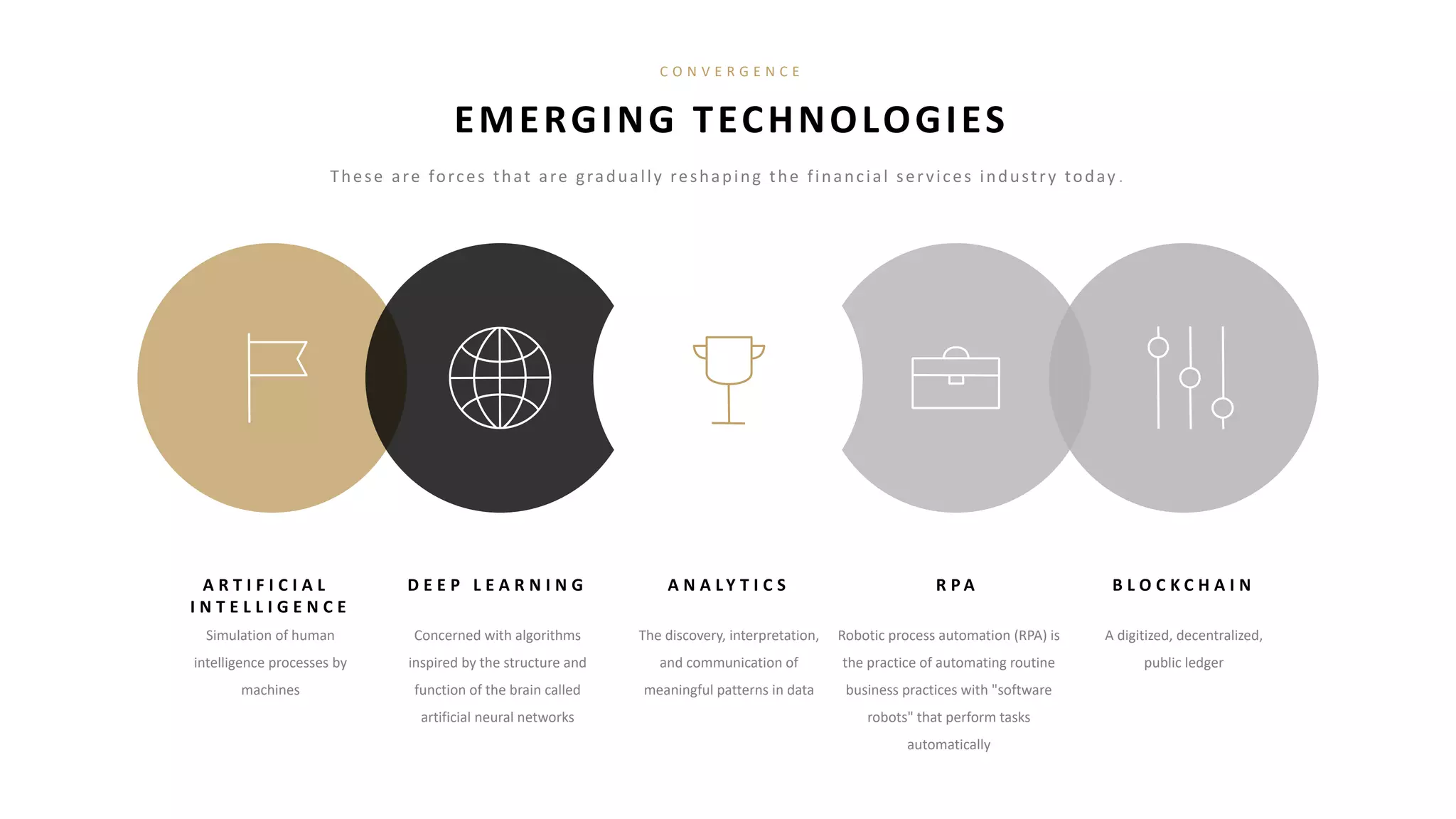
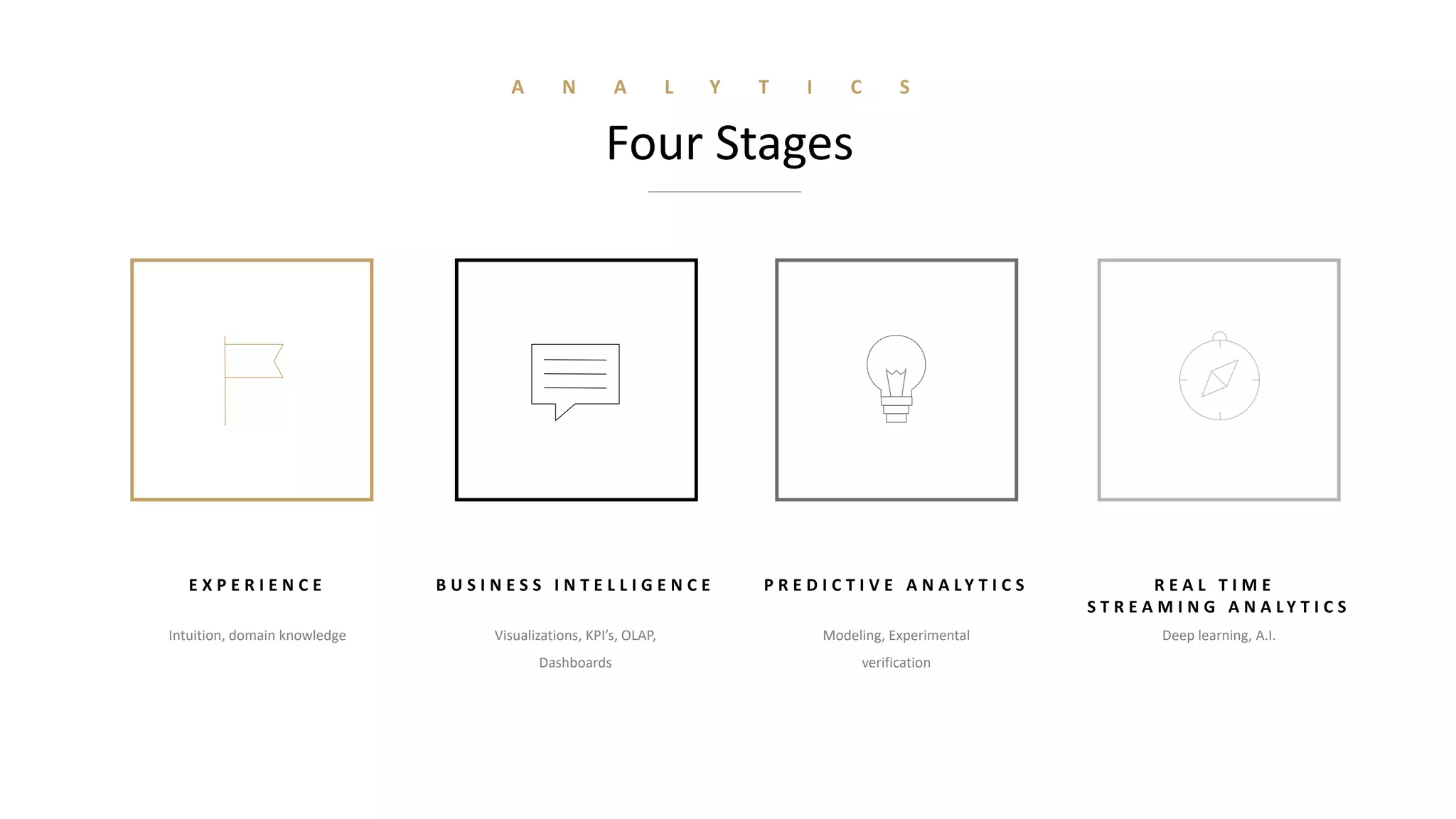
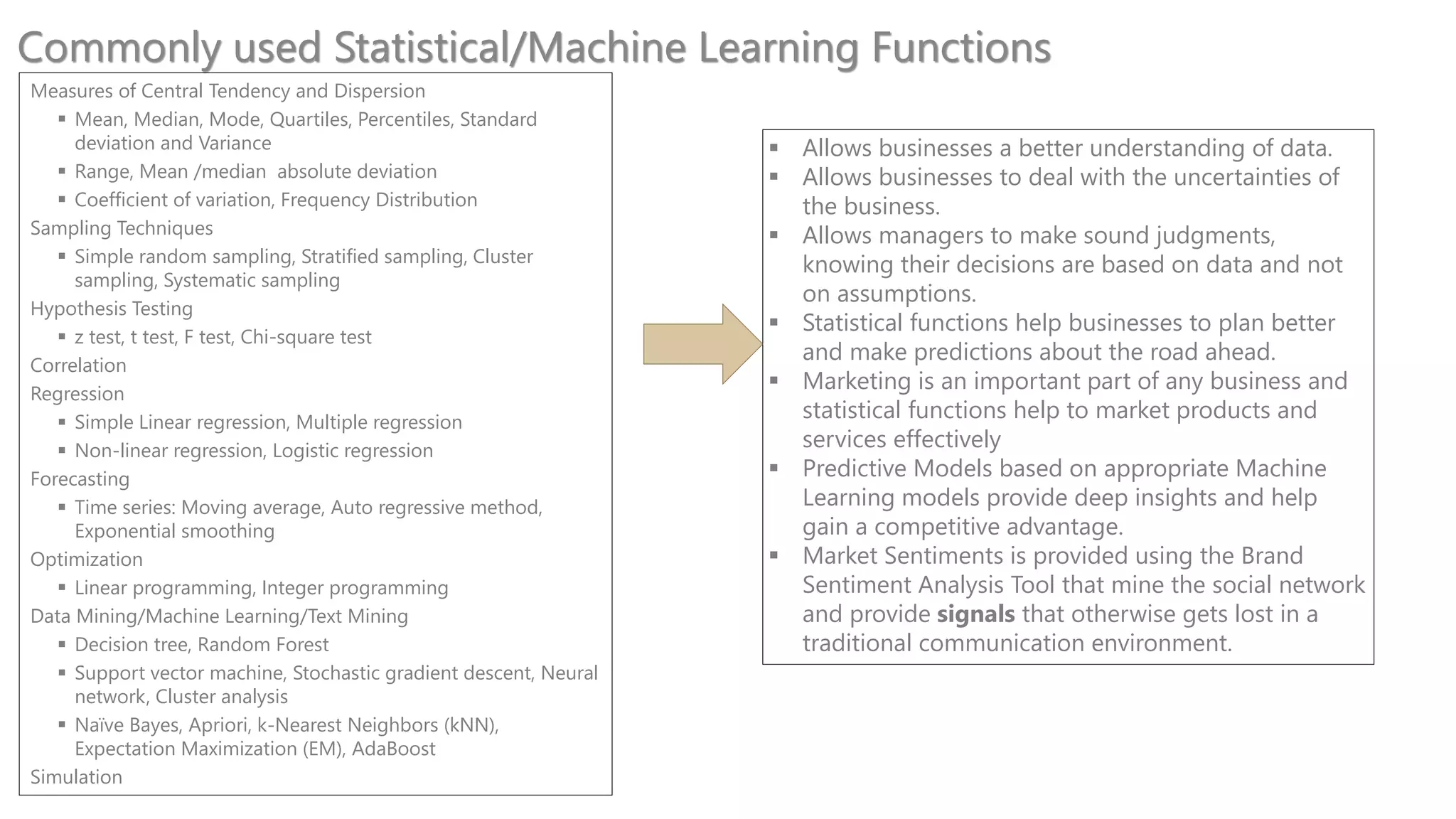
