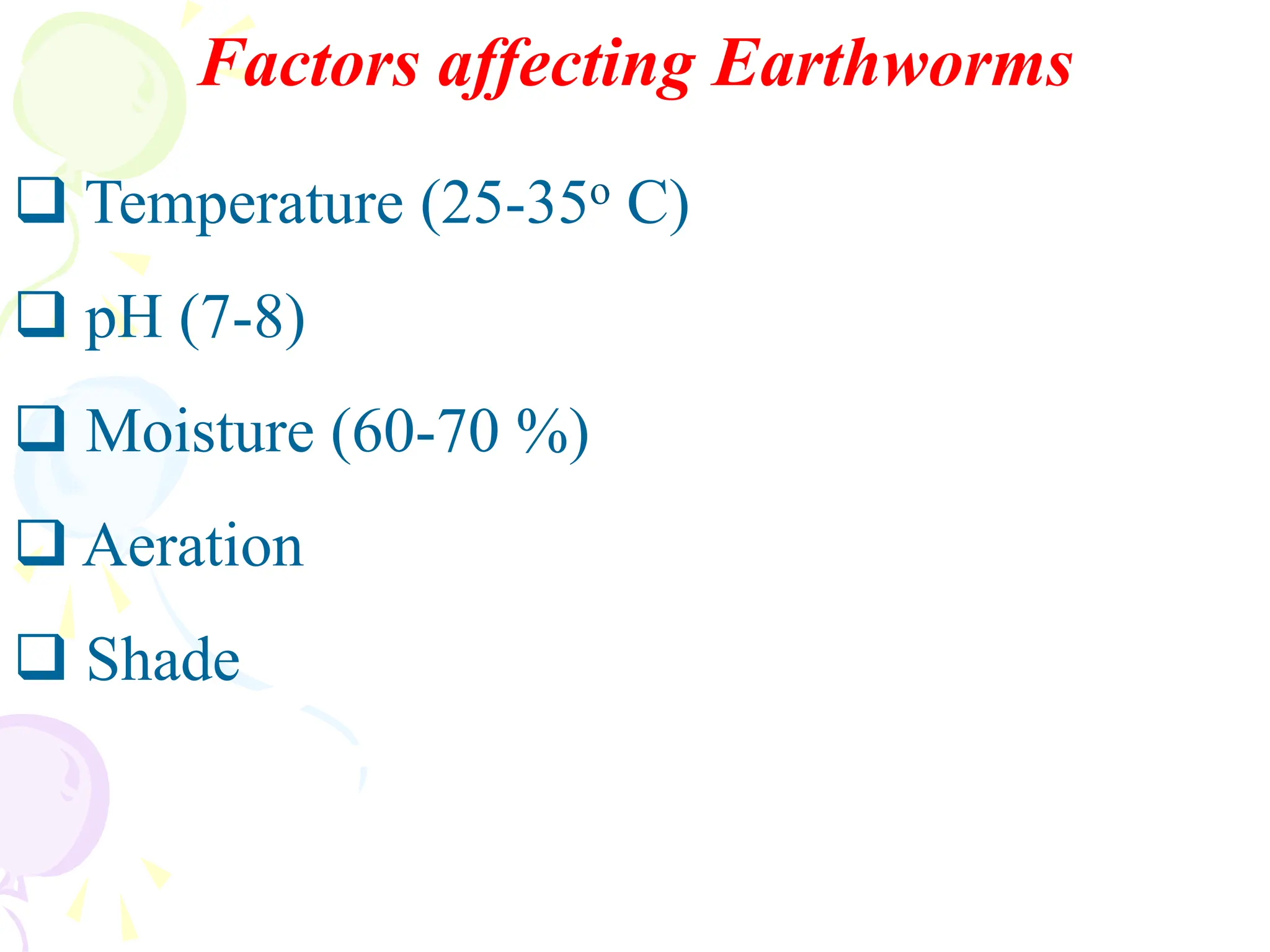
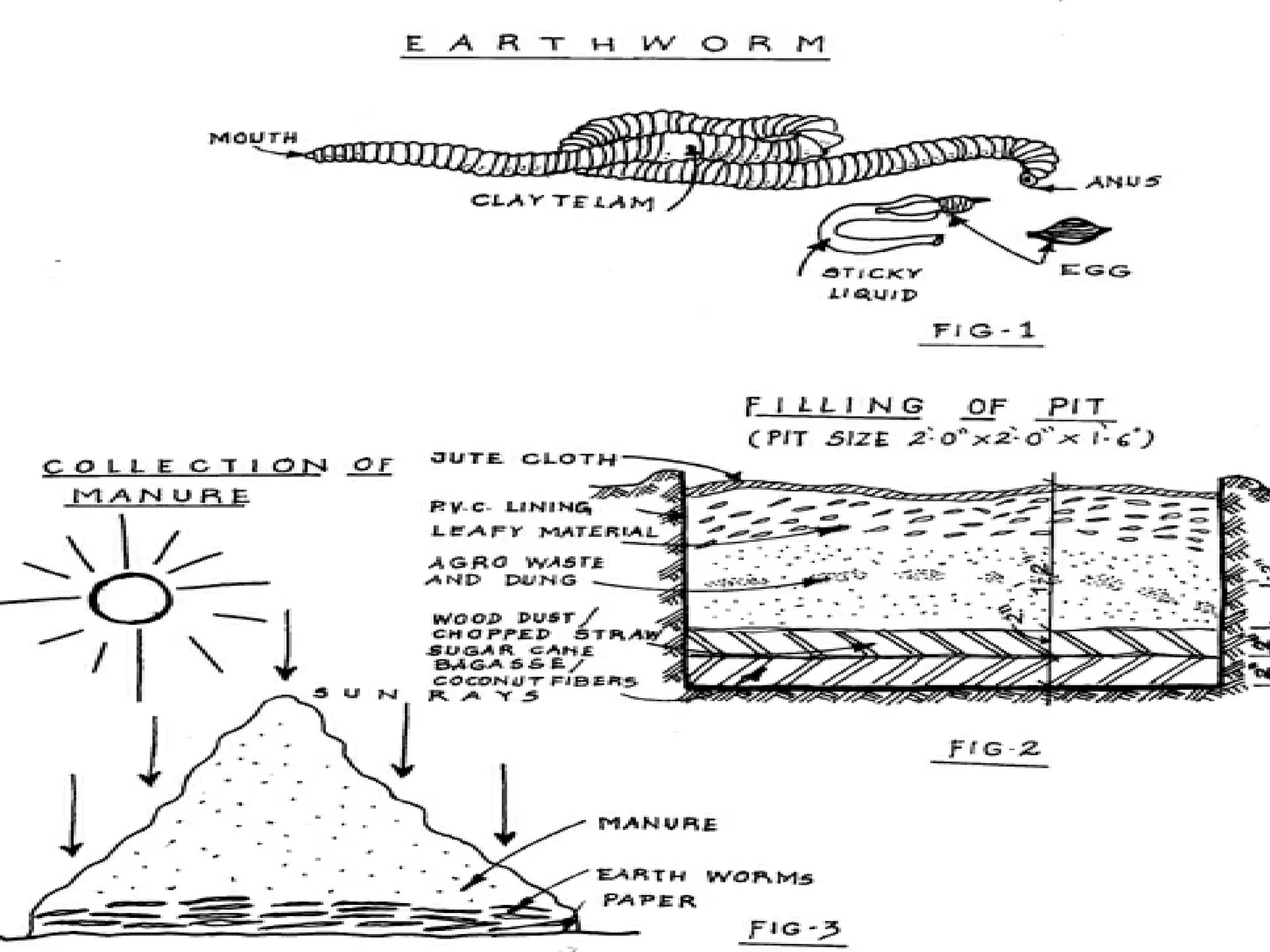
This document discusses earthworms and their role in vermicomposting. It begins by describing the types and characteristics of common earthworm species used for vermicomposting. It then explains the vermicomposting process, how earthworms break down organic waste materials, and the benefits of vermicompost over traditional composting. Finally, it provides details on setting up small and large scale vermicomposting systems and the advantages of using vermicompost in agriculture.