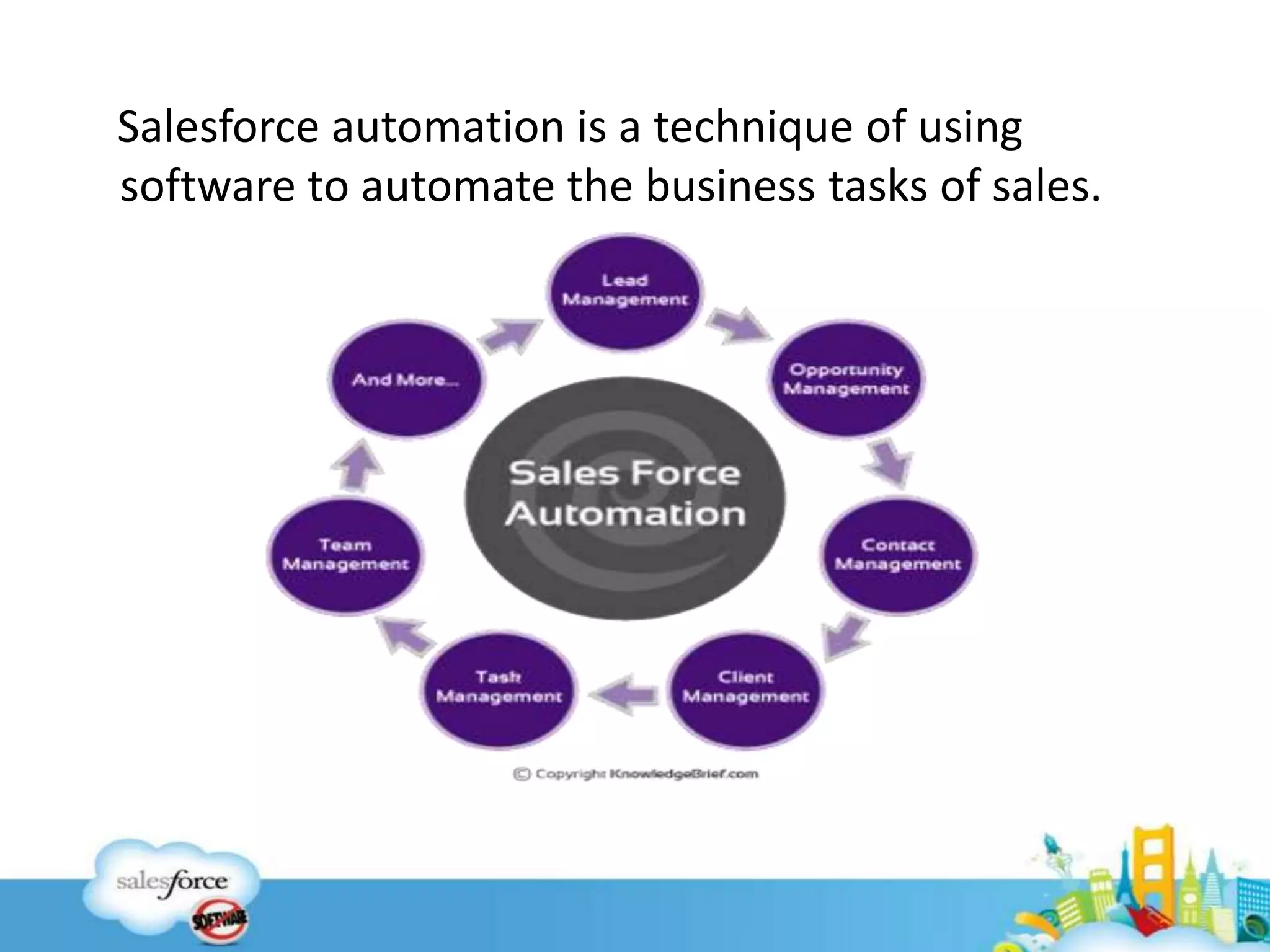
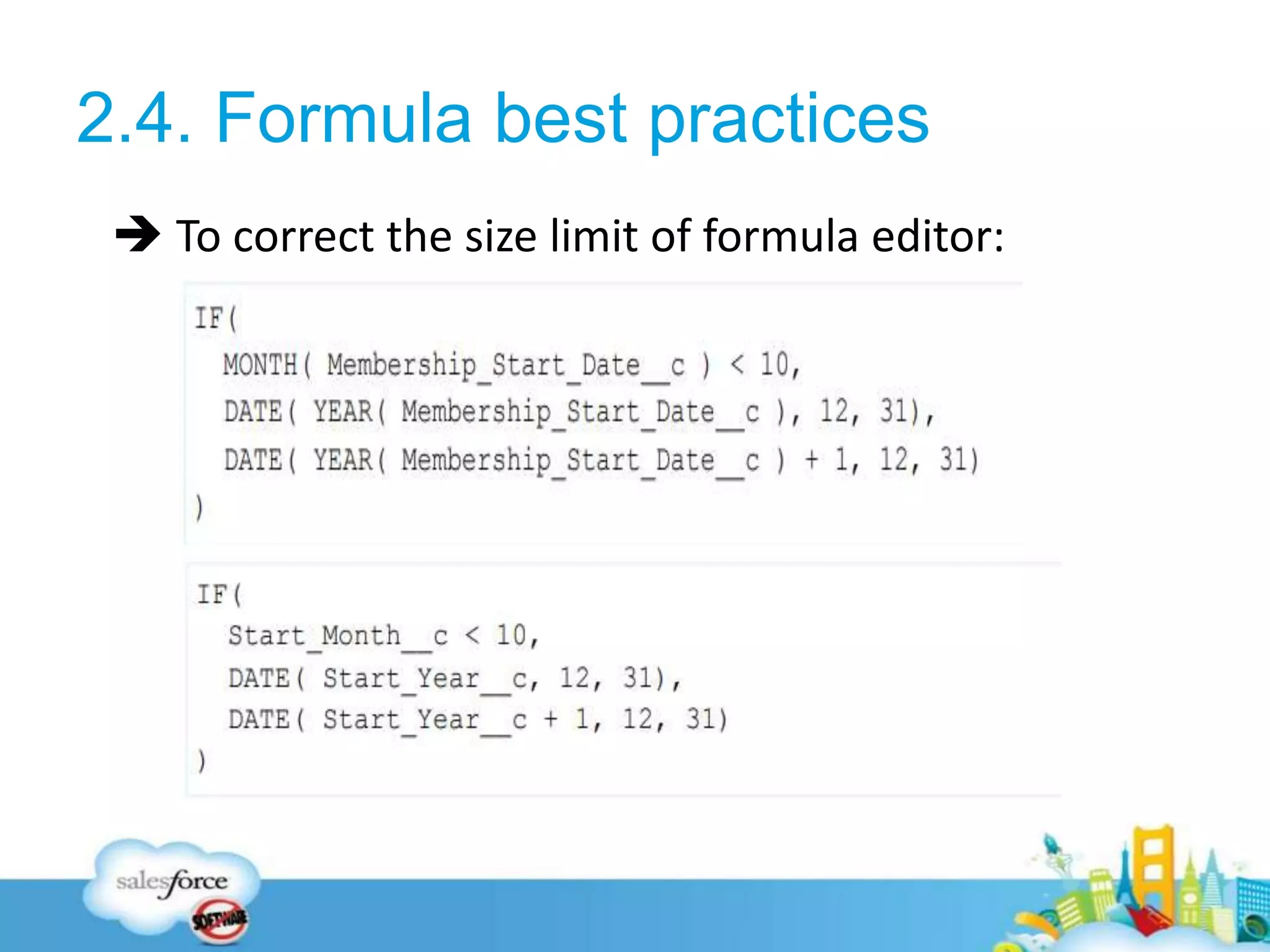
Salesforce automation techniques like formulas, workflows, process builder, and flows can be used to automate business tasks in sales. Formulas define field criteria and defaults, while workflows trigger actions based on rules. Process builder provides a graphical interface to automate processes and supports more actions than workflows. Flows are useful for complex logic and processes involving screens. The document provides examples and best practices for each technique and poses sample questions to test understanding.