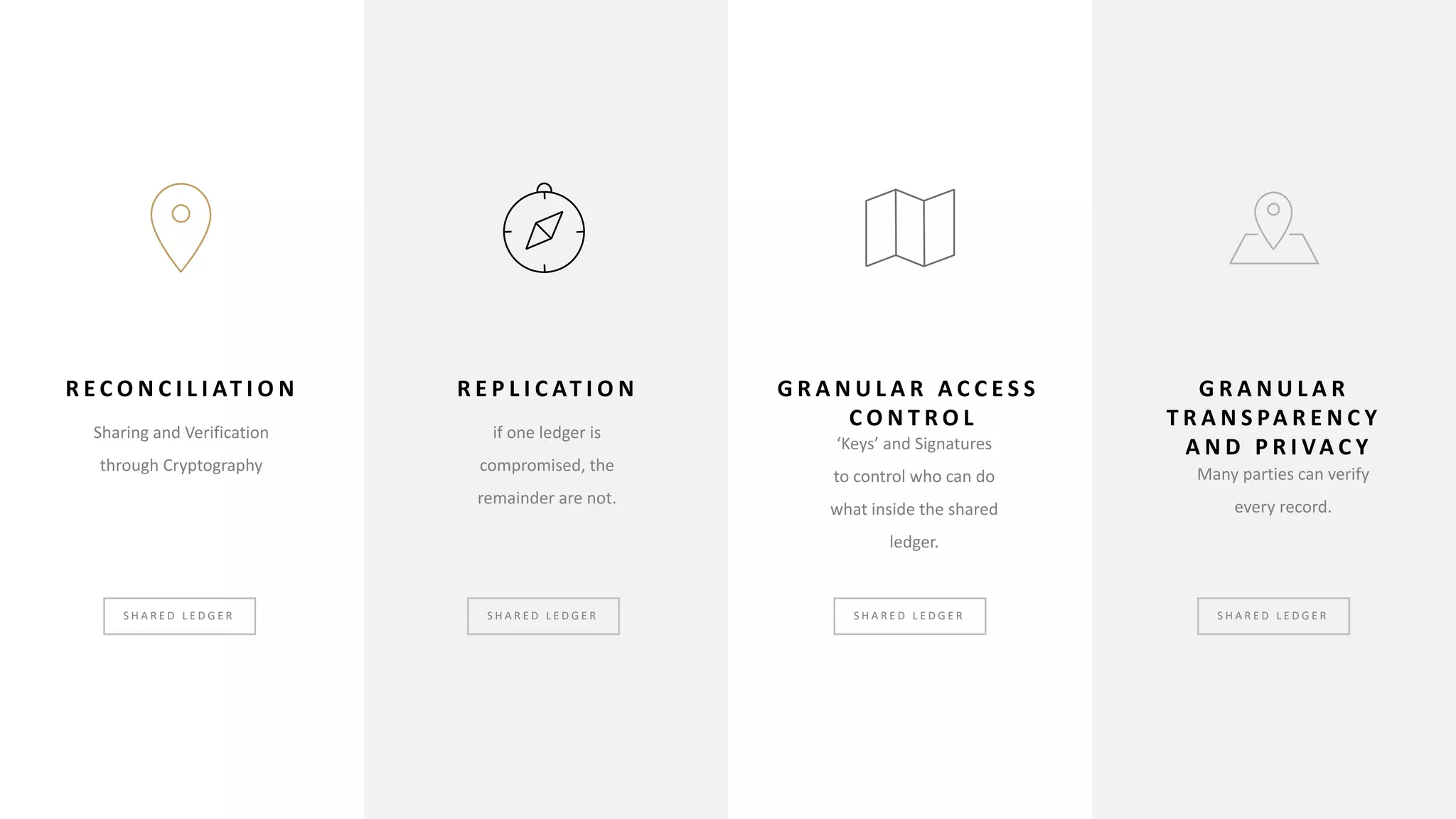
These technologies are gradually reshaping the financial services industry:
- Artificial intelligence, deep learning, analytics, blockchain, and robotic process automation are emerging technologies applied in finance.
- Analytics has been a top technology trend for over a decade and is going through four stages from basic business intelligence to real-time streaming analytics.
