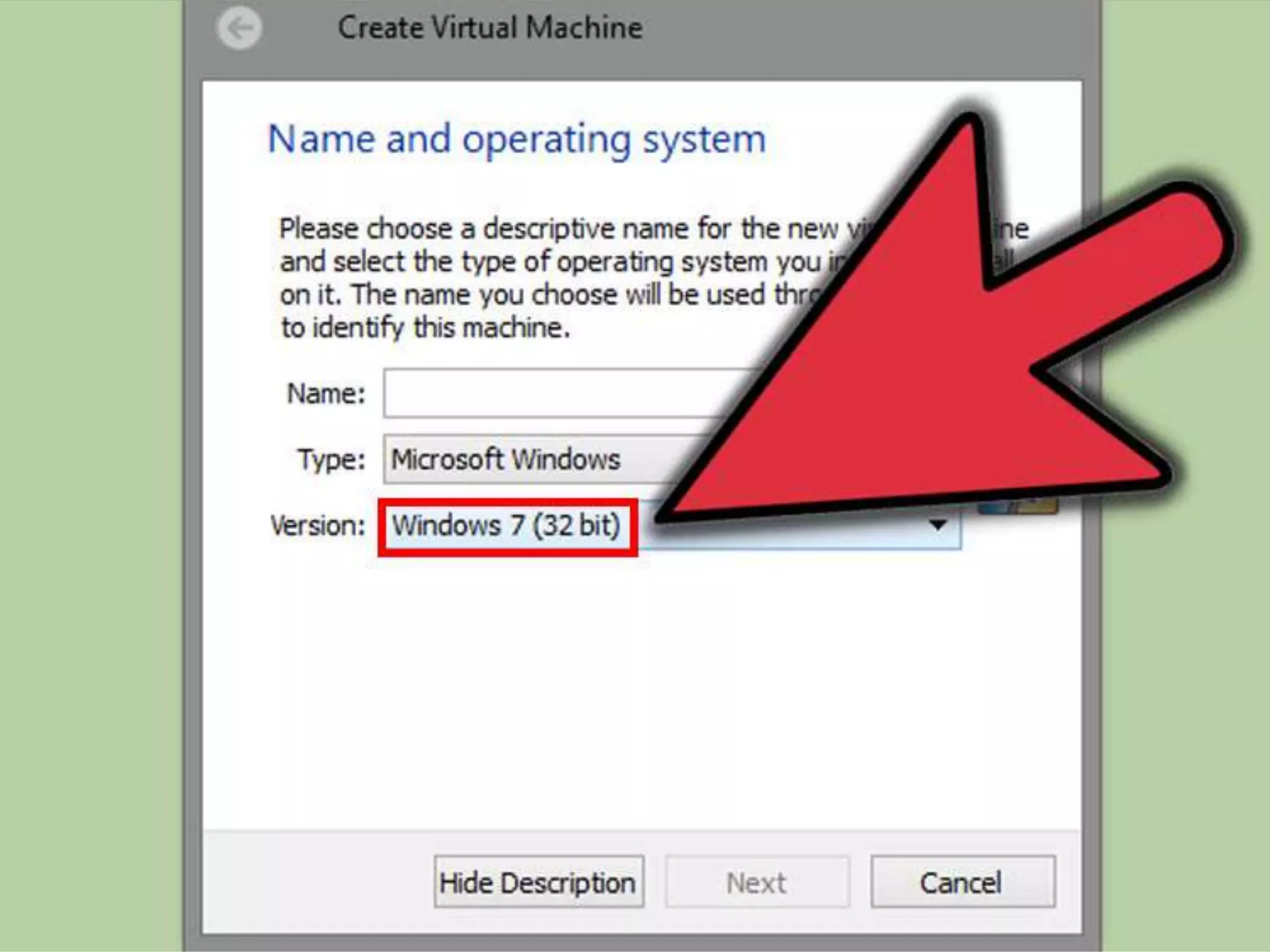
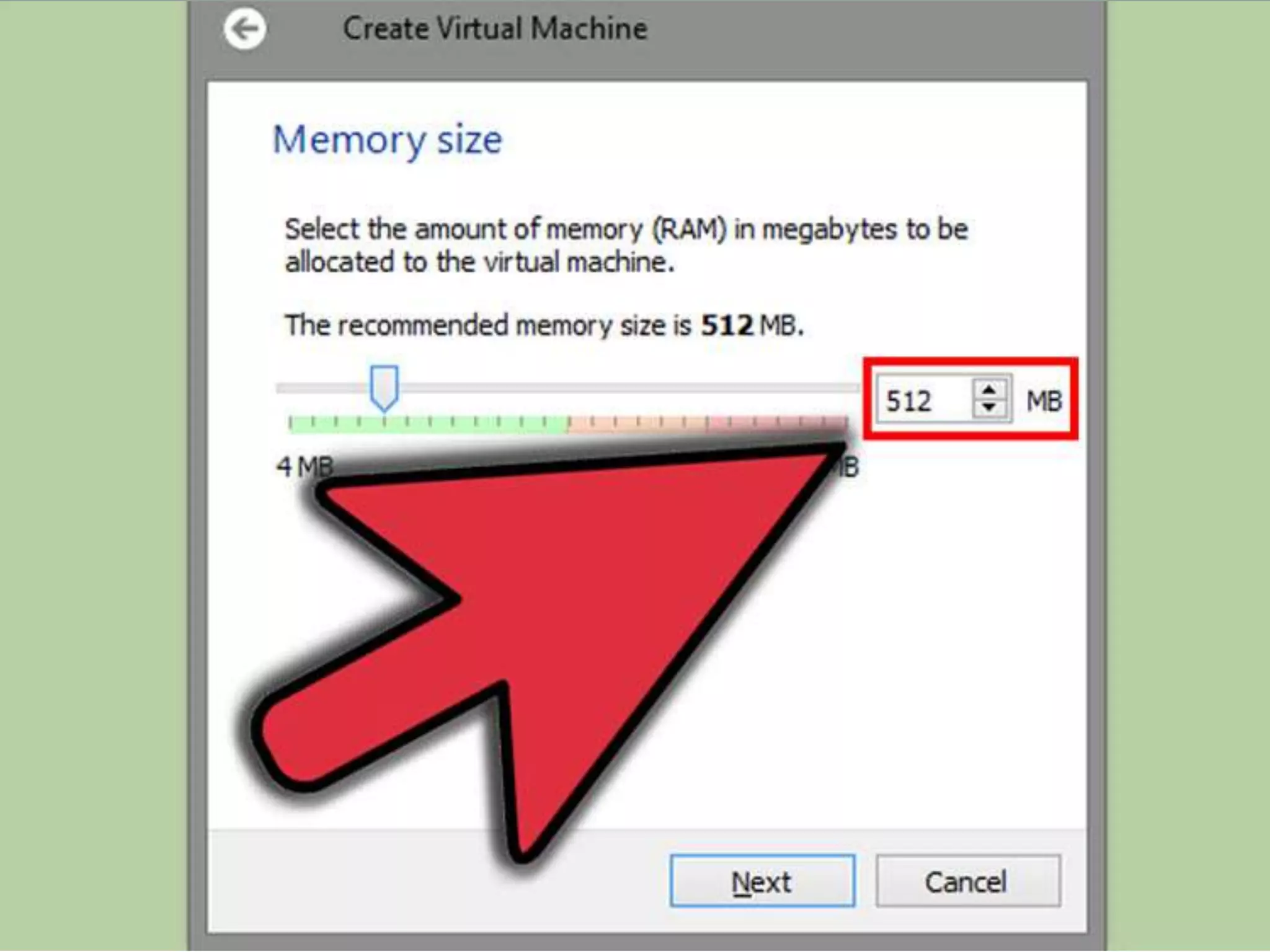
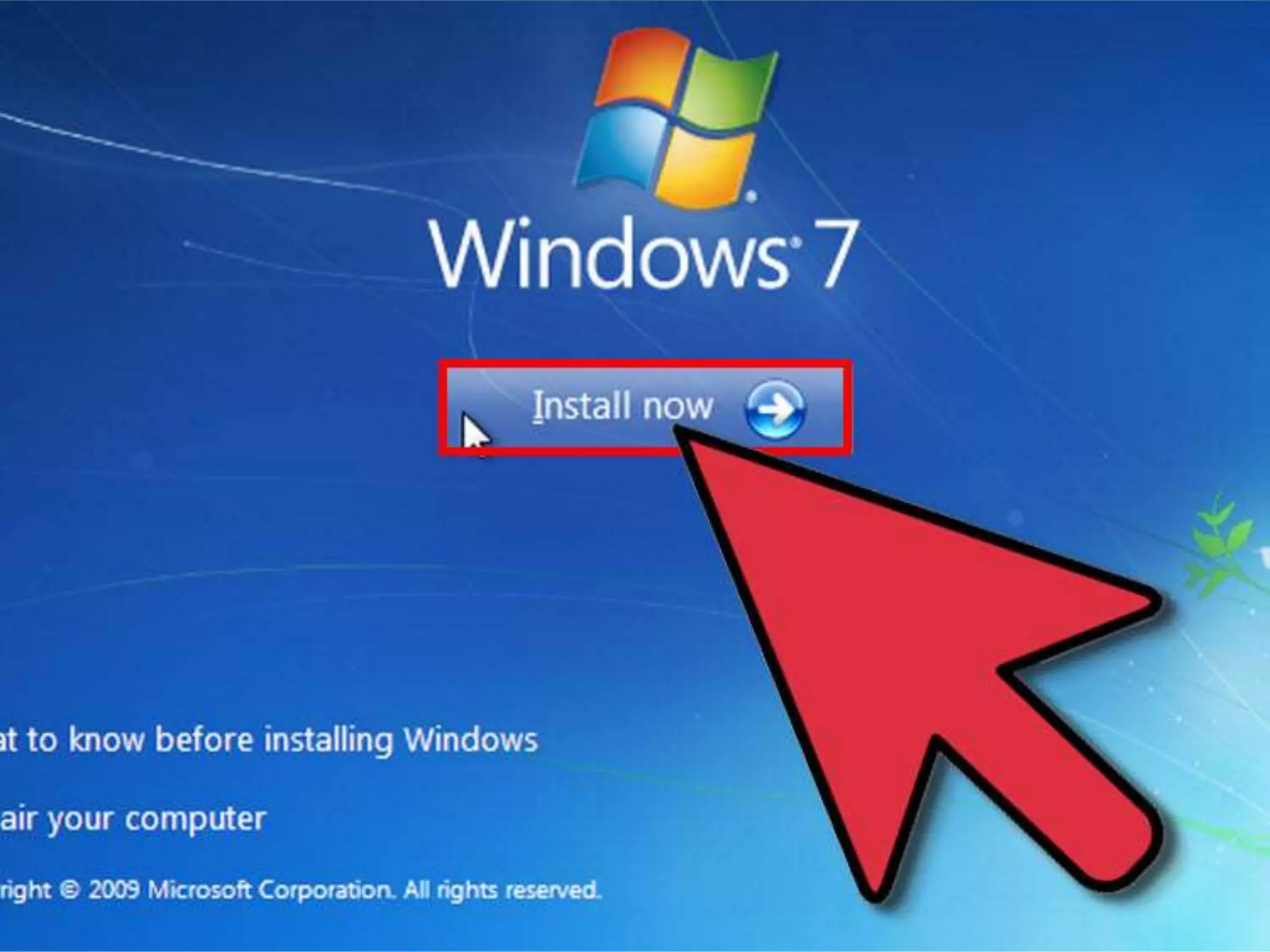
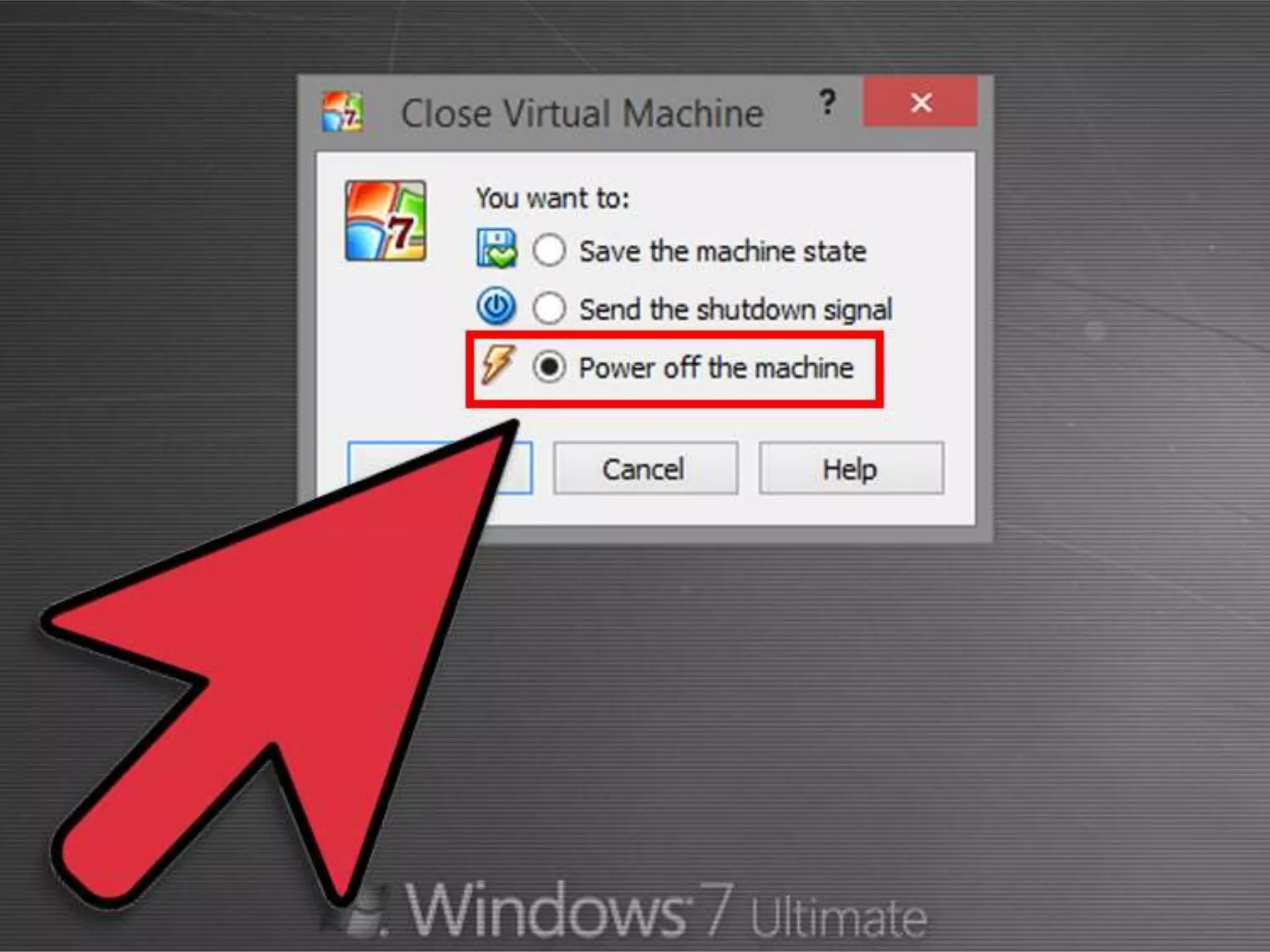
This document discusses the installation of virtual machines. It begins with an introduction to virtual machines, noting that they allow software to emulate hardware and isolate operating systems. It then covers the need for virtual machines, including isolation, testing capabilities, snapshots, and replication. Finally, it discusses advantages like running multiple operating systems simultaneously, easy maintenance and recovery, before concluding that virtual machines provide discrete identical execution environments with greater isolation than a single operating system.