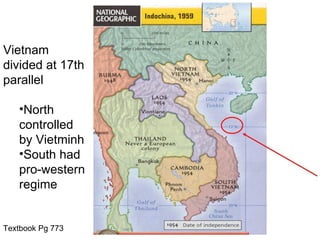
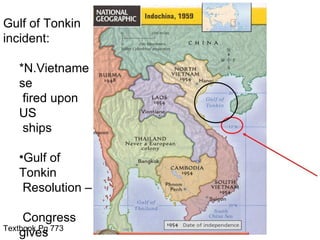
The Vietnam War involved five US presidential terms from Truman to Nixon. [1] US involvement escalated from military advisors under Eisenhower and Kennedy to sending troops under Johnson. [2] The Tet Offensive in 1968 was a surprise attack that turned US public opinion against the war. [3] Nixon took office promising to end the war and gradually withdrew troops while pursuing peace talks, leading to a ceasefire in 1973, though Vietnam was fully united under communism in 1975.