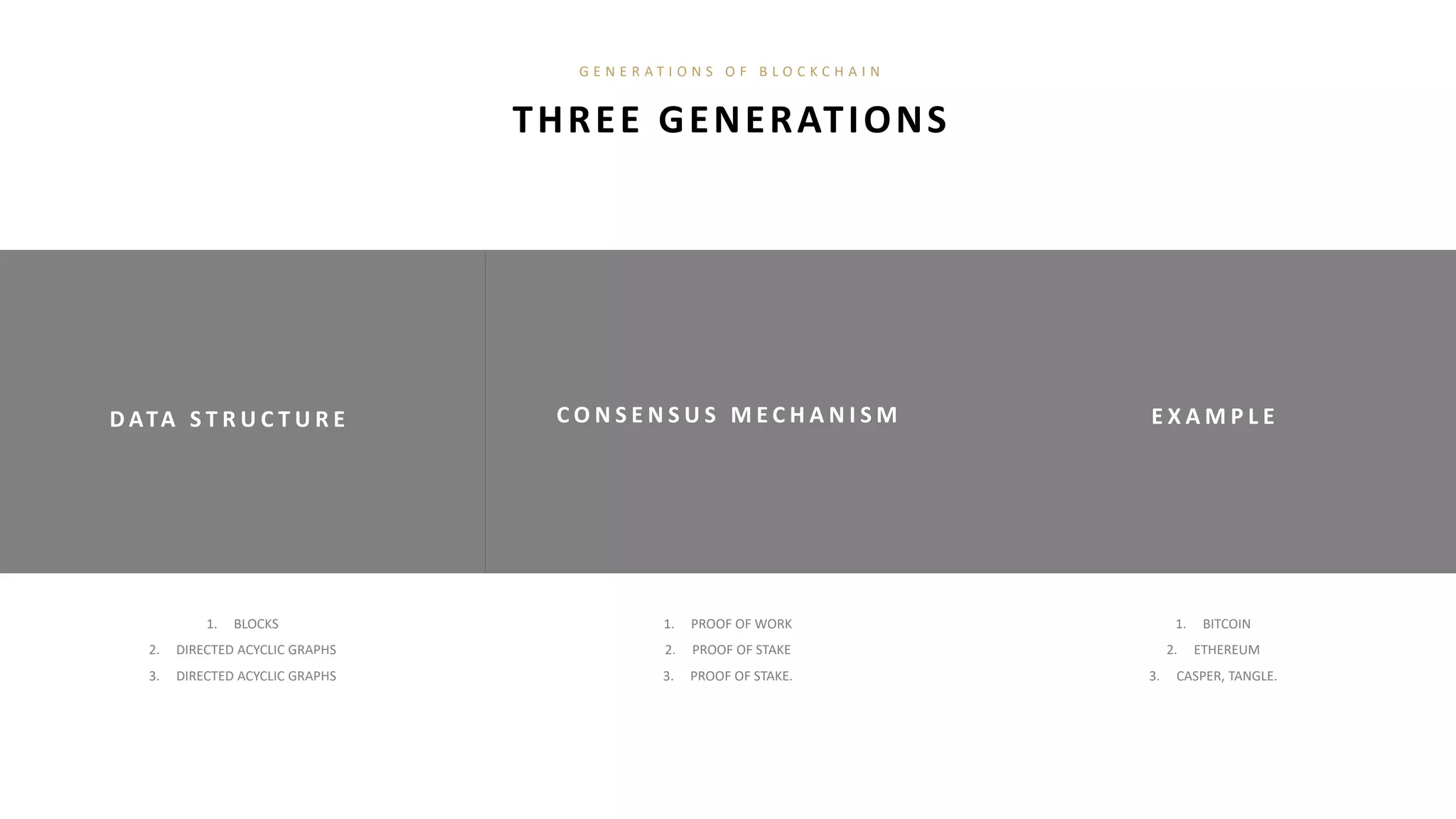
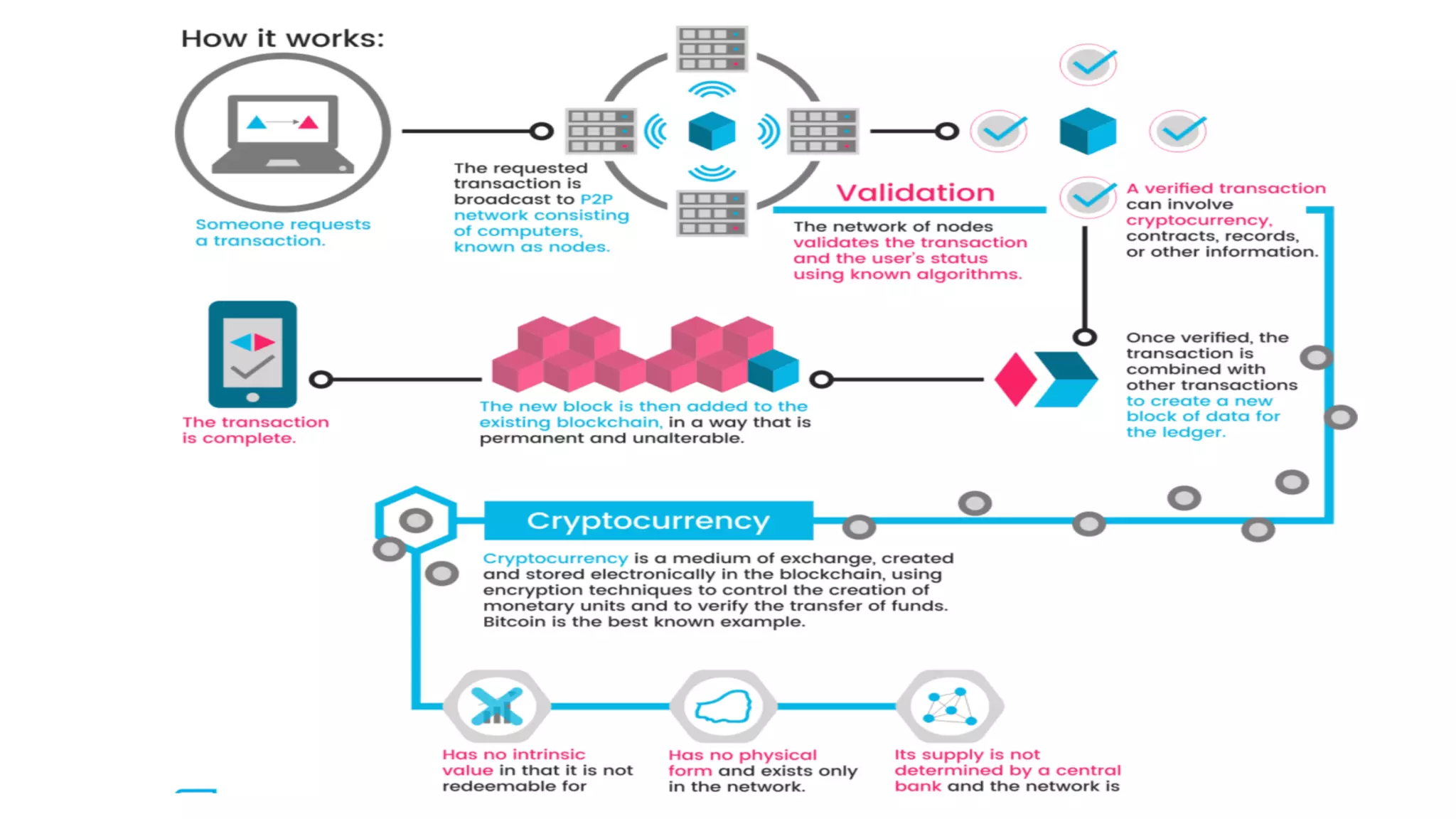
- Blockchain uses distributed ledger technologies and consensus algorithms to securely record transactions in a decentralized manner, having applications for cryptocurrency, smart contracts, and identity management.